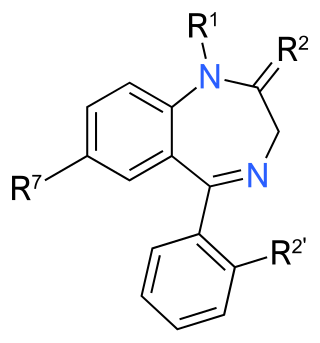
| Chemical structure |
Code |
pIC50 / IC50 |
Chemical name |
PubChem |
CAS number |
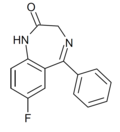 | Ro05-3061 | 7.3979 / 40nM | 7-fluoro-5-phenyl-1H-benzo[e] [1,4]diazepin-2(3H)-one | 75849 | 2648-00-2 |
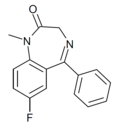 | Ro05-4865 | 7.7696 / 17nM | 7-fluoro-5-phenyl-1-methyl-1H-benzo[e] [1,4]diazepin-2(3H)-one | 44366179 | |
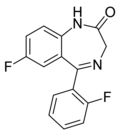 | Ro05-6820 | 8.1308 / 7.4nM | 7-fluoro-5-(2-fluorophenyl)-1H-benzo[e] [1,4]diazepin-2(3H)-one | 44366116 | |
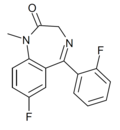 | Ro05-6822 | 8.2924 / 5.1nM | 7-fluoro-5-(2-fluorophenyl)-1-methyl-1H-benzo[e] [1,4]diazepin-2(3H)-one | 23275675 | 2024-34-2 |
 | Iso-flubromazepam | | 7-fluoro-5-(2-bromophenyl)-1H-benzo[e] [1,4]diazepin-2(3H)-one | 15292433 | 153873-96-2 |
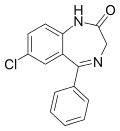 | Nordazepam | 8.0269 / 9.4nM | 7-chloro-5-phenyl-1H-benzo[e] [1,4]diazepin-2(3H)-one | 2997 | 1088-11-5 |
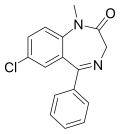 | Diazepam | 8.0915 / 8.1nM | 7-chloro-5-phenyl-1-methyl-1H-benzo[e] [1,4]diazepin-2(3H)-one | 3016 | 439-14-5 |
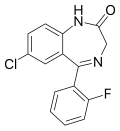 | Norflurazepam (Ro05-3367) | 8.699 | 7-chloro-5-(2-fluorophenyl)-1H-benzo[e] [1,4]diazepin-2(3H)-one | 4540 | 2886-65-9 |
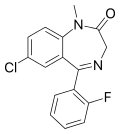 | Fludiazepam | | 7-chloro-5-(2-fluorophenyl)-1-methyl-1H-benzo[e] [1,4]diazepin-2(3H)-one | 3369 | 3900-31-0 |
 | Ro07-3953 | 8.7959 / 1.6nM | 7-chloro-5-(2,6-difluorophenyl)-1H-benzo[e] [1,4]diazepin-2(3H)-one | 23275763 | |
 | Difludiazepam (Ro07-4065) | 8.3872 / 4.1nM | 7-chloro-5-(2,6-difluorophenyl)-1-methyl-1H-benzo[e] [1,4]diazepin-2(3H)-one | 44366236 | 39080-67-6 |
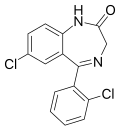 | Delorazepam | 8.7447 / 1.8nM | 7-chloro-5-(2-chlorophenyl)-1H-benzo[e] [1,4]diazepin-2(3H)-one | 17925 | 2894-67-9 |
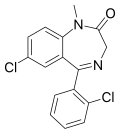 | Diclazepam (Ro05-3448) | 7.8 † | 7-chloro-5-(2-chlorophenyl)-1-methyl-1H-benzo[e] [1,4]diazepin-2(3H)-one | 76168 | 2894-68-0 |
 | Ro05-4864 | TSPO ligand | 7-chloro-5-(4-chlorophenyl)-1-methyl-1H-benzo[e] [1,4]diazepin-2(3H)-one | 1688 | 14439-61-3 |
 | Ro07-5193 | 8.5229 | 7-chloro-5-(2-chloro-6-fluorophenyl)-1H-benzo[e] [1,4]diazepin-2(3H)-one | 44366219 | |
 | Ro22-3294 | 8.1549 | 7-chloro-5-(2,6-dichlorophenyl)-1H-benzo[e] [1,4]diazepin-2(3H)-one | 12790028 | |
 | Ro07-5220 | 8.2596 | 7-chloro-5-(2,6-dichlorophenyl)-1-methyl-1H-benzo[e] [1,4]diazepin-2(3H)-one | 9975396 | 30144-88-8 |
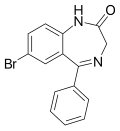 | 7-BPDBD | 7.8 † | 7-bromo-5-phenyl-1H-benzo[e] [1,4]diazepin-2(3H)-one | 76167 | 2894-61-3 |
 | QH-II-063 | | 7-bromo-5-phenyl-1-methyl-1H-benzo[e] [1,4]diazepin-2(3H)-one | 627432 | 28611-28-1 |
 | Phenazepam | 8.4 † | 7-bromo-5-(2-chlorophenyl)-1H-benzo[e] [1,4]diazepin-2(3H)-one | 40113 | 51753-57-2 |
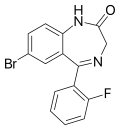 | Flubromazepam (JYI-42) | 7.6 † | 7-bromo-5-(2-fluorophenyl)-1H-benzo[e] [1,4]diazepin-2(3H)-one | 12947024 | 2647-50-9 |
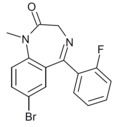 | Flubrometazepam | | 7-bromo-5-(2-fluorophenyl)-1-methyl-1H-benzo[e] [1,4]diazepin-2(3H)-one | 135809 | 86890-79-1 |
 | SH-I-048A | | (3S)-7-bromo-5-(2-fluorophenyl)-3-methyl-1H-benzo[e] [1,4]diazepin-2(3H)-one | 49850464 | 872874-11-8 |
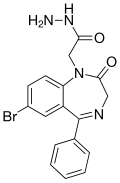 | Gidazepam | 6.4 † | 2-(7-bromo-2-oxo-5-phenyl-2,3-dihydro-1H-benzo[e] [1,4]diazepin-1-yl)acetohydrazide | 121919 | 129186-29-4 |
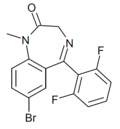 | Ro13-3780 | 8.6198 | 7-bromo-5-(2,6-difluorophenyl)-1-methyl-1H-benzo[e] [1,4]diazepin-2(3H)-one | 9975396 | 103380-73-0 |
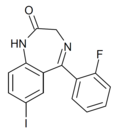 | Ro07-9749 | | 7-iodo-5-(2-fluorophenyl)-1H-benzo[e] [1,4]diazepin-2(3H)-one | 3082318 | 30843-56-2 |
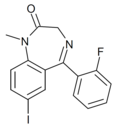 | Ro07-9957 | 8.5376 | 7-iodo-5-(2-fluorophenyl)-1-methyl-1H-benzo[e] [1,4]diazepin-2(3H)-one | 118749 | |
 | Ro05-2904 | 7.8861 / 13nM | 7-trifluoromethyl-5-phenyl-1H-benzo[e] [1,4]diazepin-2(3H)-one | 16795 | 2285-16-7 |
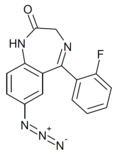 | Ro14-3074 | 8.2757 / 5.3nM | 7-azido-5-(2-fluorophenyl)-1H-benzo[e] [1,4]diazepin-2(3H)-one | | |
 | Nitrazepam | 8.0 / 10nM | 7-nitro-5-phenyl-1H-benzo[e] [1,4]diazepin-2(3H)-one | 4506 | 146-22-5 |
 | Nimetazepam | | 7-nitro-5-phenyl-1-methyl-1H-benzo[e] [1,4]diazepin-2(3H)-one | 4496 | 2011-67-8 |
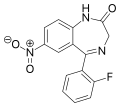 | Ro05-4435 | 8.829 / 1.5nM | 7-nitro-5-(2-fluorophenyl)-1H-benzo[e] [1,4]diazepin-2(3H)-one | 520217 | 2558-30-7 |
 | Flunitrazepam | 8.4202 / 3.8nM | 7-nitro-5-(2-fluorophenyl)-1-methyl-1H-benzo[e] [1,4]diazepin-2(3H)-one | 3380 | 1622-62-4 |
 | Clonazepam | 8.7447 / 1.8nM | 7-nitro-5-(2-chlorophenyl)-1H-benzo[e] [1,4]diazepin-2(3H)-one | 2802 | 1622-61-3 |
 | Ro05-4082 | 8.6576 | 7-nitro-5-(2-chlorophenyl)-1-methyl-1H-benzo[e] [1,4]diazepin-2(3H)-one | 528222 | 5527-71-9 |
 | Ro05-3590 | 8.4559 / 3.5nM | 7-nitro-5-[2-(trifluoromethyl)phenyl]-1H-benzo[e] [1,4]diazepin-2(3H)-one | 15024 | 1427-45-8 |
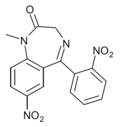 | QH-146 | | 7-nitro-5-(2-nitrophenyl)-1-methyl-1H-benzo[e] [1,4]diazepin-2(3H)-one | 44383992 | |
 | Ro20-7736 | 7.0177 / 96nM | 7-hydroxyamino-5-(2-fluorophenyl)-1-methyl-1H-benzo[e] [1,4]diazepin-2(3H)-one | | |
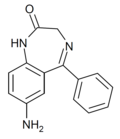 | Ro05-3072 | 6.4134 / 386nM | 7-amino-5-phenyl-1H-benzo[e] [1,4]diazepin-2(3H)-one | 78641 | 4928-02-3 |
 | Ro05-4318 | 6.3372 / 460nM | 7-amino-5-phenyl-1-methyl-1H-benzo[e] [1,4]diazepin-2(3H)-one | 23275339 | 4959-16-4 |
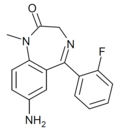 | Ro20-1815 | 7.1871 / 65nM | 7-amino-5-(2-fluorophenyl)-1-methyl-1H-benzo[e] [1,4]diazepin-2(3H)-one | 92294 | 34084-50-9 |
 | Ro05-4619 | 7.1249 / 75nM | 7-amino-5-(2-chlorophenyl)-1H-benzo[e] [1,4]diazepin-2(3H)-one | 188298 | 4959-17-5 |
| Ro05-3308 | IC50 >1000nM | N-(2-oxo-5-phenyl-2,3-dihydro-1H-benzo[e] [1,4]diazepin-7-yl)acetamide | | |
