語音學
語言嘅研究 From Wikipedia, the free encyclopedia
Remove ads
語音學(粵拼:jyu5 jam1 hok6)係語言學嘅分支,顧名思義專門研究語言嘅聲,亦即係語音,包括研究人類產生語音背後嘅生理機制、語音嘅聲特性、同埋人類點樣感知語音... 呀噉。語音學可以話係語言學當中最根基嗰個領域,而呢一個領域可以再細分做三個子領域:
- 發聲語音學—研究人點樣發出語音,會思考例如脷同嘴唇嘅郁動會點主宰語音嘅特性;
- 語言聲學—研究語音嘅聲學特性,即係將語音當做聲波,剖析呢啲聲波嘅頻率同振幅等;同埋
- 聽覺語音學—研究人點樣感知語音,例如係用神經造影技術監察住人嘅腦,睇吓佢感知語音嗰陣個腦會有咩變化。

講嘢嘅聲可以用好多唔同方法分類。首先,語音可以按「聽落有幾響亮」分做元音同輔音兩種;而元音同輔音又有得各自按「發出語音嗰陣聲道結構點變化」再細分,分做鼻音(會有空氣由鼻嗰度噴出—想像粵拼 m)等嘅類型;除此之外,語音仲可以按音高(音高反映聲學上講嘅頻率)嚟分類,而音高係聲調嘅基礎。
Remove ads
基本定位

内文:語言學
定義上,語音學係語言學嘅子領域,專研究語言嘅聲:聲本質上係一種波動(聲波[e 1]),具有頻率等嘅物理量;語音學家會剖析呢啲聲特性,亦會嘗試將呢啲聲特性概念化,研究呢啲聲嘅產生、傳遞同埋接收[1]。
語音學,旨在想研究講嘢嘅聲以及係呢啲聲喺生理上嘅產生同聲學特性。語音學會處理聲道產生語音嗰陣點變化(發聲語音學)、語音嘅聲學特性(語言聲學),同埋係聲點樣砌埋一齊組成音節、字詞同句子(語言學性質嘅語音學)。
語音學仲可以再細分做三大領域:
- 發聲語音學[e 2](產生):研究人類點樣發出語音,尤其係講到分析聲道當中發生嘅空氣流動會點樣產生講嘢嘅聲—想像而家有個人坐低一路望住塊鏡一路講幾隻輔音同元音唔同嘅字詞,就會發覺自己發出唔同嘅語音嗰時,嘴唇同脷等嘅聲道結構會以唔同嘅方式郁動[3]。
- 語言聲學[e 3](傳遞):研究語音嘅聲學特性,尤其係講緊聲波喺空氣當中嘅傳遞,會分析語音聲波嘅頻率、振幅同相位... 等嘅物理量,會用訊號處理嘅視角嚟觀察語音[4]:Ch 7;呢個領域同物理性質嘅聲學有相關嘅重疊[5][6]。
- 聽覺語音學[e 4](接收):研究人點樣聽語言嘅聲;事實表明,當語音聲波到達人嘅耳仔,佢嘅各種感官同腦入邊都會發生好多事;有關聽覺語音學嘅簡單例子,可以想像研究者用神經造影(泛指一啲能夠用圖像方式表示腦狀態嘅技術)監察住受試者嘅腦活動,再畀受試者聽語音,睇吓人類聽其他人講嘢嗰陣個腦會有咩變化。可以睇吓認知心理學上講到嘅語音感知[5]。
Remove ads
國際音標
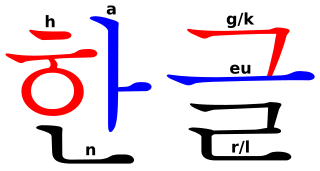
國際音標[e 5],英文名簡稱 IPA(可作粵拼:aai1 pi1 ei1),係語音學研究成日用嘅工具。IPA 做嘅係精確噉將講嘢嘅語音寫低:要做語音學研究就要分析語音,而噉就表示語音學家會想搵方法用紙筆將語音寫落嚟;喺現實世界,人類好多時會用文字寫低自己講嘅嘢,但係人類平時生活用開嘅文字同自然語言一樣,或多或少梗會有啲混沌,唔同嘅語言對同一個符號會有唔同嘅發音[7],例如
- 淨係留意用廿一世紀初嘅粵語讀漢字嘅話[註 1]:
