Flubromazolam
Triazolobenzodiazepine drug From Wikipedia, the free encyclopedia
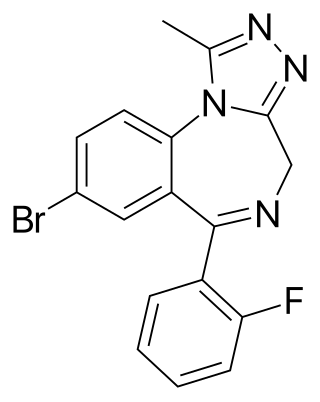
Flubromazolam (JYI-73) [2][3][4] is a triazolobenzodiazepine (TBZD), which are benzodiazepine (BZD) derivatives.[5][6][7][8][9][10][11] Flubromazolam is reputed to be highly potent, and concerns have been raised that clonazolam and flubromazolam in particular may pose comparatively higher risks than other designer benzodiazepines, due to their ability to produce strong sedation and amnesia at oral doses of as little as 0.5 mg.[12][13] Life-threatening adverse reactions have been observed at doses of only 3 mg of flubromazolam.[14]
 | |
| Legal status | |
|---|---|
| Legal status |
|
| Identifiers | |
| |
| CAS Number | |
| PubChem CID | |
| ChemSpider | |
| UNII | |
| KEGG | |
| CompTox Dashboard (EPA) | |
| ECHA InfoCard | 100.428.311 |
| Chemical and physical data | |
| Formula | C17H12BrFN4 |
| Molar mass | 371.213 g·mol−1 |
| 3D model (JSmol) | |
| |
| |
| (what is this?) | |
Legal status
Sweden
Flubromazolam has been classified as an illegal substance in Sweden after seizures by customs and police, as well as indications from the EMCDDA of wider use as a recreational drug.[15]
Switzerland
Flubromazolam is illegal in Switzerland as of December 2015.[16]
United Kingdom
In the UK, flubromazolam has been classified as a Class C drug by the May 2017 amendment to The Misuse of Drugs Act 1971 along with several other designer benzodiazepine drugs.[17]
Australia
In Australia, flubromazolam is Schedule 9 under federal law.[18]
United States
Flubromazolam is controlled in Virginia. On December 23, 2022, the DEA announced it had begun consideration on the matter of placing Flubromazolam under temporary Schedule I status. [19] Later on July 25, 2023, the DEA published a pre-print notice that Flubromazolam would become temporarily scheduled as a Schedule I controlled substance from 26 July 2023 to 26 July 2025.[20]
See also
References
Wikiwand - on
Seamless Wikipedia browsing. On steroids.