| Ro12-6377 | 7.1249 / 455nM | 1-(5-(2-fluorophenyl)-1-methyl-2-oxo-2,5-dihydro-1H-benzo[e] [1,4]diazepin-7-yl)-3-methylurea | | |
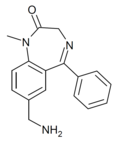 | Ro05-9090 | IC50 >1000nM | 7-(aminomethyl)-1-methyl-5-phenyl-1H-benzo[e] [1,4]diazepin-2(3H)-one | | |
 | Ro05-3343 | IC50 >1000nM | N,N-dimethyl-2-oxo-5-phenyl-2,3-dihydro-1H-benzo[e] [1,4]diazepine-7-sulfonamide | 214460 | 12037-79-5 |
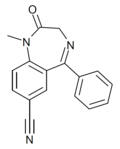 | Ro05-4528 | 6.4202 / 380nM | 7-cyano-5-phenyl-1-methyl-1H-benzo[e] [1,4]diazepin-2(3H)-one | | |
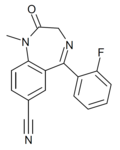 | Ro20-2541 | 7.5229 / 30nM | 7-cyano-5-(2-fluorophenyl)-1-methyl-1H-benzo[e] [1,4]diazepin-2(3H)-one | | |
 | Ro20-2533 | 7.4437 / 36nM | 7-ethyl-5-phenyl-1H-benzo[e] [1,4]diazepin-2(3H)-one | 10264786 | |
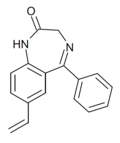 | Ro20-5747 | 7.6198 / 24nM | 7-vinyl-5-phenyl-1H-benzo[e] [1,4]diazepin-2(3H)-one | 44366036 | |
 | QH-ii-066 | 7.4 † | 7-ethynyl-5-phenyl-1-methyl-1H-benzo[e] [1,4]diazepin-2(3H)-one | 9838431 | 183239-39-6 |
 | OMB-18 | | 7-ethynyl-5-(2-fluorophenyl)-1-methyl-1H-benzo[e] [1,4]diazepin-2(3H)-one | 89276170 | |
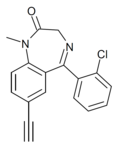 | XLI-352 | | 7-ethynyl-5-(2-chlorophenyl)-1-methyl-1H-benzo[e] [1,4]diazepin-2(3H)-one | 21065236 | |
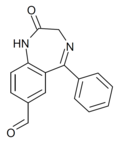 | Ro20-5397 | 7.3665 / 43nM | 7-formyl-5-phenyl-1H-benzo[e] [1,4]diazepin-2(3H)-one | | |
 | Ro20-3053 | 7.7447 / 18nM | 7-acetyl-5-phenyl-1H-benzo[e] [1,4]diazepin-2(3H)-one | 21828109 | |
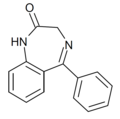 | Ro05-2921 | 6.4559 / 350nM | 5-phenyl-1H-benzo[e] [1,4]diazepin-2(3H)-one | 76175 | 2898-08-0 |
 | Ro05-3663 | IC50 >1000nM | 5-methyl-1H-benzo[e] [1,4]diazepin-2(3H)-one | 5080 | 70656-87-0 |
 | Ro05-4336 | 7.6778 / 21nM | 5-(2-fluorophenyl)-1H-benzo[e] [1,4]diazepin-2(3H)-one | 13292074 | |
 | Ro07-4419 | 7.7212 / 19nM | 5-(2,6-difluorophenyl)-1H-benzo[e] [1,4]diazepin-2(3H)-one | 44366255 | |
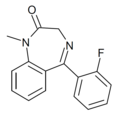 | Ro05-4520 | 7.8539 / 14nM | 5-(2-fluorophenyl)-1-methyl-1H-benzo[e] [1,4]diazepin-2(3H)-one | 193319 | 844-11-1 |
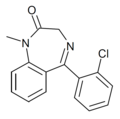 | Ro05-4608 | 8.4202 | 5-(2-chlorophenyl)-1-methyl-1H-benzo[e] [1,4]diazepin-2(3H)-one | 10469149 | |
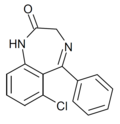 | Ro05-3546 | 6.4949 / 320nM | 6-chloro-5-phenyl-1H-benzo[e] [1,4]diazepin-2(3H)-one | 14590445 | |
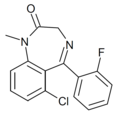 | Ro13-0699 | 6.8239 / 150nM | 6-chloro-5-(2-fluorophenyl)-1-methyl-1H-benzo[e] [1,4]diazepin-2(3H)-one | 44377764 | |
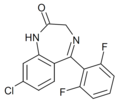 | Ro07-6198 | 7.5528 / 28nM | 8-chloro-5-(2,6-difluorophenyl)-1H-benzo[e] [1,4]diazepin-2(3H)-one | 23275762 | |
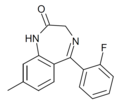 | Ro20-8895 | 7.7212 / 19nM | 8-methyl-5-(2-fluorophenyl)-1H-benzo[e] [1,4]diazepin-2(3H)-one | 44366169 | |
 | Ro13-0593 | 7.1427 / 72nM | 9-chloro-5-(2-fluorophenyl)-1-methyl-1H-benzo[e] [1,4]diazepin-2(3H)-one | | |
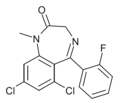 | Ro13-0882 | IC50 300nM | 6,8-dichloro-5-(2-fluorophenyl)-1-methyl-1H-benzo[e] [1,4]diazepin-2(3H)-one | | |
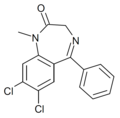 | Ro22-6762 | 7.3979 / 40nM | 7,8-dichloro-5-phenyl-1-methyl-1H-benzo[e] [1,4]diazepin-2(3H)-one | 44366089 | |
 | Ro20-8065 | 8.4437 / 3.6nM | 7,8-dichloro-5-(2-fluorophenyl)-1H-benzo[e] [1,4]diazepin-2(3H)-one | 10358803 | 88695-06-1 |
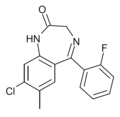 | Ro20-8552 | 7.8539 / 14nM | 7-methyl-8-chloro-5-(2-fluorophenyl)-1H-benzo[e] [1,4]diazepin-2(3H)-one | 44366138 | |
 | Ro05-2750 | 7.4318 / 37nM | 6,8-dichloro-5-phenyl-1H-benzo[e] [1,4]diazepin-2(3H)-one | | |
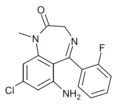 | Ro14-2312 | IC50 >1000nM | 6-amino-8-chloro-5-(2-fluorophenyl)-1-methyl-1H-benzo[e] [1,4]diazepin-2(3H)-one | | |
| Ro07-3609 | 7.284 | | | |
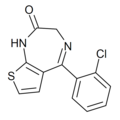 | Ro11-8125 | 7.4318 / 37nM | 5-(2-chlorophenyl)-1H-thieno[2,3-e] [1,4]diazepin-2(3H)-one | | |
 | Ro08-6739 | IC50 70nM | 7-chloro-5-phenyl-1H-thieno[2,3-e] [1,4]diazepin-2(3H)-one | | |
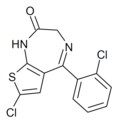 | Ro09-9212 | 8.4089 / 3.9nM | 7-chloro-5-(2-chlorophenyl)-1H-thieno[2,3-e] [1,4]diazepin-2(3H)-one | 135721042 | |
 | Ro10-2643 | IC50 9.4nM | 7-chloro-5-(2-chlorophenyl)-1H-thieno[3,2-e] [1,4]diazepin-2(3H)-one | | |
 | Clotiazepam | | 7-ethyl-5-(2-chlorophenyl)-1-methyl-1H-thieno[2,3-e] [1,4]diazepin-2(3H)-one | 2811 | 33671-46-4 |
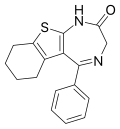 | Bentazepam | 8.5 † | 5-phenyl-3,5a,6,7,8,9-hexahydro-2H-[1]benzothieno[2,3-e] [1,4]diazepin-2(3H)-one | 34592 | 29462-18-8 |
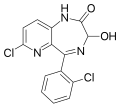 | Lopirazepam | | 7-chloro-5-(2-chlorophenyl)-3-hydroxy-1,3-dihydro-2H-pyrido[3,2-e] [1,4]diazepin-2-one | 68672 | 42863-81-0 |
 | Premazepam | 6.7696 / 170nM | 6,7-dimethyl-5-phenyl-3,7-dihydropyrrolo[3,4-e] [1,4]diazepin-2(1H)-one | 72104 | 57435-86-6 |
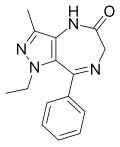 | Ripazepam | | 1-ethyl-3-methyl-8-phenyl-4,6-dihydropyrazolo[4,3-e] [1,4]diazepin-5(1H)-one | 33474 | 26308-28-1 |
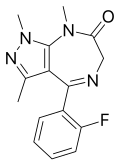 | Zolazepam | | 1,3,8-trimethyl-4-(2-fluorophenyl)-6,8-dihydropyrazolo[3,4-e] [1,4]diazepin-7(1H)-one | 35775 | 31352-82-6 |
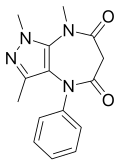 | Zomebazam | 8.1 † | 1,3,8-trimethyl-4-phenyl-6,8-dihydropyrazolo[4,3-b] [1,4]diazepine-5,7(1H,4H)-dione | 132677 | 78466-70-3 |
 | Ro17-2221 | 6.585 / 260nM | 1-(2-aminoethyl)-5-phenyl-1H-benzo[e] [1,4]diazepin-2(3H)-one | | |
| Ro07-5096 | IC50 >1000nM | 2-(7-chloro-5-(2-fluorophenyl)-2-oxo-2,3-dihydro-1H-benzo[e] [1,4]diazepin-1-yl)acetic acid | | |
| Ro08-3026 | 7.2007 | | | |
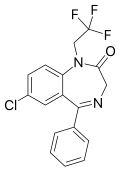 | Halazepam | 7.0362 / 92nM | 7-chloro-5-phenyl-1-(2,2,2-trifluoroethyl)-1H-benzo[e] [1,4]diazepin-2(3H)-one | 31640 | 23092-17-3 |
 | Quazepam | | 7-chloro-5-(2-fluorophenyl)-1-(2,2,2-trifluoroethyl)-1H-benzo[e] [1,4]diazepin-2(3H)-thione | 4999 | 36735-22-5 |