- 聲有兩個可能嘅讀音-sing1(聲音)或者 seng1(佢把聲);
- 精有兩個可能嘅讀音-zing1(精確)或者 zeng1(精叻);
- 間有兩個可能嘅讀音-gaan3(間中)或者 gaan1(中間);
- 就算係好似羅馬字噉嘅表音文字[e 6](指每隻文字素都表達緊某隻音素嘅文字系統)都有類似嘅情況:
—好明顯,一般平時用開嘅文字系統根本做唔到精確噉標示字詞嘅發音。有見及此,語言學家就製定咗 IPA 呢套標準。IPA 最大特徵係夠晒精確,有一套符號(主要建基於羅馬字)用嚟寫低講嘢嘅聲,而且更加重要嘅係
隻隻符號都淨係會對應一個音,
同時每個音亦淨係得一個符號對應。
—而且佢哋仲會用方括弧([];嚴式)或者斜棟(//;寛式)噉嘅符號括住佢哋記嘅音,向睇嘅人強調返「串符號係寫緊 IPA,唔係一般羅馬字」[8]。噉樣語音學研究者望住一串 IPA 符號嗰陣時,唔會有「吖,呢個符號有兩個可能嘅音喎,到底寫嗰個人想表達嘅係邊一個音呢?」噉嘅情況[註 4]。
例字詞:
—英文同葡文傳統上慣咗用羅馬字寫,而標準官話傳統上慣咗用漢字寫,但無論用嘅文字系統係乜,IPA 都會用同一套符號寫嗰隻語言出嚟,方便語音學研究免受文字系統嘅特性干擾。
Remove ads
語音產生
睇埋:源-濾波器模型
首先,語言嘅起始點係人講嘢發出聲(所謂嘅單音[e 8])。呢啲聲源自空氣嘅流動,而喺包括粵語在內嘅絕大多數語言當中,呢股空氣流動係由個肺嗰度開始嘅(肺部氣流音[e 9])。空氣由個肺流出[註 5],通過氣管、喉、咽同口腔等嘅部位,當中喉係聲帶[e 10]嘅所在。空氣流過身體咁多唔同部位嗰陣,呢啲身體部份嘅狀態(例如係條脷嘅郁動)都會影響最後發出嚟嘅聲有乜特性—噉就表示人可以發出好多種唔同款嘅聲,噉亦表示佢哋可以用發出嚟嘅聲表達好多唔同嘅意思[4]:2.0。
喺廿一世紀初嘅源-濾波器模型[e 11]當中,一種元音或者輔音嘅產生過程可以想像成「起源再過濾」嘅雙階段過程,即係(例如)肺部嘅空氣流動產生聲音,然後聲道嘅各部會擔當好似「過濾器」噉嘅角色,好似係篩走其中一啲頻率嘅聲波,最後決定股聲波嘅特質。
元音同輔音
首先,要講解吓元音[e 12]、輔音[e 13]同固有音響[e 14]呢三個關係密切嘅概念。固有音響可以大致界定做一吓聲「同音高等因素對等嘅聲比有幾響」,反映咗吓聲帶有幾多聲能;例如 [a](想像粵拼:aa1)噉嘅元音就固有音響高,人發出 [a] 音嗰陣聲道大開,令吓聲帶有大嘅聲能,而相比之下,好似 [t](想像粵拼:d)噉嘅音就係固有音響低,人發出 [t] 等嘅輔音嗰時聲道會局部或者完全閂埋,能夠通過聲道嘅空氣量就少咗[11]。
以下係廿一世紀初粵語音系當中嘅輔音,分別用 IPA、粵拼同「以呢隻輔音開頭嘅漢字」表示[12][註 6]:
而廿一世紀初粵語音系裡邊嘅元音如下:
唔同語言或者方言喺「有啲咩元音同輔音」呢一點上可以爭幾遠,例如清齦腭擦音([ɕ];普通話拼音:x)就係標準官話有、但粵語冇嘅輔音,又或者例如廿一世紀初嘅粵語有 [ŋ] 呢隻開頭輔音,係歐洲語言缺少嘅[註 8],歐美人學粵語等嘅東亞語言嗰陣,成日都會喺呢個音嗰度遇到困難。有關唔同語言嘅輔音同元音特性比較,可以睇吓音系類型嘅概念。
|
調音分類法