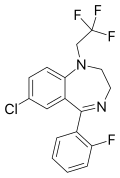 | Fletazepam | | 7-chloro-5-(2-fluorophenyl)-1-(2,2,2-trifluoroethyl)-1H-benzo[e] [1,4]diazepine | 36834 | 34482-99-0 |
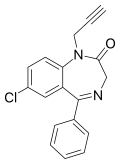 | Pinazepam | 7.0339 / 92.5nM | 7-chloro-5-phenyl-1-(prop-2-yn-1-yl)-1H-benzo[e] [1,4]diazepin-2(3H)-one | 40391 | 52463-83-9 |
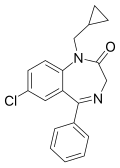 | Prazepam | IC50 110nM | 7-chloro-5-phenyl-1-cyclopropylmethyl-1H-benzo[e] [1,4]diazepin-2(3H)-one | 4890 | 2955-38-6 |
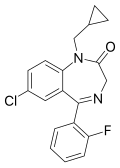 | Flutoprazepam | 6.6 † | 7-chloro-5-(2-fluorophenyl)-1-cyclopropylmethyl-1H-benzo[e] [1,4]diazepin-2(3H)-one | 3400 | 25967-29-7 |
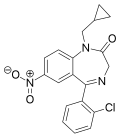 | Cloniprazepam | 7.8 † | 7-nitro-5-(2-chlorophenyl)-1-cyclopropylmethyl-1H-benzo[e] [1,4]diazepin-2(3H)-one | | |
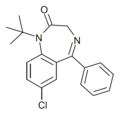 | Ro20-1310 | 6.2076 / 620nM | 7-chloro-5-phenyl-1-(t-butyl)-1H-benzo[e] [1,4]diazepin-2(3H)-one | | |
 | Fosazepam | | 7-chloro-5-phenyl-1-(dimethylphosphorylmethyl)-1H-benzo[e] [1,4]diazepin-2(3H)-one | 37114 | 35322-07-7 |
 | Iclazepam | | 7-chloro-5-phenyl-1-[2-(cyclopropylmethoxy)ethyl]-1H-benzo[e] [1,4]diazepin-2(3H)-one | 68777 | 57916-70-8 |
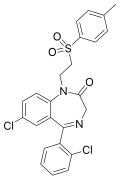 | Tolufazepam | | 7-chloro-5-(2-chlorophenyl)-1-[2-(4-methylphenyl)sulfonylethyl]-1H-benzo[e] [1,4]diazepin-2(3H)-one | 65647 | 86273-92-9 |
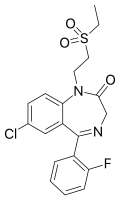 | Elfazepam | 6.9 † | 7-chloro-5-(2-fluorophenyl)-1-(2-ethylsulfonylethyl)-1H-benzo[e] [1,4]diazepin-2(3H)-one | 65445 | 52042-01-0 |
 | Reclazepam | | 2-[7-chloro-5-(2-chlorophenyl)-2,3-dihydro-1H-1,4-benzodiazepin-1-yl]-1,3-oxazol-4(5H)-one | 3052777 | 76053-16-2 |
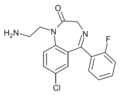 | Ro07-1986 | 8.0809 / 8.3nM | 1-(2-aminoethyl)-7-chloro-5-(2-fluorophenyl)-1H-benzo[e] [1,4]diazepin-2(3H)-one | | |
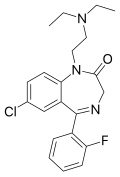 | Flurazepam | 7.8297 | 7-chloro-1-[2-(diethylamino)ethyl]-5-(2-fluorophenyl)-1,3-dihydro-2H-1,4-benzodiazepin-2-one | 3393 | 17617-23-1 |
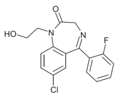 | Ro07-2750 | 7.6108 / 24.5nM | 7-chloro-5-(2-fluorophenyl)-1-(2-hydroxyethyl)-1H-benzo[e] [1,4]diazepin-2(3H)-one | | |
 | Motrazepam | IC50 430nM | 1-(methoxymethyl)-7-nitro-5-phenyl-1H-benzo[e] [1,4]diazepin-2(3H)-one | 65764 | 29442-58-8 |
| Ro08-9013 | 7.3716 | | | |
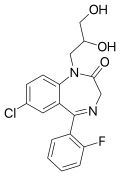 | Proflazepam | 6.8539 / 140nM | 7-chloro-1-(2,3-dihydroxypropyl)-5-(2-fluorophenyl)-1H-benzo[e] [1,4]diazepin-2(3H)-one | 3050433 | 52829-30-8 |
 | Ro22-4683 | 6.5229 / 300nM | 7-nitro-5-(2-fluorophenyl)-1-(t-butyl)-1H-benzo[e] [1,4]diazepin-2(3H)-one | | |
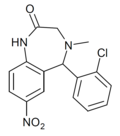 | Ro15-8852 | 6.1391 / 726nM | 5-(2-chlorophenyl)-4-methyl-7-nitro-4,5-dihydro-1H-benzo[e] [1,4]diazepin-2(3H)-one | | |
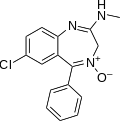 | Chlorodiazepoxide | 6.4535 / 352nM | 7-chloro-2-methylamino-5-phenyl-3H-benzo[e] [1,4]diazepine-4-oxide | 2712 | 58-25-3 |
 | Cyprazepam | | 7-chloro-N-(cyclopropylmethyl)-4-hydroxy-5-phenyl-3H-benzo[e] [1,4]diazepin-2-imine | 27452 | 15687-07-7 |
 | Uldazepam | 7.6 † | 7-chloro-5-(2-chlorophenyl)-N-prop-2-enoxy-3H-benzo[e] [1,4]diazepin-2-amine | 34274 | 28546-58-9 |
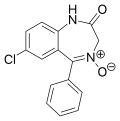 | Demoxepam | 6.5086 / 310nM | 7-chloro-1,3-dihydro-5-phenyl-2H-benzo[e] [1,4]diazepin-2-one-4-oxide | 13756 | 963-39-3 |
 | Medazepam | IC50 870nM | 7-chloro-5-phenyl-1-methyl-1H-benzo[e] [1,4]diazepine | 4041 | 2898-12-6 |
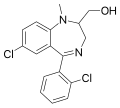 | Tuclazepam | 7.7 † | 7-chloro-5-(2-chlorophenyl)-2-(hydroxymethyl)-1-methyl-2,3-dihydro-1H-benzo[e] [1,4]diazepine | 3050405 | 51037-88-8 |
 | Metaclazepam | | 7-bromo-5-(2-chlorophenyl)-2-(methoxymethyl)-1-methyl-2,3-dihydro-1H-benzo[e] [1,4]diazepine | 71272 | 84031-17-4 |
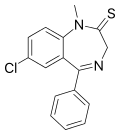 | Sulazepam | 7.7 † | 7-chloro-5-phenyl-1-methyl-1H-benzo[e] [1,4]diazepin-2(3H)-thione | 17931 | 2898-13-7 |
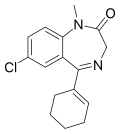 | Tetrazepam | 7.4685 / 34nM | 7-chloro-5-(cyclohexen-1-yl)-1-methyl-1H-benzo[e] [1,4]diazepin-2(3H)-one | 25215 | 10379-14-3 |
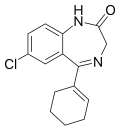 | Nortetrazepam | IC50 34nM | 7-chloro-5-(cyclohexen-1-yl)-1H-benzo[e] [1,4]diazepin-2(3H)-one | 166581 | 10379-11-0 |
 | Menitrazepam | | 7-nitro-5-(cyclohexen-1-yl)-1-methyl-1H-benzo[e] [1,4]diazepin-2(3H)-one | 189875 | 28781-64-8 |
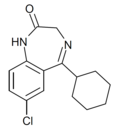 | Ro05-3328 | 7.0605 / 87nM | 7-chloro-5-cyclohexyl-1H-benzo[e] [1,4]diazepin-2(3H)-one | | |
 | Clazolam | 8.1 † | 2-chloro-5-methyl-5,9,10,14b-tetrahydroisoquino[2,1-d] [1,4]benzodiazepin-6(7H)-one | 24107 | 7492-29-7 |
 | Bromazepam | 7.7447 / 18nM | 7-bromo-5-(pyridin-2-yl)-1H-benzo[e] [1,4]diazepin-2(3H)-one | 2441 | 1812-30-2 |
 | Methylbromazepam | | 7-bromo-5-(pyridin-2-yl)-1-methyl-1H-benzo[e] [1,4]diazepin-2(3H)-one | 630183 | 1812-33-5 |
 | Pyridazino-diazepam | | 7-chloro-5-(pyridazin-3-yl)-1-methyl-1H-benzo[e] [1,4]diazepin-2(3H)-one | | |
 | Ro5-3335 | | 7-Chloro-1,3-dihydro-5-(1H-pyrrol-2-yl)-2H-1,4-benzodiazepin-2-one | 64983 | |
 | SCHEMBL9684958 | | 7-chloro-5-(1H-pyrazol-5-yl)-1H-benzo[e] [1,4]diazepin-2(3H)-one | 21738192 | |
 | Compound 6a | 9.5 † | 7-chloro-5-(3,5-dimethyl-4H-1,2,4-triazol-4-yl)-1,3-dihydro-2H-1,4-benzodiazepin-2-one | |
 | JC-184 | | 7-bromo-5-(2-thienyl)-1H-benzo[e] [1,4]diazepin-2(3H)-one | 21065240 | |
 | BDBM50083903 | | 7-chloro-5-(2-furanyl)-1-methyl-1H-benzo[e] [1,4]diazepin-2(3H)-one | 10423506 | |
| Ro05-5605 | 6.5376 | | | |
| Ro11-3129 | 8.1871 | (+)-2-amino-N-[2-(2-chlorobenzoyl)-4-nitrophenyl]propanamide | 21413751 | 65607-70-7 |
| Ro03-7355 | 6.3768 | | | |
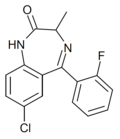 | Ro11-4878 | 8.4559 / 3.5nM | 7-chloro-5-(2-fluorophenyl)-3-methyl-1H-benzo[e] [1,4]diazepin-2(3H)-one | | |
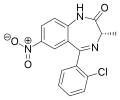 | Meclonazepam | 8.9208 / 1.2nM | (3S)-7-nitro-5-(2-chlorophenyl)-3-methyl-1H-benzo[e] [1,4]diazepin-2(3H)-one | 3033985 | 58662-84-3 |
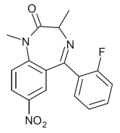 | Ro11-6896 | 8.1549 / 7nM | 7-nitro-5-(2-fluorophenyl)-1,3-dimethyl-1H-benzo[e] [1,4]diazepin-2(3H)-one | | |
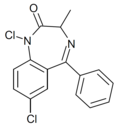 | Ro06-7263 | 7.3098 / 49nM | 1,7-dichloro-5-phenyl-3-methyl-1H-benzo[e] [1,4]diazepin-2(3H)-one | | |
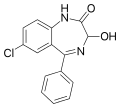 | Oxazepam | 7.7447 / 18nM | 7-chloro-3-hydroxy-5-phenyl-1H-benzo[e] [1,4]diazepin-2(3H)-one | 4616 | 604-75-1 |
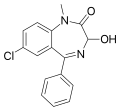 | Temazepam | 7.7959 / 16nM | 7-chloro-3-hydroxy-5-phenyl-1-methyl-1H-benzo[e] [1,4]diazepin-2(3H)-one | 5391 | 846-50-4 |
 | Lorazepam | 8.4559 / 3.5nM | 7-chloro-3-hydroxy-5-(2-chlorophenyl)-1H-benzo[e] [1,4]diazepin-2(3H)-one | 3958 | 846-49-1 |
 | Lormetazepam | | 7-chloro-3-hydroxy-5-(2-chlorophenyl)-1-methyl-1H-benzo[e] [1,4]diazepin-2(3H)-one | 13314 | 848-75-9 |
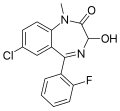 | Flutemazepam | 8.1 † | 7-chloro-3-hydroxy-5-(2-fluorophenyl)-1-methyl-1H-benzo[e] [1,4]diazepin-2(3H)-one | 40344 | 52391-89-6 |
 | Cinolazepam | | 7-chloro-3-hydroxy-5-(2-fluorophenyl)-1-(2-cyanoethyl)-1H-benzo[e] [1,4]diazepin-2(3H)-one | 3033621 | 75696-02-5 |
 | Doxefazepam | | 7-chloro-3-hydroxy-5-(2-fluorophenyl)-1-(2-hydroxyethyl)-1H-benzo[e] [1,4]diazepin-2(3H)-one | 38668 | 40762-15-0 |
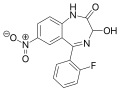 | Nifoxipam | 8.5 † | 7-nitro-3-hydroxy-5-(2-fluorophenyl)-1H-benzo[e] [1,4]diazepin-2(3H)-one | 3058221 | 74723-10-7 |
 | Nitemazepam | | 7-nitro-3-hydroxy-5-phenyl-1-methyl-1H-benzo[e] [1,4]diazepin-2(3H)-one | 12362353 | 40762-03-6 |
 | 3-Hydroxyphenazepam | 8.7 † | 7-bromo-3-hydroxy-5-(2-chlorophenyl)-1H-benzo[e] [1,4]diazepin-2(3H)-one | 125820 | 70030-11-4 |
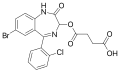 | Cinazepam | | 7-bromo-3-succinyloxy-5-(2-chlorophenyl)-1H-benzo[e] [1,4]diazepin-2(3H)-one | 629281 | 172986-25-3 |
 | Pivoxazepam | | 7-chloro-3-pivalyloxy-5-phenyl-1H-benzo[e] [1,4]diazepin-2(3H)-one | 68722 | 55299-10-0 |
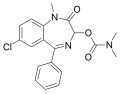 | Camazepam | 6.0458 | 7-chloro-1-methyl-2-oxo-5-phenyl-2,3-dihydro-1H-benzo[e] [1,4]diazepin-3-yl N,N-dimethylcarbamate | 37367 | 36104-80-0 |
 | Clorazepate | IC50 59nM | 7-chloro-2-oxo-5-phenyl-1H-benzo[e] [1,4]diazepine-3-carboxylic acid | 2809 | 23887-31-2 |
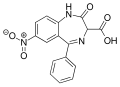 | Nitrazepate | | 7-nitro-2-oxo-5-phenyl-1H-benzo[e] [1,4]diazepine-3-carboxylic acid | 21740 | 5571-84-6 |
 | Ethyl carfluzepate | 8.0 † | ethyl 7-chloro-5-(2-fluorophenyl)-1-(methylcarbamoyl)-2-oxo-3H-benzo[e] [1,4]diazepine-3-carboxylate | 68856 | 65400-85-3 |
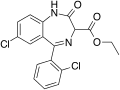 | Ethyl dirazepate | 7.5 † | ethyl 7-chloro-5-(2-chlorophenyl)-2-oxo-3H-benzo[e] [1,4]diazepine-3-carboxylate | 208941 | 23980-14-5 |
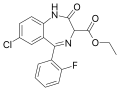 | Ethyl loflazepate | | ethyl 7-chloro-5-(2-fluorophenyl)-2-oxo-3H-benzo[e] [1,4]diazepine-3-carboxylate | 3299 | 29177-84-2 |
 | Carburazepam | 7.9 † | 7-chloro-1-methyl-2-oxo-5-phenyl-1,2,3,5-tetrahydro-4H-benzo[e] [1,4]diazepine-4-carboxamide | 68787 | 59009-93-7 |
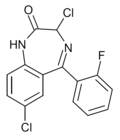 | Ro20-7078 | 8.2757 / 5.3nM | 3,7-dichloro-5-(2-fluorophenyl)-1H-benzo[e] [1,4]diazepin-2(3H)-one | | |
 | Clobazam | 6.8861 / 130nM | 7-chloro-1-methyl-5-phenyl-1H-1,5-benzodiazepine-2,4(3H,5H)-dione | 2789 | 22316-47-8 |
 | Desmethylclobazam | 6.6778 / 210nM | 7-chloro-5-phenyl-1H-1,5-benzodiazepine-2,4(3H,5H)-dione | | |
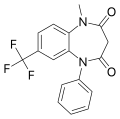 | Triflubazam | 8.4 † | 7-trifluoromethyl-1-methyl-5-phenyl-1H-1,5-benzodiazepine-2,4(3H,5H)-dione | 2789 | 22316-47-8 |
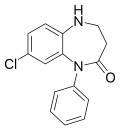 | Lofendazam | | 7-chloro-5-phenyl-1,3,4,5-tetrahydro-4H-1,5-benzodiazepin-4-one | 71709 | 29176-29-2 |
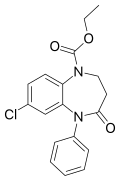 | Arfendazam | 8.3 † | ethyl 7-chloro-4-oxo-5-phenyl-2,3-dihydro-1,5-benzodiazepine-1-carboxylate | 65803 | 37669-57-1 |
 | CP-1414S | 7.9 † | 8-nitro-1-phenyl-4-amino-3H-1,5-benzodiazepin-2-one | 37594 | 36975-99-2 |
 | Compound 6i | 8.6 † | 9-chloro-11-phenyl-6,11-dihydro-5H-pyrimido[4,5-b][1,5]benzodiazepin-5-one | |
 | Oxazolam | | 10-chloro-2-methyl-11b-phenyl-2,3,7,11b-tetrahydrobenzo[f]oxazolo[3,2-d] [1,4]diazepin-6(5H)-one | 62779 | 24143-17-7 |
 | Cloxazolam | | 10-chloro-11b-(2-chlorophenyl)-2,3,5,7-tetrahydro-[1,3]oxazolo[3,2-d] [1,4]benzodiazepin-6(5H)-one | 2816 | 24166-13-0 |
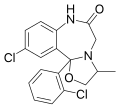 | Mexazolam | | 10-chloro-11b-(2-chlorophenyl)-3-methyl-2,3,7,11b-tetrahydro[1,3]oxazolo[3,2-d] [1,4]benzodiazepin-6(5H)-one | 4177 | 31868-18-5 |
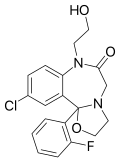 | Flutazolam | | 10-chloro-11b-(2-fluorophenyl)-7-(2-hydroxyethyl)-3,5-dihydro-2H-[1,3]oxazolo[3,2-d] [1,4]benzodiazepin-6(5H)-one | 3398 | 27060-91-9 |
 | Haloxazolam | | 10-bromo-11b-(2-fluorophenyl)-2,3,5,7-tetrahydro-[1,3]oxazolo[3,2-d] [1,4]benzodiazepin-6(5H)-one | 3563 | 59128-97-1 |
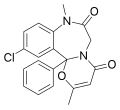 | Ketazolam | | 11-chloro-8,12b-dihydro-2,8-dimethyl-12b-phenyl-4H-[1,3]oxazino[3,2-d] [1,4]benzodiazepine-4,7(6H)-dione | 33746 | 27223-35-4 |
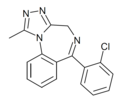 | U-35005 | 8.3665 / 4.3nM | 6-(2-chlorophenyl)-1-methyl-4H-benzo[f] [1,2,4]triazolo[4,3-a] [1,4]diazepine | 21680194 | |
 | 4'-Chlorodeschloroalprazolam | | 6-(4-chlorophenyl)-1-methyl-4H-[1,2,4]triazolo[4,3-a][1,4]benzodiazepine | 142641556 | 92262-72-1 |
 | Estazolam | 8.0706 / 8.5nM | 8-chloro-6-phenyl-4H-benzo[f] [1,2,4]triazolo[4,3-a] [1,4]diazepine | 3261 | 29975-16-4 |
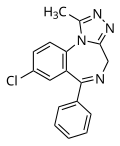 | Alprazolam | 7.699 / 20nM | 8-chloro-6-phenyl-1-methyl-4H-benzo[f] [1,2,4]triazolo[4,3-a] [1,4]diazepine | 2118 | 28981-97-7 |
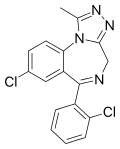 | Triazolam | 8.3979 / 4nM | 8-chloro-6-(2-chlorophenyl)-1-methyl-4H-benzo[f] [1,2,4]triazolo[4,3-a] [1,4]diazepine | 5556 | 28911-01-5 |