要將輔音分類,要理解調音部位[e 16]同調音方法[e 17]嘅概念。
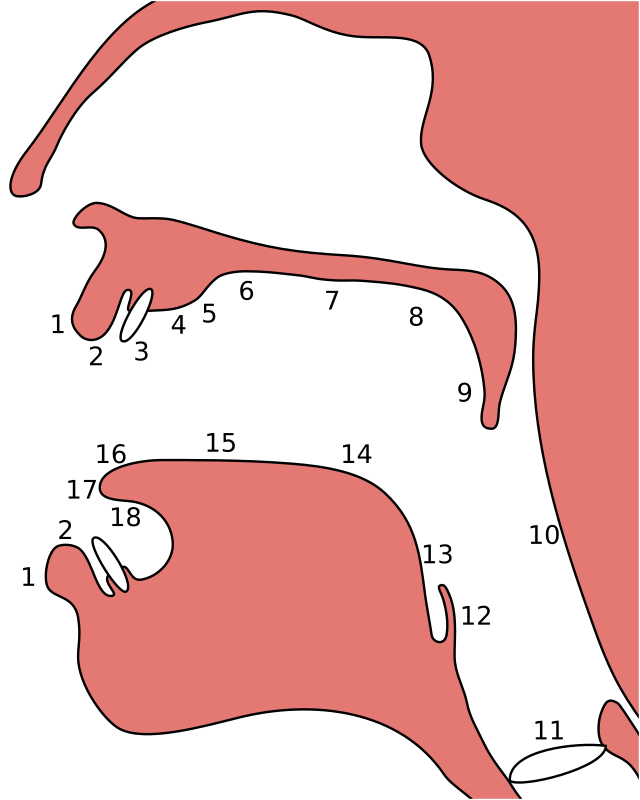
輔音嘅調音部位,係指講嘢嘅人發出輔音嗰陣,佢嗰拃聲道結構係喺邊個位閂埋(閂埋就阻斷空氣流動)嘅[14]:p 10。用廿一世紀初嘅粵語有嘅輔音做例子,以下呢兩個輔音調音方法一樣,但係調音部位唔同:
輔音 粵語例子 解說 雙唇鼻音 /m/ maa1(媽) 係一種雙唇音,發音嗰時會用到上下兩塊嘴唇阻斷空氣流動,即係調音部位好前。想像附圖 A 入便 1 同 2 嗰兩個位中間,喺發出呢種聲嗰陣會閂埋。 軟腭鼻音 /ŋ/ ngaa1 同雙唇鼻音比起嚟,軟腭鼻音阻斷空氣流動嗰個部位就後好多。想像附圖 A 入便 8 嘅位,喺發出呢種聲嗰陣會閂埋。
除咗調音部位,調音方法都可以攞嚟將輔音分類。人要發出語音嗰陣,空氣會經聲道流動再由口鼻噴出,中途「條脷嘅位置同郁動」等嘅多個變數會影響聲有咩特性,而調音方法簡單講就係反映緊啲發聲器有幾咁「收縮埋一齊」[4]:Ch 4。用廿一世紀初粵語有嘅雙唇輔音做例子,以下呢兩個輔音調音部位一樣,但調音方法唔同:
輔音 粵語例子 解說 雙唇鼻音 /m/ maa1(媽) 係一種雙唇音,發音嗰時會用到上下兩塊嘴唇阻斷空氣流動。 清雙唇破音 /p/ baa1(巴) /p/ 都係一種雙唇音,不過調音方法就同 /m/ 唔同,/m/ 係一種鼻音,而 /p/ 就係一種塞音,鼻音涉及空氣由鼻嗰度自由噉噴出[註 9],而塞音就係成條聲道受到阻斷,令到空氣暫時完全停止流動。 清唇齒擦音 /f/ faa1(花) 屬於唇齒音,同時喺調音方法上係一種擦音,擦音指個輔音發出嗰陣時,發音人會有兩個發聲器靠得好埋組成一條狹窄通道,再迫空氣通過呢條通道[註 10],而喺 /f/ 當中「兩個發聲器」就係嘴唇同牙,所以叫唇齒嘅擦音。
啲人用圖表列出輔音嗰陣,通常係用打橫嗰條軸反映調音部位,同時用打戙嗰條軸反映調音方法嘅。例子可以睇返上面嘅粵語輔音圖表。
其他分法
以下呢啲概念都成日畀人用嚟將輔音或者元音分類:
- 清音[e 18]同濁音[e 19]:講緊一吓單音「有冇涉及聲帶嘅振動」,冇嘅話嗰吓聲就算係清音,有嘅話嗰吓聲就算係濁音;一吓聲係清音定濁音,可以簡單噉用手嚟感覺—想像將自己隻手擺喺自己嘅喉核嗰個位,如果發嗰個音係濁音嘅話,隻手會感受到自己嘅喉部有振動。廿一世紀初嘅粵語冇乜濁音可言[15][註 11],用英文做例子嘅話[16][17]:
- 送氣[e 20]:指一吓聲發出嚟嗰時會帶有一吓空氣噴出,喺 IPA 寫做上標嘅細階 h(h);觀察者可以擺隻手掌係自己個口前面,如果吓聲有送氣,佢可以感覺到有股空氣噴落佢隻手[18];用粵語做例子:
- 雙元音[e 21]:指一橛音節包含兩個單一元音;例如粵語裏面 saai1(可能漢字:嘥)呢段音節噉,隻字個元音(aai1)由兩截組成-aa1 同 i1,所以就算係雙元音[19]。
呀噉。
例子:諺文嘅設計
韓字喺韓國話入邊叫 hangeul,而呢幅圖顯示 hangeul 用韓字寫嘅樣,韓字每一隻符號代表咗某個元音或者輔音。 諺文[e 22],又叫「韓字」,係一套字母,源自李氏朝鮮,由朝鮮世宗李裪[e 23]喺 15 世紀中率領一班學者發明嘅。
話韓字係一套字母,意思係指呢種文字入邊每個符號都係表示元音或者輔音:相比之下,漢字係語素文字,每隻字符表達緊字詞或者形態素,而唔係元音或者輔音;韓字就係表音嘅(呢點似羅馬字),隻隻符號都表示緊元音或者輔音,而且佢個做法,仲將啲輔音符號設計到望落似人讀嗰個音嗰陣嘅聲道狀態[20],例如
- ㄴ → 用嚟書寫 /n/(接近粵拼:n),留意人發出 /n/ 音嗰陣條脷嘅形狀。
- ㄱ → 用嚟書寫 /k/(接近粵拼:g),留意人發出 /k/ 音嗰陣條脷嘅形狀。
- ㅁ → 用嚟書寫 /m/(接近粵拼:m),人發出 /m/ 音嗰時嘴唇會合埋,然後再打返開。
圖解可以睇下邊。
韓字吸引咗唔少語文工作者嘅注意:一般認為,韓字係極少有嘅特徵文字,達致字符設計到形狀似聲道狀態;呢點被指係令到呢套文字非常合乎直覺非常易學,能夠有效噉提升識字率[21][22]。
Remove ads
語音分析
内文:語言聲學
語音學研究成日都會分析語音嘅聲學[e 24]特性:語音係一種聲,聲係一種波動,涉及介質粒子(最常見嘅係空氣粒子)振動,而一股波動嘅各種特性,主宰咗聲有咩特性—例如聲學上嘅研究已知,一段聲波聽落「有幾高音」取決於佢嘅頻率,而股聲波「有幾大聲」就取決於佢嘅振幅。如果要將語音分類,除咗可以按「發聲嗰時聲道係咩狀態」(調音部位同調音方法等)嚟分,仲可以用示波器[e 25]等嘅架生量度語音嘅聲學特性,用呢啲特性將語音分類[4]:Ch 7 [23]。當中一個出名嘅例子有廿一世紀初漢語都有嘅聲調—聲調簡單講就係用語音嘅音高嚟分辨唔同嘅字詞[24]。
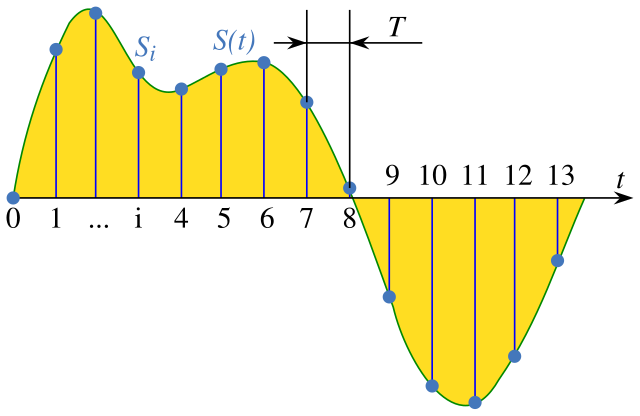
值得一提嘅係,量度語音嘅聲學特性可以幾有學問:語音學跟從嘅係科學方法,一定要有方法量度研究緊嘅現象,不過如果量度方法錯咗,搞到數據出現咗扭曲,就可能會搞到語音學家嘅理論跟住出錯。有唔少語音學家都好關注「語音數據要點樣量度」呢條問題,例如訊號取樣[e 26]呢樣嘢就幾受關注[4]:8.1:訊號取樣涉及將一個連續嘅訊號變做離散;想像而家有個人喺度講嘢,語音學家想錄低佢講嘢嘅聲做分析,問題係,佢講嘢嘅聲原則上係連續嘅—而家設
- 做嗰位語音學家想量度嘅聲學特性,
- 做「時間點 嘅 」,
- 佢部儀器做到每 秒咁耐就量度一次(每隔 秒做一次取樣)
—想像 嘅實際變化規律係好似下圖嗰條曲線所表示嘅噉。因為研究者部儀器淨係每 秒咁耐先量度到一次 嘅數值,所以例如 喺 同 之間嘅變化,部儀器就睇唔到。要降低 嘅數值係有可能嘅,但可能會好嘥時間或者精神,而「 要設到幾細」就會係一條大問題[25]。
共振峰

内文:共振峰
是但攞一段語音嚟睇,段語音入邊往往會帶有多股唔同頻率嘅聲波。對語音嘅聲學研究表明,唔同元音喺「邊種頻率嘅聲波振幅勁啲」呢一點上可以幾唔同—即係例如對比 [i] 嘅聲波同 [u] 嘅聲波,兩者都有頻率 3,500 Hz 左右嘅聲波,但前者有比較多呢啲噉嘅聲波。呢種噉嘅現象可以用時頻譜[e 27]表達,達致用圖像化方式表達唔同語音嘅聲學特性。