 | alpha-Hydroxytriazolam | 8.3768 / 4.2nM | 8-chloro-6-(2-chlorophenyl)-1-hydroxymethyl-4H-benzo[f] [1,2,4]triazolo[4,3-a] [1,4]diazepine | 1963 | 37115-45-0 |
 | Flualprazolam | 8.3 † | 8-chloro-6-(2-fluorophenyl)-1-methyl-4H-benzo[f] [1,2,4]triazolo[4,3-a] [1,4]diazepine | 10359044 | 28910-91-0 |
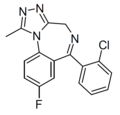 | Iso-flualprazolam | | 8-fluoro-6-(2-chlorophenyl)-1-methyl-4H-benzo[f] [1,2,4]triazolo[4,3-a] [1,4]diazepine | | |
 | Desmethyltriazolam | 8.3 † | 8-chloro-6-(2-chlorophenyl)-4H-benzo[f] [1,2,4]triazolo[4,3-a] [1,4]diazepine | 826660 | 42292-42-2 |
 | Nitrazolam | 8.5 † | 8-nitro-6-phenyl-1-methyl-4H-benzo[f] [1,2,4]triazolo[4,3-a] [1,4]diazepine | 20317278 | 28910-99-8 |
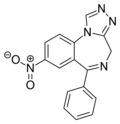 | Desmethylnitrazolam | 8.8 † | 8-nitro-6-phenyl-4H-benzo[f] [1,2,4]triazolo[4,3-a] [1,4]diazepine | 20317280 | 30858-58-3 |
 | Clonazolam | 9.5 † | 8-nitro-6-(2-chlorophenyl)-1-methyl-4H-benzo[f] [1,2,4]triazolo[4,3-a] [1,4]diazepine | 12317881 | 33887-02-4 |
 | Flunitrazolam | 8.8 † | 8-nitro-6-(2-fluorophenyl)-1-methyl-4H-benzo[f] [1,2,4]triazolo[4,3-a] [1,4]diazepine | 137700379 | 2243815-18-9 |
 | Flubromazolam (JYI-73) | 8.8 † | 8-bromo-6-(2-fluorophenyl)-1-methyl-4H-benzo[f] [1,2,4]triazolo[4,3-a] [1,4]diazepine | 21930924 | 612526-40-6 |
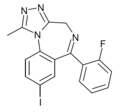 | Fluiodomazolam (BDBM50011621) | | 8-iodo-6-(2-fluorophenyl)-1-methyl-4H-benzo[f] [1,2,4]triazolo[4,3-a] [1,4]diazepine | 14851835 | |
 | Triflumazolam (SCHEMBL7327294) | | 8-trifluoromethyl-6-phenyl-1-methyl-4H-benzo[f] [1,2,4]triazolo[4,3-a] [1,4]diazepine | 19010444 | 28910-98-7 |
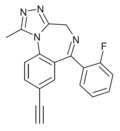 | JYI-70 | | 8-ethynyl-6-(2-fluorophenyl)-1-methyl-4H-benzo[f] [1,2,4]triazolo[4,3-a] [1,4]diazepine | 14851900 | |
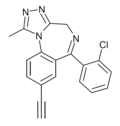 | XLI-296 | | 8-ethynyl-6-(2-chlorophenyl)-1-methyl-4H-benzo[f] [1,2,4]triazolo[4,3-a] [1,4]diazepine | 14851901 | |
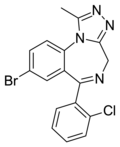 | Clobromazolam (DM-II-90) | 8.2 † | 8-bromo-6-(2-chlorophenyl)-1-methyl-4H-benzo[f] [1,2,4]triazolo[4,3-a] [1,4]diazepine | 1032830 | 87213-50-1 |
 | Bromazolam (XLI-268) | 8.5 † | 8-bromo-6-phenyl-1-methyl-4H-benzo[f] [1,2,4]triazolo[4,3-a] [1,4]diazepine | 12562546 | 71368-80-4 |
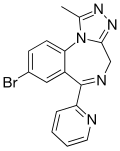 | Pyrazolam (SH-I-04) | 8.1 † | 8-bromo-6-(pyridin-2-yl)-1-methyl-4H-benzo[f] [1,2,4]triazolo[4,3-a] [1,4]diazepine | 12562545 | 39243-02-2 |
 | Pyclazolam | 8.2 † | 8-chloro-6-(pyridin-2-yl)-1-methyl-4H-benzo[f] [1,2,4]triazolo[4,3-a] [1,4]diazepine | 20368150 | |
 | Pynazolam | 9.4 † | 8-nitro-6-(pyridin-2-yl)-1-methyl-4H-benzo[f] [1,2,4]triazolo[4,3-a] [1,4]diazepine | 20368157 | 2034366-97-5 |
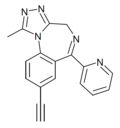 | Pyeazolam (SH-TRI-108) | 7.9 † | 8-ethynyl-6-(pyridin-2-yl)-1-methyl-4H-benzo[f] [1,2,4]triazolo[4,3-a] [1,4]diazepine | 71811108 | 1349115-59-8 |
 | Adinazolam | 6.8697 / 135nM | 8-chloro-6-phenyl-1-(N,N-dimethylaminomethyl)-4H-benzo[f] [1,2,4]triazolo[4,3-a] [1,4]diazepine | 37632 | 37115-32-5 |
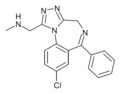 | U-42352 | | 8-chloro-6-phenyl-1-(N-methylaminomethyl)-4H-benzo[f] [1,2,4]triazolo[4,3-a] [1,4]diazepine | 119094 | 37115-33-6 |
 | Fluadinazolam | 7.1 † | 8-chloro-6-(2-fluorophenyl)-1-(N,N-dimethylaminomethyl)-4H-benzo[f] [1,2,4]triazolo[4,3-a] [1,4]diazepine | 21537253 | 37391-59-6 |
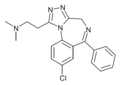 | U-43465 F | 7.9431 | 8-chloro-1-[2-(dimethylamino) ethyl]-6-phenyl-4H-s-triazolo[4,3-a][1,4]benzodiazepine | 134388 | 83983-74-8 |
 | Ro11-5073 | 8.4815 / 3.3nM | (4S)-8-chloro-6-(2-fluorophenyl)-1,4-dimethyl-4H-benzo[f] [1,2,4]triazolo[4,3-a] [1,4]diazepine | 101637147 | |
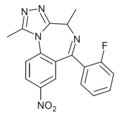 | Ro11-6679 | 8.3979 / 4nM | 8-nitro-6-(2-fluorophenyl)-1,4-dimethyl-4H-benzo[f] [1,2,4]triazolo[4,3-a] [1,4]diazepine | | |
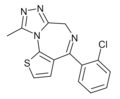 | Ro17-4582 | 8.4559 / 3.5nM | 4-(2-chlorophenyl)-9-methyl-6H-thieno[3,2-f] [1,2,4]triazolo[4,3-a] [1,4]diazepine | | |
 | Etizolam | 8.5086 / 3.1nM | 2-ethyl-4-(2-chlorophenyl)-9-methyl-6H-thieno[3,2-f] [1,2,4]triazolo[4,3-a] [1,4]diazepine | 3307 | 40054-69-1 |
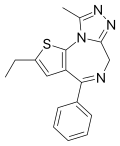 | Deschloroetizolam | 8.5 † | 2-ethyl-4-phenyl-9-methyl-6H-thieno[3,2-f] [1,2,4]triazolo[4,3-a] [1,4]diazepine | 827322 | 40054-73-7 |
 | Desmethyletizolam | | 2-ethyl-4-(2-chlorophenyl)-6H-thieno[3,2-f] [1,2,4]triazolo[4,3-a] [1,4]diazepine | 12434325 | 40054-68-0 |
 | Fluetizolam | 8.8 † | 2-ethyl-4-(2-fluorophenyl)-9-methyl-6H-thieno[3,2-f] [1,2,4]triazolo[4,3-a] [1,4]diazepine | 12434320 | 40054-88-4 |
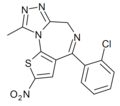 | Nitizolam | | 2-nitro-4-(2-chlorophenyl)-9-methyl-6H-thieno[3,2-f] [1,2,4]triazolo[4,3-a] [1,4]diazepine | 70600959 | |
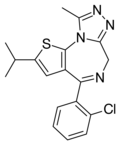 | Iprotizolam | | 2-isopropyl-4-(2-chlorophenyl)-9-methyl-6H-thieno[3,2-f] [1,2,4]triazolo[4,3-a] [1,4]diazepine | 67727941 | |
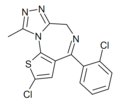 | Clotizolam (Ro11-1465) | 8.8539 / 1.4nM | 2-chloro-4-(2-chlorophenyl)-9-methyl-4H-thieno[3,2-f] [1,2,4]triazolo[4,3-a] [1,4]diazepine | 3041455 | 54123-06-7 |
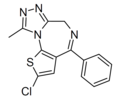 | Deschloroclotizolam | | 2-chloro-4-phenyl-9-methyl-4H-thieno[3,2-f] [1,2,4]triazolo[4,3-a] [1,4]diazepine | 157010678 | 1629324-97-5 |
 | Fluclotizolam | 9.1 † | 2-chloro-4-(2-fluorophenyl)-9-methyl-4H-thieno[3,2-f] [1,2,4]triazolo[4,3-a] [1,4]diazepine | 21317700 | 54123-15-8 |
 | Difluclotizolam | | 2-chloro-4-(2,6-difluorophenyl)-9-methyl-4H-thieno[3,2-f] [1,2,4]triazolo[4,3-a] [1,4]diazepine | 21317683 | |
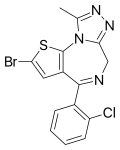 | Brotizolam | 8.9208 | 2-bromo-4-(2-chlorophenyl)-9-methyl-6H-thieno[3,2-f] [1,2,4]triazolo[4,3-a] [1,4]diazepine | 2451 | 57801-81-7 |
 | Flubrotizolam (LS-152,574) | 9.6 † | 2-bromo-4-(2-fluorophenyl)-9-methyl-6H-thieno[3,2-f] [1,2,4]triazolo[4,3-a] [1,4]diazepine | 3044878 | 57801-95-3 |