實證研究表明,元音通常有三個共振峰[e 28],每個共振峰係指一笪「振幅去到最勁」嘅頻率區,例如想像而家錄低啲人用美國某地嘅口音讀 [i] 再睇吓幅時頻譜,發現段聲波喺 280 Hz、2,250 Hz 同 2,890 Hz 呢三個頻率區有最大嘅振幅,噉呢三笪區域就算係嗰段聲波嘅共振峰,當中 280 Hz 係 F1、2,250 Hz 係 F2 而 2,890 Hz 係 F3 — F 取自共振峰嘅英文名開頭字母,F 後面掕嘅數字就係按頻率由低至高排嘅[26]。一個音嘅共振峰反映咗聲道嘅共振頻率[e 29]。
語音嘅共振峰特性同佢相應嘅聲道特性有一定嘅統計相關。例如研究表明,人發出元音嗰陣
- 條脷嘅高度,同
- 嗰種元音嘅 F1 嘅頻率
成負相關,即係條脷位置愈高,F1 就傾向愈低頻;而實際嘅研究睇過輔音嘅共振峰,亦發現唔同輔音嘅共振峰特性有明顯嘅差異[27]。
音節概念
喺廿一世紀初,音節[e 30]嘅一個定義係「畀固有音響冇咁高嘅聲包圍嘅固有音響頂峰」,可以大致想像成「一段元音,前面或者後面掕住輔音,亦可以係前後都掕或者前後都唔掕」。用英文做例子嘅話,英文
- Television(指電視;/ˈtɛlɪˌvɪʒn,ˌtɛlɪˈvɪʒn/)
一字有 4 橛音節;tel-e-vi-sion [11]。一段音節會分做音節首[e 31]、音節核[e 32]同埋音節尾[e 33],當中音節核一般係唯一嘅必要部份而且通常會係元音,音節核同音節尾合稱韻基[e 34]。用粵語做例:
值得一提嘅係,語音嘅聲學分析顯示,音節之間(由聲波睇嘅話)冇乜明確嘅分界,如果人正常噉講嘢,聲學架生唔會話量度到音節同音節之間有明顯嘅「冇晒聲」階段,但係音節核傾向會明顯大聲啲[註 13][e 35]。
音節可以帶有以下呢啲韻律[e 36]特性。語言學講嘅韻律係一隻有啲籠統嘅字詞,大致可以包晒所有元音同輔音以外嘅音節特性。韻律特性對表達情緒嚟講好重要,例如有研究確定咗,人類就算係聽緊自己完全唔識嘅語言,都可以靠住輕重同音高等嘅資訊得知講嘢嘅人(例如)係咪發緊嬲[28]。
重音
内文:輕重讀
輕重讀,又或者叫重音[e 37],可以大致理解做一截音節有幾「強勁」—當中「強勁」可以由多個聲學特性反映,最主要嘅一般係睇嗰截音節「有幾大聲」,愈大聲就算係愈強勁。除此之外,「強勁程度」亦都局部取決於嗰截音節嘅長度(愈長愈勁)同音高(愈高音愈勁)等嘅因素[29]。喺 IPA 當中,主重音會用上撇號(ˈ)標,而次重音就會用下撇號(ˌ)嚟標。
廿一世紀初嘅粵語被指係冇咩明顯嘅輕重讀現象,但係好多語言同方言都有。例如:
隻字詞羅馬字點寫 詞彙 1 詞彙 2 Present [30] /'pre-zənt/,名詞指禮物 /pri-'zent/,動詞指匯報 Permit [31] /ˈpər-ˌmit/,名詞指准許證 /pər-ˈmit/,動詞指准許 Subject [32]:2. "Stress" /ˈsʌb dʒɪkt/,名詞指科目或者課題 /səbˈdʒɛkt/,動詞大致指支配或者佔領
聲調
現代語言學上講嘅聲調[e 40],係指附喺音節嗰喥嘅音高變化抑揚,每一段音節都會有佢嘅聲調,聲調表示呢段音節講出嚟嗰陣音高要點樣變化—音高要高同平、初時低音跟住升、定係初時高音跟住跌... 呀噉[註 15]。有聲調系統嘅語言就謂之聲調語言[e 41],聲調語言嘅例子有粵語、中古漢語、標準官話、閩南話同埋越南話呀噉。用粵語做例子[36]:
詩 (陰平)、史 (陰上)、試 (陰去)、時 (陽平)、市 (陽上)、事 (陽去)
—同樣嘅元音同輔音,因為聲調(音高變化規律)唔同咗,段音節表示嘅字詞或者形態素就唔同咗。有啲聲調語言仲會用聲調嚟做詞形變化,即係例如改變聲調嚟表示隻動詞係過去式定現在式。
聲調輪廓[e 42]係講緊一隻聲調語言入面啲聲調,可能會有「喺音節中途音高改變」噉嘅情況。如果畫幅圖 Y 軸做音高[註 16] X 軸做時間,啲聲調會成唔平嘅線,描繪啲聲調嘅「輪廓」,例如下圖就係粵語「詩史試時市事」六調嘅輪廓。

而下圖就係越南話(北越南嘅音)六調嘅輪廓。留意越南話都係有六個調,但啲聲調嘅輪廓同粵語嘅有顯著差異。


亦都有啲聲調語言係冇乜輪廓可言,即係啲聲調冚唪唥都大致係平嘅,唔同聲調嘅唯一分別係在於音高唔同[37]。
唔同聲調語言嘅書寫系統,可能會用唔同嘅方法嚟寫聲調,例如喺廿一世紀初,越南話同標準官話都係用變音符號嚟表示聲調嘅,唔似得粵拼噉用阿拉伯數字嚟標聲調。語言學研究為咗方便分析,通常會想搵返套統一嘅系統同唔同嘅聲調語言標聲調,當中五度標記法[e 43]就幾多人用,呢套方案將音高分做五度,然後用阿拉伯數字 1 到 5 標調,1 係最低音而 5 係最高音,每個聲調會掕住多過一個數字,表示音高點樣變化。如果用呢套方法標粵語聲調嘅話[38]:
- 詩([si55])、史([si35])、試([si33])、
- 時([si21])、市([si23])、事([si22])
—詩個聲調高音同大致平,係 55;史個聲調開頭中音然後升上高音,係 35;時個聲調初頭低低哋然後跌到更低,係 21... 如此類推。用同樣嘅做法嚟同其他聲調語言標調,就可以噉思考:
話 幾多調 示例 標準官話 四調 媽([ma55])、麻([ma35])、馬([ma214])、罵([ma51]) 越南話[註 17] 六調 ba(33)、bà(21)、bả(313)、bã(3ˀ5)、bá(35)、bạ(3ˀ2ʔ)
越南話聲調有一啲粵語同標準官話冇嘅符號(ˀ 同 ʔ 等),呢啲符號表示個聲調有聲門塞音化[e 44](指發出嗰吓聲嗰陣聲門局部或者完全噉關閉)嘅情況。
高低重音
内文:高低重音
睇埋:音高
世上仲有所謂嘅高低重音語言[e 45]。高低重音語言會有輕重讀,但係就只靠音高嚟表示邊截音節係重音(通常重音音節高音啲),唔似得例如英文噉會靠音高加埋響度同長度嚟表示重音。喺高低重音語言入邊,多音節字詞「邊截音節重音」可能會令到隻字詞意思唔同咗。
舉個具體例子說明,廿一世紀初嘅日本話就被指係高低重音語言。睇睇日本話 kinō(平假名:
用日文漢字寫嘅話,前者會寫做昨日而後者會寫做機能,不過口語傾談嗰時冇得話靠漢字辨義,只可以靠音高變化規律[註 19]嚟辨別兩隻字詞。呢種情況喺日本話入邊唔算常見,有估計話得嗰 20% 嘅字詞有好似 kinō 噉嘅情況,有更多嘅字詞係好似 arigatō(平假名:
—Arigatō 呢幾串音節,並冇因為音高規律而意思唔同咗,東京腔同京都腔完全明對方講乜,差異在於聽對方嘅音高規律,佢哋能夠作出「佢九成係出身於京都嘅」呢類判斷。除咗日本話,被指有高低重音嘅仲有挪威話、瑞典話、中古韓語(現代韓國話嘅祖先,存在於 11 至 16 世紀)[42]、現代韓國話某啲方言[43]、同埋包括上海話在內嘅多種吳語方言[44]。