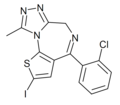 | Ro14-1636 | 8.8239 | 2-iodo-4-(2-chlorophenyl)-9-methyl-6H-thieno[3,2-f] [1,2,4]triazolo[4,3-a] [1,4]diazepine | 14851924 | |
 | Ciclotizolam | 8.0 † | 2-bromo-4-(2-chlorophenyl)-9-cyclohexyl-6H-thieno[3,2-f] [1,2,4]triazolo[4,3-a] [1,4]diazepine | 71949 | 58765-21-2 |
| Ro11-7800 | 8.5376 / 2.9nM | (2-chloro-4-(2-chlorophenyl)-6H-thieno[3,2-f] [1,2,4]triazolo[4,3-a] [1,4]diazepin-9-yl)methanamine | | |
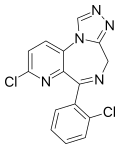 | Zapizolam | 8.8 † | 8-chloro-6-(2-chlorophenyl)-4H-pyrido[2,3-f] [1,2,4]triazolo[4,3-a] [1,4]diazepine | 68832 | 64098-32-4 |
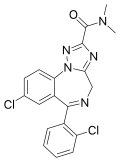 | Rilmazolam (LS-188,599) | 7.3 † | 8-chloro-6-(2-chlorophenyl)-N,N-dimethyl-4H-1,2,4-triazolo[1,5-a] [1,4]benzodiazepine-2-carboxamide | 148494 | 50330-59-1 |
 | Midazolam | 8.3188 / 4.8nM | 8-chloro-6-(2-fluorophenyl)-1-methyl-4H-imidazo[1,5-a] [1,4]benzodiazepine | 4192 | 59467-70-8 |
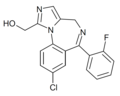 | alpha-Hydroxymidazolam | 8.3468 / 4.5nM | 8-chloro-6-(2-fluorophenyl)-1-hydroxymethyl-4H-imidazo[1,5-a] [1,4]benzodiazepine | 107917 | 59468-90-5 |
 | Ro22-0284 | | 8-chloro-6-(2-fluorophenyl)-1-hydroxymethyl-4-hydroxy-4H-imidazo[1,5-a] [1,4]benzodiazepine | 10316307 | 64740-68-7 |
 | Climazolam | 8.1 † | 8-chloro-6-(2-chlorophenyl)-1-methyl-4H-imidazo[1,5-a] [1,4]benzodiazepine | 68790 | 59467-77-5 |
 | Remimazolam | 8.3 † | methyl 3-[(4S)-8-bromo-1-methyl-6-(pyridin-2-yl)-4H-imidazo[1,2-a] [1,4]benzodiazepin-4-yl]propanoate | 9824461 | 308242-62-8 |
 | Ro15-8670 | 7.8239 / 15nM | ethyl 8-chloro-6-phenyl-4H-benzo[f]imidazo[1,5-a] [1,4]diazepine-3-carboxylate | 14907889 | |
 | JYI-32 | | ethyl 8-bromo-6-(2-fluorophenyl)-4H-benzo[f]imidazo[1,5-a] [1,4]diazepine-3-carboxylate | 21930922 | |
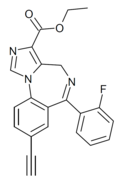 | JY-XHE-057 | | ethyl 8-ethynyl-6-(2-fluorophenyl)-4H-benzo[f]imidazo[1,5-a] [1,4]diazepine-3-carboxylate | 21065283 | |
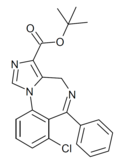 | Ro16-0529 | 7.8539 / 14nM | tert-butyl 7-chloro-6-phenyl-4H-benzo[f]imidazo[1,5-a] [1,4]diazepine-3-carboxylate | | |
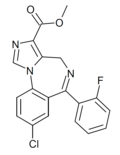 | Ro21-5205 | 8.1308 / 7.4nM | methyl 8-chloro-6-(2-fluorophenyl)-4H-benzo[f]imidazo[1,5-a] [1,4]diazepine-3-carboxylate | 12801973 | |
 | SH-053-R-CH3-2'F | 7.9 † | ethyl (4R)-8-ethynyl-6-(2-fluorophenyl)-4-methyl-4H-benzo[f]imidazo[1,5-a] [1,4]diazepine-3-carboxylate | 11574585 | 872874-14-1 |
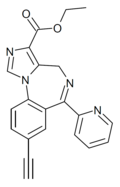 | HZ-166 | | ethyl 8-ethynyl-6-(pyridin-2-yl)-4H-benzo[f]imidazo[1,5-a] [1,4]diazepine-3-carboxylate | 10309028 | 612527-56-7 |
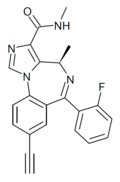 | MP-III-022 | 9.1 † | (4R)-8-ethynyl-6-(2-fluorophenyl)-N,4-dimethyl-4H-benzo[f]imidazo[1,5-a] [1,4]diazepine-3-carboxamide | 130439777 | |
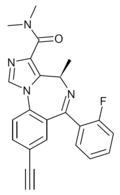 | GL-II-73 | | (4R)-8-ethynyl-6-(2-fluorophenyl)-N,N,4-trimethyl-4H-benzo[f]imidazo[1,5-a] [1,4]diazepine-3-carboxamide | 130439778 | |
 | YT-III-31 | | 8-ethynyl-6-phenyl-N-methyl-4H-benzo[f]imidazo[1,5-a] [1,4]diazepine-3-carboxamide | 49848318 | |
| Ro22-1892 | 7.9208 / 12nM | 8-chloro-6-(2-fluorophenyl)-3-(isopropoxycarbonyl)-4H-benzo[f]imidazo[1,5-a] [1,4]diazepine 5-oxide | | |
 | Ro22-0992 | 7.8861 / 13nM | 8-chloro-6-(2-chlorophenyl)-4H-benzo[f]imidazo[1,5-a] [1,4]diazepine-3-carboxylic acid | | |
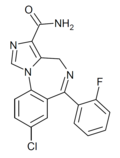 | Ro21-8137 | 8.4559 / 3.5nM | 8-chloro-6-(2-fluorophenyl)-4H-benzo[f]imidazo[1,5-a] [1,4]diazepine-3-carboxamide | | |
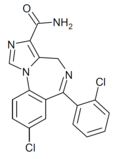 | Ro21-8384 | 8.4202 | 8-chloro-6-(2-chlorophenyl)-4H-benzo[f]imidazo[1,5-a] [1,4]diazepine-3-carboxamide | 162997 | 63176-94-3 |
 | Imidazenil | 8.8 † | 8-fluoro-6-(2-bromophenyl)-4H-benzo[f]imidazo[1,5-a] [1,4]diazepine-3-carboxamide | 119194 | 151271-08-8 |
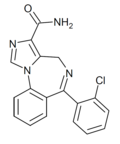 | Ro23-0364 | | 6-(2-chlorophenyl)-4H-benzo[f]imidazo[1,5-a] [1,4]diazepine-3-carboxamide | 194998 | 113066-25-4 |
 | Ro21-8482 | 7.585 / 26nM | 8-chloro-6-(2-chlorophenyl)-1-[(dimethylamino)methyl]-4H-benzo[f]imidazo[1,5-a] [1,4]diazepine-3-carboxamide | | |
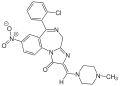 | Loprazolam | 8.2007 | (2Z)-6-(2-chlorophenyl)-2-[(4-methyl-1-piperazinyl)methylene]-8-nitro-2,4-dihydro-1H-imidazo[1,2-a] [1,4]benzodiazepin-1-one | 3033860 | 61197-73-7 |
 | Fluloprazolam | 8.0 † | (2Z)-6-(2-fluorophenyl)-2-[(4-methyl-1-piperazinyl)methylene]-8-nitro-2,4-dihydro-1H-imidazo[1,2-a] [1,4]benzodiazepin-1-one | 12371485 | |
 | PS-I-35 | | (2Z)-6-phenyl-2-[(4-methyl-1-piperazinyl)methylene]-8-bromo-2,4-dihydro-1H-imidazo[1,2-a] [1,4]benzodiazepin-1-one | 72660859 | |
| Ro14-1359 | 7.1549 / 70nM | 7-chloro-5-(2-fluorophenyl)-1H-benzo[b]azepin-2(3H)-one | | |
| Ro15-8867 | 7.6021 / 25nM | 7-nitro-5-(2-chlorophenyl)-1H-benzo[b]azepin-2(3H)-one | | |
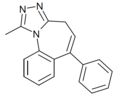 | Ro14-7187 | 6.3872 / 410nM | 1-methyl-6-phenyl-4H-benzo[f] [1,2,4]triazolo[4,3-a]azepine | 85687871 | |
| Ro13-9868 | 7.3768 / 42nM | 8-chloro-1-methyl-6-phenyl-4H-benzo[f] [1,2,4]triazolo[4,3-a]azepine | | |
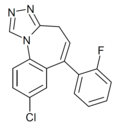 | Ro14-5921 | 7.7212 / 19nM | 8-chloro-6-(2-fluorophenyl)-4H-benzo[f] [1,2,4]triazolo[4,3-a]azepine | 20449965 | |
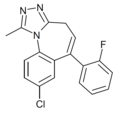 | Ro14-0304 | 8.1871 / 6.5nM | 8-chloro-6-(2-fluorophenyl)-1-methyl-4H-benzo[f] [1,2,4]triazolo[4,3-a]azepine | 20449964 | |
| Ro14-2652 | 8.2518 / 5.6nM | (8-chloro-6-(2-fluorophenyl)-4H-benzo[f] [1,2,4]triazolo[4,3-a]azepin-1-yl)methanamine | | |
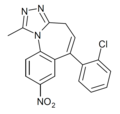 | Ro15-9270 | 8.301 / 5nM | 6-(2-chlorophenyl)-1-methyl-8-nitro-4H-benzo[f] [1,2,4]triazolo[4,3-a]azepine | 20450010 | |
| Ro14-0609 | 7.6126 / 24.4nM | 8-chloro-6-(2-fluorophenyl)-5,6-dihydro-4H-benzo[f] [1,2,4]triazolo[4,3-a]azepine | | |
| Ro15-2201 | 8.8239 / 1.5nM | methyl 6-phenyl-4H-benzo[f]imidazo[1,5-a]azepine-3-carboxylate | | |