好似日本話噉嘅高低重音語言,有別於聲調語言—聲調語言係所有音節都要啱晒音高特性,先至會正確表達到意思嘅,而且一截音節嘅音高並唔取決於佢喺字詞入邊嘅位置。
音長
音長[e 46]顧名思義,就係指緊音節嘅長度。音節長度可以受到好多因素影響,局部受制住輕重讀。喺某啲語言當中,元音或者輔音嘅長度可以形成最細對立體[e 47],即係話元音、輔音同其他音節特性完全唔變,但係其中一個元音或者輔音長咗或者短咗,有可能會令到段語音變咗做意思好唔同嘅另一隻字詞。例如廿一世紀初嘅意大利文入邊就有呢兩隻字詞(IPA 嘅孖細三角符號 ː 表示長咗嘅元音或者輔音)[4]:11.3:
羅馬字串法 IPA 意思 Fato [ˈfato] 命運 Fatto [ˈfatːo] 完成
除咗意大利文,有唔少歐洲、中東至南亞嘅語言都有噉嘅情況,例如芬蘭話、阿拉伯話、孟加拉話同埋土耳其話等等[4]:11.3。
Remove ads
聽語音
内文:聽覺語音學
講嘢嘅人由佢聲道發出語音,語音嘅聲波通過空氣傳到去聽者嘅耳仔嗰度。聽者聽覺感官嘅神經細胞感應到聲波,就會傳訊號上腦部,話畀個腦知嗰股聲波有咩特性。個腦跟住就會處理啲語音資訊,令到個人能夠理解啲語音。
聽覺語音學成日會結合認知心理學同腦神經學等領域嘅研究,集合呢啲唔同方面嘅知識,剖析人類係點樣處理聽到嘅語音嘅。舉個簡單例子嘅話,語音學家可以搵一班受試者返嚟,畀佢哋聽唔同嘅語音,一路操縱啲語音嘅聲波特性,再睇吓受試者對啲語音嘅判斷會唔會唔同咗,從而窺探人腦係點處理語音嘅。
聽覺基礎
睇埋:神經編碼
人類嘅聽覺感官位於個頭嘅兩側。外耳[e 48]顧名思義係耳仔最外邊嗰忽,包括下圖 gg 同以外嘅結構。外耳個形狀有少少似個漏斗噉,會將接收到嘅聲「引導」入去耳仔嘅內部,令到人類更加能夠聽得出啲聲波「係由邊度嚟嘅」,亦起到放大接收到嘅語音嘅作用。除此之外,外耳亦都有助保護耳仔內部啲嘅結構,例如外耳嘅毛就能夠阻擋環境入邊嘅塵[45]。
中耳[e 49]嘅主要結構包括耳膜[e 50](下圖 tf 個位)、聽小骨[e 51](人體最細嗰三嚿骨;下圖嘅 h a 同 s)同埋耳咽管[e 52](下圖 ot 個位)等等。聲涉及咗介質粒子(介質粒子通常會係空氣)嘅振動,耳膜一接觸到聲波就會振動,帶動埋聽小骨一齊振,同時耳咽管會一路保持耳內同耳外嘅壓力大致相同[45]。
內耳[e 53]顧名思義係耳仔最入嗰忽,包括咗耳蝸[e 54](最裡邊螺旋噉形嗰嚿)。耳蝸唔大,得嗰大約 35 mm 咁長。耳蝸入面有一個特別嘅器官—柯蒂氏器[e 55],柯蒂氏器內有特別嘅感官神經細胞,呢啲細胞表面有細細條嘅毛,啲毛能夠對耳膜嘅振動起反應,將感受到嘅嘢(例如係振動頻率有幾高)傳上去個腦嗰度[45]。

語音感知
内文:語音感知
語音感知[e 56]泛指人聽、詮釋同理解語音嘅過程[46]。呢個過程並唔簡單:事實表明咗,語音嘅語言特性好少可會同聲學特性有咩一對一嘅對應;例如廿一世紀初嘅研究已經清楚顯示,冇任何一個語音聲學特性可以單獨噉預測聽者對「元音同輔音係乜」嘅判斷,即係話人腦判斷聽到嘅語音有乜元音同輔音嗰時,實係會同時考慮多個唔同嘅變數。數學化啲噉講,音高(可以睇返聲調同高低重音)喺語音感知上算係一個簡單嘅語言特性,因為人腦對音高嘅判斷主要只係取決於頻率一個因素:
而相比之下,對「聽到嗰段音節,有邊啲元音同輔音」嘅感知過程(人腦明顯能夠做呢種判斷),就冇得齋靠一個物理量嚟預測。語音感知研究想解答嘅問題,包括咗以下呢啲:
- 「人腦係點做語音分割[e 57]嘅呢?」:首先好明顯嘅係,人類會將語音聽做一個個離散嘅單位,例如一段段音節或者一隻隻詞語呀噉;但係語音學家一睇啲語音數據就發現,單位之間(音節同音節之間,或者字詞同字詞之間)喺聲波特性上根本冇明顯嘅分界—想像例如粵語 gong2 je5(漢字:講嘢)呢隻字詞嘅語音,以粵語做母語嘅人會聽得出「段聲有兩段音節」,但係睇時頻譜嘅話就會發現兩段音節之間並冇一段「咩聲都冇晒」嘅時間;噉即係表示人腦實係喺腦海入邊將嗰段連續嘅語音斬咗做兩截,作出「段聲有兩段音節」噉嘅判斷。呢種認知功能就係所謂嘅語音分割。電腦化啲噉諗,語音分割可以想像成以下嘅算法:
- 不變異問題[e 58]:事實表明,一個音素可以以好多種唔同嘅聲波呈現,例如講講粵語嘅 si1(漢字:詩、絲同斯... 等)音節,想像而家搵男女老幼嘅多個粵人齊齊發出呢個音節—男人嘅聲平均嚟講低音過女人嘅,成年女人同細路女嘅聲又有啲唔同,而且就算性別同年齡層都一樣,個個人把聲都唔同,有啲人講嘢快啲有啲人講嘢慢啲,而事實係如果用時頻譜等嘅架生睇呢班人發出嘅聲波,就會發現個個人產生嘅聲波都唔一樣,同時好明顯嘅係,以粵語做母語嘅人能夠將呢啲唔同聲波冚唪唥當做同一款音節—於是就引起咗噉嘅思考[47]:
聽者响腦海入邊對呢啲聲波作出一樣嘅判斷,但係呢啲聲波明顯缺少咗「唔變異」呢種特性。點解呢?
等等。
Remove ads
起源

睇埋:語言學史
喺現代科學興起之前,人類已經一路都有喺度研究語音[49]。例如唐朝人同宋朝人已經有喺度分析自己嘅語言(中古漢語等),提出咗例如平仄(當中仄讀音係則)嘅概念,講到中古漢語有四個聲調,而且唔同聲調之間有平直(平)同高低變化(仄)之分—佢哋呢一個諗頭,同現代語言學提到嘅聲調輪廓概念好相似。一般認為,世上最早嘅語音研究出自公元前 4 世紀嘅古印度學者波你尼[e 59]—波你尼佢寫咗好幾本書,喺書入邊討論梵語嘅語音,提到講嘢嗰陣會發出乜嘢聲,係取決於聲道嘅某啲狀態嘅[50]。
現代科學方法[e 60]係喺 16 世紀後嘅歐美成形嘅。根據紀錄,英文圈嘅人用
- Phonetics
一詞嚟指「研究語音嘅科學」呢樣嘢,始於 1841 年[51][52]—當時嘅歐美產出咗大量嘅科學同科技新知,包括醫學上認識咗人類嘅聲道結構,以及係發明咗能夠準確噉記錄語音同聲道狀態嘅儀器。呢啲新技術令到語音學研究易做咗好多—喺有呢啲儀器之前,語音學家吓吓都要親自聽人講嘢,做研究好多時都好唔方便。而喺 1880 年代後半,一班英國同法國嘅語言學家同語言老師聚埋一齊,整咗一套用嚟客觀紀錄語音嘅符號,而呢套系統後嚟成為咗國際音標[53]。
Remove ads
睇吓
註釋
- 但好多東亞語言都有。
- 可以試吓一路發出 /m/ 音,一路擺隻手指喺自己鼻窿前面。
- 可以試吓一路發出 /f/ 音,一路擺隻手指喺個嘴前面。
- 實證嘅研究表明,啲人判斷聲調嗰陣,會按講嘢嗰方把聲(例如男人嘅聲傾向低音啲)嚟調整自己嘅預期。
Remove ads
引述
外拎
Wikiwand - on
Seamless Wikipedia browsing. On steroids.
Remove ads