| Ro15-0791 | 8.6021 / 2.5nM | ethyl 6-phenyl-4H-benzo[f]imidazo[1,5-a]azepine-3-carboxylate | | |
| Ro15-2200 | 8.3768 / 4.2nM | ethyl 6-(2-fluorophenyl)-4H-benzo[f]imidazo[1,5-a]azepine-3-carboxylate | | |
| Ro14-3929 | 7.7959 / 16nM | ethyl 8-chloro-6-(2-fluorophenyl)-4H-benzo[f]imidazo[1,5-a]azepine-3-carboxylate | | |
| Ro14-3930 | 7.8239 / 15nM | 8-chloro-6-(2-fluorophenyl)-4H-benzo[f]imidazo[1,5-a]azepine-3-carboxamide | | |
| Ro14-5568 | 6.6383 / 230nM | 8-chloro-6-(2-fluorophenyl)-4H-benzo[f]imidazo[1,5-a]azepine | | |
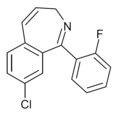 | Ro22-1274 | 7.1249 / 75nM | 8-chloro-1-(2-fluorophenyl)-3H-benzo[c]azepine | 13271760 | 89376-31-8 |
| Ro22-1251 | 7.9586 / 11nM | 9-chloro-2-methyl-7-phenyl-5H-benzo[c]pyrimido[4,5-e]azepine | | |
| Ro22-1366 | 8.3979 / 4nM | 9-chloro-7-(2-fluorophenyl)-2-methyl-5H-benzo[c]pyrimido[4,5-e]azepine | | |
| Ro22-2038 | 8.5528 / 2.8nM | 9-chloro-7-(2-fluorophenyl)-5H-benzo[c]pyrimido[4,5-e]azepin-2-amine | | |
| Ro22-3245 | 8.5528 / 2.8nM | 9-chloro-7-(2-chlorophenyl)-5H-benzo[c]pyrimido[4,5-e]azepine | | |
| Ro22-3148 | 6.3768 / 420nM | 6-phenyl-2,4-dihydrobenzo[c] [1,2,3]triazolo[4,5-e]azepine | | |
| Ro22-3147 | 8.284 / 5.2nM | 6-(2-chlorophenyl)-2,4-dihydrobenzo[c] [1,2,3]triazolo[4,5-e]azepine | | |
| Ro22-0780 | 7.9586 / 11nM | 8-chloro-6-phenyl-2,4-dihydrobenzo[c] [1,2,3]triazolo[4,5-e]azepine | | |
| Ro22-2466 | 8.7212 / 1.9nM | 8-chloro-6-(2-fluorophenyl)-2,4-dihydrobenzo[c] [1,2,3]triazolo[4,5-e]azepine | | |
| Ro22-2468 | 8.6021 | | | |
 | Ro22-8515 | | 8-chloro-6-(2-chlorophenyl)-1,4-dihydropyrrolo[3,4-d] [2]benzazepin-3(2H)-one | 145981 | |
 | Ro14-5974 | 8.1938 / 6.4nM | (S)-ethyl 9-oxo-11,12,13,13a-tetrahydro-9H-benzo[e]imidazo[5,1-c]pyrrolo[1,2-a] [1,4]diazepine-1-carboxylate | 10041121 | 88552-32-3 |
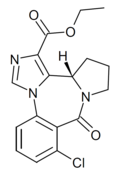 | Ro15-4941 | 8.7696 / 1.7nM | (S)-ethyl 8-chloro-9-oxo-11,12,13,13a-tetrahydro-9H-benzo[e]imidazo[5,1-c]pyrrolo[1,2-a] [1,4]diazepine-1-carboxylate | | |
 | Ro14-5975 | 7.2076 / 62nM | (S)-ethyl 7-chloro-9-oxo-11,12,13,13a-tetrahydro-9H-benzo[e]imidazo[5,1-c]pyrrolo[1,2-a] [1,4]diazepine-1-carboxylate | | |
 | Ro16-3607 | 7.3372 / 46nM | (S)-tert-butyl 8-methoxy-9-oxo-11,12,13,13a-tetrahydro-9H-benzo[e]imidazo[5,1-c]pyrrolo[1,2-a] [1,4]diazepine-1-carboxylate | | |
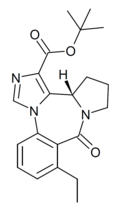 | Ro16-6624 | 8 / 10nM | (S)-tert-butyl 8-ethyl-9-oxo-11,12,13,13a-tetrahydro-9H-benzo[e]imidazo[5,1-c]pyrrolo[1,2-a] [1,4]diazepine-1-carboxylate | | |
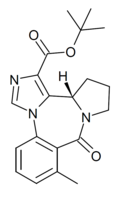 | Ro16-3774 | 8.4949 / 3.2nM | (S)-tert-butyl 8-methyl-9-oxo-11,12,13,13a-tetrahydro-9H-benzo[e]imidazo[5,1-c]pyrrolo[1,2-a] [1,4]diazepine-1-carboxylate | | |
| Ro16-0071 | 8.4949 / 3.2nM | (S)-tert-butyl 9-oxo-11,12,13,13a-tetrahydro-9H-benzo[e]imidazo[5,1-c]pyrrolo[1,2-a] [1,4]diazepine-1-carboxylate | | |
| Ro16-5824 | 8.4685 / 3.4nM | (S)-tert-butyl 8-(methylthio)-9-oxo-11,12,13,13a-tetrahydro-9H-benzo[e]imidazo[5,1-c]pyrrolo[1,2-a] [1,4]diazepine-1-carboxylate | | |
| Ro16-8912 | 8.2076 / 6.2nM | (S)-tert-butyl 8-fluoro-9-oxo-11,12,13,13a-tetrahydro-9H-benzo[e]imidazo[5,1-c]pyrrolo[1,2-a] [1,4]diazepine-1-carboxylate | | |
| Ro16-4261 | 8.1135 / 7.7nM | (S)-tert-butyl 7-fluoro-9-oxo-11,12,13,13a-tetrahydro-9H-benzo[e]imidazo[5,1-c]pyrrolo[1,2-a] [1,4]diazepine-1-carboxylate | | |
| Ro16-0075 | 8.6021 | | | |
| Ro16-6127 | 8.5086 / 3.1nM | (S)-tert-butyl 8-chloro-7-fluoro-9-oxo-11,12,13,13a-tetrahydro-9H-benzo[e]imidazo[5,1-c]pyrrolo[1,2-a] [1,4]diazepine-1-carboxylate | | |
| Ro16-3058 | 7.0458 | | | |
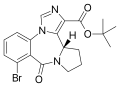 | Bretazenil | 8.6576 | (S)-tert-butyl 8-bromo-9-oxo-11,12,13,13a-tetrahydro-9H-imidazo[1,5-a]pyrrolo[2,1-c] [1,4]benzodiazepine-1-carboxylate | 107926 | 84379-13-5 |
 | EVT-201 | | 7-chloro-3-(5-[(dimethylamino)methyl]-1,2,4-oxadiazol-3-yl)-5-methyl-4,5-dihydro-6H-imidazo[1,5-a] [1,4]benzodiazepin-6-one | 9885841 | 308239-86-3 |
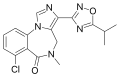 | FG-8205 | | 7-chloro-5-methyl-3-(5-propan-2-yl-1,2,4-oxadiazol-3-yl)-4H-imidazo[1,5-a] [1,4]benzodiazepin-6-one | 129710 | 122384-14-9 |
 | L-655,708 | | ethyl (13aS)-7-methoxy-9-oxo-11,12,13,13a-tetrahydro-9H-imidazo[1,5-a]pyrrolo[2,1-c] [1,4]benzodiazepine-1-carboxylate | 5311203 | 130477-52-0 |
 | PWZ-029 | | 8-chloro-3-(methoxymethyl)-5-methyl-4H-imidazo[1,5-a] [1,4]benzodiazepin-6-one | 9971547 | |
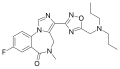 | Ro48-6791 | | 8-fluoro-5-methyl-3-(5-[(dipropylamino)methyl]-1,2,4-oxadiazol-3-yl)-4H-imidazo[1,5-a] [1,4]benzodiazepin-6-one | 9953485 | 172407-17-9 |
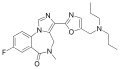 | Ro48-8684 | | 8-fluoro-5-methyl-3-(5-[(dipropylamino)methyl]-1,3-oxazol-2-yl)-4H-imidazo[1,5-a] [1,4]benzodiazepin-6-one | 9866317 | |
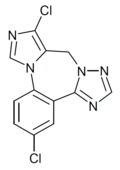 | Ro4882224 | | 3,10-dichloro-9H-benzo[f]imidazo[1,5-a] [1,2,4]triazolo[1,5-d] [1,4]diazepine | 11673720 | |
 | Ro4938581 | | 3-bromo-10-(difluoromethyl)-9H-benzo[f]imidazo[1,5-a] [1,2,4]triazolo[1,5-d] [1,4]diazepine | 11624499 | 883093-10-5 |
| Ro16-6605 | 8.6778 | | | |
| Ro16-6048 | 8.4815 / 3.3nM | (S)-tert-butyl 9-oxo-8-(trifluoromethyl)-11,12,13,13a-tetrahydro-9H-benzo[e]imidazo[5,1-c]pyrrolo[1,2-a] [1,4]diazepine-1-carboxylate | | |
| Ro16-6950 | 8.5528 / 2.8nM | (S)-tert-butyl 8-nitro-9-oxo-11,12,13,13a-tetrahydro-9H-benzo[e]imidazo[5,1-c]pyrrolo[1,2-a] [1,4]diazepine-1-carboxylate | | |
| Ro16-4019 | 8.8539 / 1.4nM | (S)-propyl 8-chloro-9-oxo-11,12,13,13a-tetrahydro-9H-benzo[e]imidazo[5,1-c]pyrrolo[1,2-a] [1,4]diazepine-1-carboxylate | | |
| Ro16-3031 | 8.6021 / 2.5nM | (S)-isopropyl 8-chloro-9-oxo-11,12,13,13a-tetrahydro-9H-benzo[e]imidazo[5,1-c]pyrrolo[1,2-a] [1,4]diazepine-1-carboxylate | | |
| Ro16-9906 | 8.7696 / 1.7nM | (S)-allyl 8-chloro-9-oxo-11,12,13,13a-tetrahydro-9H-benzo[e]imidazo[5,1-c]pyrrolo[1,2-a] [1,4]diazepine-1-carboxylate | | |
| Ro16-7081 | 8.585 | | | |
| Ro16-7082 | 8.2007 / 6.3nM | (S)-isobutyl 8-chloro-9-oxo-11,12,13,13a-tetrahydro-9H-benzo[e]imidazo[5,1-c]pyrrolo[1,2-a] [1,4]diazepine-1-carboxylate | | |
| Ro16-7083 | 8.5376 / 2.9nM | (13aS)-sec-butyl 8-chloro-9-oxo-11,12,13,13a-tetrahydro-9H-benzo[e]imidazo[5,1-c]pyrrolo[1,2-a] [1,4]diazepine-1-carboxylate | | |
| Ro16-9918 | 8.6383 / 2.3nM | (S)-cyclopropylmethyl 8-chloro-9-oxo-11,12,13,13a-tetrahydro-9H-benzo[e]imidazo[5,1-c]pyrrolo[1,2-a] [1,4]diazepine-1-carboxylate | | |
| Ro16-4020 | 8.585 | | | |
| Ro16-6654 | 8.3979 / 4nM | (S)-cyclohexyl 8-chloro-9-oxo-11,12,13,13a-tetrahydro-9H-benzo[e]imidazo[5,1-c]pyrrolo[1,2-a] [1,4]diazepine-1-carboxylate | | |
| Ro17-3206 | 8.4685 | | | |
| Ro17-3207 | 8.284 | | | |
| Ro16-4021 | 8.8239 | | | |
| Ro17-1302 | 8.2757 / 5.3nM | (S)-phenyl 8-chloro-9-oxo-11,12,13,13a-tetrahydro-9H-benzo[e]imidazo[5,1-c]pyrrolo[1,2-a] [1,4]diazepine-1-carboxylate | | |
| Ro15-2427 | IC50 >1000nM | 5-methyl-6-oxo-5,6-dihydro-4H-benzo[f]imidazo[1,5-a] [1,4]diazepine-3-carboxamide | | |
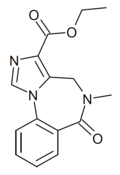 | Ro14-7437 | 8.5229 / 3nM | ethyl 5-methyl-6-oxo-4H-imidazo[1,5-a] [1,4]benzodiazepine-3-carboxylate | 127597 | 83210-63-3 |
 | Sarmazenil (Ro15-3505) | 8.5686 / 2.7nM | ethyl 7-chloro-5-methyl-6-oxo-5,6-dihydro-4H-benzo[f]imidazo[1,5-a] [1,4]diazepine-3-carboxylate | 71231 | 78771-13-8 |
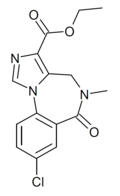 | Ro15-1310 | 8.1675 / 6.8nM | ethyl 8-chloro-5-methyl-6-oxo-5,6-dihydro-4H-benzo[f]imidazo[1,5-a] [1,4]diazepine-3-carboxylate | 114888 | 78756-33-9 |
 | Ro15-1746 | IC50 >1000nM | ethyl 9-chloro-5-methyl-6-oxo-5,6-dihydro-4H-benzo[f]imidazo[1,5-a] [1,4]diazepine-3-carboxylate | | |
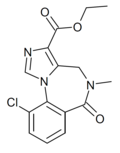 | Ro15-3237 | IC50 >1000nM | ethyl 10-chloro-5-methyl-6-oxo-5,6-dihydro-4H-benzo[f]imidazo[1,5-a] [1,4]diazepine-3-carboxylate | | |
| Ro15-5623 | 8.699 | | | |
 | Flumazenil | 8.6021 | ethyl 8-fluoro-5-methyl-6-oxo-5,6-dihydro-4H-benzo[f]imidazo[1,5-a] [1,4]diazepine-3-carboxylate | 3373 | 78755-81-4 |
 | Ro15-4513 | | ethyl 8-azido-5-methyl-6-oxo-5,6-dihydro-4H-benzo[f]imidazo[1,5-a] [1,4]diazepine-3-carboxylate | 5081 | 91917-65-6 |
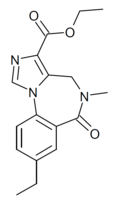 | RY-031 | | ethyl 8-ethyl-5-methyl-6-oxo-5,6-dihydro-4H-benzo[f]imidazo[1,5-a] [1,4]diazepine-3-carboxylate | 10245056 | |
 | TG-4-29 | | ethyl 8-vinyl-5-methyl-6-oxo-5,6-dihydro-4H-benzo[f]imidazo[1,5-a] [1,4]diazepine-3-carboxylate | 10591116 | |
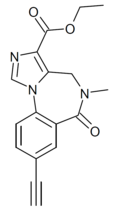 | RY-080 | | ethyl 8-ethynyl-5-methyl-6-oxo-5,6-dihydro-4H-benzo[f]imidazo[1,5-a] [1,4]diazepine-3-carboxylate | 5311418 | |
 | YT-II-76 | | ethyl 8-cyclopropyl-5-methyl-6-oxo-5,6-dihydro-4H-benzo[f]imidazo[1,5-a] [1,4]diazepine-3-carboxylate | 46214569 | |
 | SVO-8-14 | | ethyl 8-allyl-5-methyl-6-oxo-5,6-dihydro-4H-benzo[f]imidazo[1,5-a] [1,4]diazepine-3-carboxylate | 15316982 | |
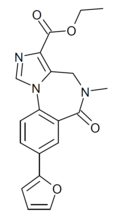 | SVO-8-30 | | ethyl 8-(furan-2-yl)-5-methyl-6-oxo-5,6-dihydro-4H-benzo[f]imidazo[1,5-a] [1,4]diazepine-3-carboxylate | 15316986 | |
 | SVO-8-67 | | ethyl 8-phenyl-5-methyl-6-oxo-5,6-dihydro-4H-benzo[f]imidazo[1,5-a] [1,4]diazepine-3-carboxylate | 15316984 | |
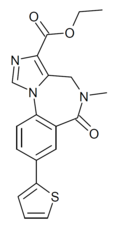 | TG-4-39 | | ethyl 8-(thiophen-2-yl)-5-methyl-6-oxo-5,6-dihydro-4H-benzo[f]imidazo[1,5-a] [1,4]diazepine-3-carboxylate | 15316985 | |
 | CD-214 | | cyclopropyl 8-chloro-5-methyl-6-oxo-5,6-dihydro-4H-benzo[f]imidazo[1,5-a] [1,4]diazepine-3-carboxylate | 101652266 | |
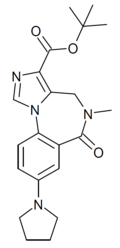 | DM-139 | | t-butyl 8-(pyrrolidin-1-yl)-5-methyl-6-oxo-5,6-dihydro-4H-benzo[f]imidazo[1,5-a] [1,4]diazepine-3-carboxylate | 10547937 | |
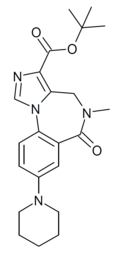 | DM-146 | | t-butyl 8-(piperidin-1-yl)-5-methyl-6-oxo-5,6-dihydro-4H-benzo[f]imidazo[1,5-a] [1,4]diazepine-3-carboxylate | 10834569 | |
 | DM-173 | | t-butyl 8-(dimethylamino)-5-methyl-6-oxo-5,6-dihydro-4H-benzo[f]imidazo[1,5-a] [1,4]diazepine-3-carboxylate | 10808192 | |
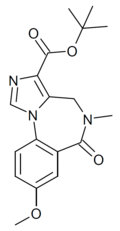 | DM-215 | | t-butyl 8-methoxy-5-methyl-6-oxo-5,6-dihydro-4H-benzo[f]imidazo[1,5-a] [1,4]diazepine-3-carboxylate | 10807310 | |
 | Ro19-4603 | | t-butyl 5,6-dihydro-5-methyl-6-oxo-4H-imidazo[1,5-a]thieno[2,3-f][1,4]diazepine-3-carboxylate | 127382 | 99632-94-7 |
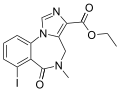 | Iomazenil | | ethyl 7-iodo-5-methyl-6-oxo-5,6-dihydro-4H-benzo[f]imidazo[1,5-a] [1,4]diazepine-3-carboxylate | 10251042 | 127985-21-1 |
| Ro17-9741 | 8.6198 / 2.4nM | (S)-methyl 8-chloro-9-oxo-9,11,12,12a-tetrahydroazeto[1,2-a]benzo[e]imidazo[5,1-c] [1,4]diazepine-1-carboxylate | | |
| Ro16-0858 | 8.8861 | ethyl 8-chloro-9-oxo-12,12a-dihydro-9H,11H-azeto[1,2-a]benzo[e]imidazo[5,1-c] [1,4]diazepine-1-carboxylate | | |
| Ro16-0153 | 8.2757 | tert-butyl 8-chloro-9-oxo-12,12a-dihydro-9H,11H-azeto[2,1-c]benzo[e]imidazo[1,5-a] [1,4]diazepine-1-carboxylate | | |
 | Ro17-1812 | 8.8861 | (S)-cyclopropylmethyl 8-chloro-9-oxo-9,11,12,12a-tetrahydroazeto[1,2-a]benzo[e]imidazo[5,1-c] [1,4]diazepine-1-carboxylate | 146197 | 90450-01-4 |
| Ro17-3211 | 8.62 | | | |
| Ro17-3401 | 9.0458 | | | |
| Ro17-3620 | 8.2924 | | | |
| Ro16-9351 | 8.4318 | | | |
| Ro16-9905 | 8.9208 | | | |
| Ro17-1338 | 9 | | | |
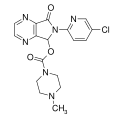 | Zopiclone | 7.5086 | 6-(5-chloropyridin-2-yl)-7-oxo-6,7-dihydro-5H-pyrrolo[3,4-b]pyrazin-5-yl 4-methylpiperazine-1-carboxylate | 5735 | 43200-80-2 |
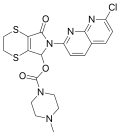 | Suriclone | 8.6778 | [6-(7-chloro- 1,8-naphthyridin-2-yl)- 5-oxo- 3,7-dihydro- 2H-[1,4]dithiino[2,3-c]pyrrol- 7-yl]4-methylpiperazine- 1-carboxylate | 40903 | 53813-83-5 |
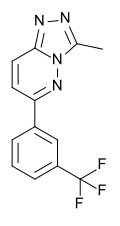 | CL-218,872 | 6.9208 | 3-methyl-6-[3-(trifluoromethyl)phenyl]-[1,2,4]triazolo[3,4-f]pyridazine | 107950 | 66548-69-4 |
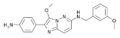 | GBLD-345 | 9 | 2-(4-aminophenyl)-3-methoxy-N-[(3-methoxyphenyl)methyl]imidazo[2,1-f]pyridazin-6-amine | 4602899 | 122479-08-7 |
|