Loading AI tools
来自维基百科,自由的百科全书
肝素(英文:heparin)又稱普通肝素、未裂解肝素(unfractionated heparin,UFH),是一種天然且高度硫化的糖胺聚糖抗凝血劑[3][4],也是所有生物分子中陰電密度最高的分子[5],平均分子量約15,000道爾頓。肝素可用來治療及預防深靜脈血栓、肺栓塞、動脈栓塞,也可用於治療心肌梗塞以及不穩定型心絞痛。通常以靜脈注射方式給藥,也可以應用在採血管以及血液透析機。[4][6]
 | |
 | |
| 臨床資料 | |
|---|---|
| 讀音 | ['hɛpərɪn] HEP-ə-rin |
| AHFS/Drugs.com | Monograph |
| 懷孕分級 |
|
| 給藥途徑 | 靜脈注射、皮下注射 |
| ATC碼 | |
| 法律規範狀態 | |
| 法律規範 |
|
| 藥物動力學數據 | |
| 生物利用度 | Erratic |
| 藥物代謝 | 肝臟 |
| 生物半衰期 | 1.5 小時 |
| 排泄途徑 | Urine[2] |
| 識別資訊 | |
| CAS號 | 9005-49-6 |
| PubChem CID | |
| IUPHAR/BPS | |
| DrugBank | |
| ChemSpider | |
| UNII | |
| ChEMBL | |
| CompTox Dashboard (EPA) | |
| ECHA InfoCard | 100.029.698 |
| 化學資訊 | |
| 化學式 | C12H19NO20S3 |
| 摩爾質量 | 12000–15000 g/mol |
| |
肝素於1916年自狗的肝細胞分離而發現,故而得名[7]。使用肝素常見的副作用包括出血、注射部位疼痛以及血小板減少症,嚴重可導致肝素誘發的血小板減少症(HIT)。雖然腎功能不佳者在使用肝素時需要特別留意,但對於孕婦及授乳的媽媽來說肝素是相當安全的。[8]
低分子量肝素(low-molecular-weight heparin,LMWH)是平均分子量4500Da的肝素鹽[9],由高分子肝素通過多種分提或解聚方法得到。
肝素已列入世界衛生組織基本藥物標準清單中(能列入這個清單的,都是被認定為健康照護系統中最安全與最有效的藥物)[10]。 在預防用途上,開發中國家的批發價大約是每個月9.63到 37.95 美金[11];在美國則是25到50美金[12]。另外也有低分子量的肝素[13]。

體內的嗜鹼性球與肥大細胞都可以合成肝素[14] 。雖然它只能預防血栓形成,不能像組織纖溶酶原激活劑(tPA 或PLAT)一樣把血栓溶解,但它可以防血栓擴大,接著體內的纖維蛋白溶解機制便可以將血栓溶解。適應症包括:
雖然肝素與低分子量肝素(包括依諾肝素、達肝素鈉與錫扎肝素鈉)對於預防深靜脈血栓與肺栓塞都很有效[15][16],但目前的研究並未發現任何一種效果特別好[17]。
最嚴重的副作用是肝素誘發的血小板減少症(HIT)。肝素誘發的血小板減少症是一種免疫反應,造成血小板成為免疫反應攻擊的目標,導致血小板分解、血小板減少。通常停用後症狀會消失,而且可藉由使用合成肝素來避免其發生。除此之外,一開始使用肝素時也會出現輕微的血小板減少症,不過不需要停用。
另外兩個與出血無關的副作用是:有八成的患者在使用肝素後會出現血清轉胺酶上升的現象,另外有百分之五到十的患者則會在使用肝素後出現高鉀血症。使用肝素造成的血清轉胺酶上升與肝功能無關,在停用後就會恢復正常;高鉀血症則是因為肝素誘發了醛固酮分泌抑制所導致。長期使用肝素的患者有少數會出現脫髮與骨質疏鬆。
對於有出血顧慮(尤其是血壓控制困難、肝病、中風)的患者,嚴重肝病、高血壓的患者不宜使用肝素[19]。
肝素在體內的功能未知。肥大細胞合成肝素後會儲存在分泌泡中,直到組織受傷時便會釋出。因此,它被認為在體內可能與防禦細菌與其他物質入侵有關[22]。肝素被懷疑在體內與抗凝血無關的另一個原因是,許多不具有與人類類似的凝血系統的無脊椎動物也會製造肝素。
除了可以由豬與牛的組織中萃取出製藥級的肝素之外,在以下這些生物中也都曾萃取出肝素:
由於項目6-11的生物並不具有與人類類似的凝血系統,進一步支持了肝素可能與抗凝血無關的說法。
自然界的肝素是一群分子量多變的聚合物。普通肝素指的是沒有將低分子量肝素分離出來的肝素,而低分子量肝素則是將低分子量部分分離出來,以使其療效變得較為可預測。不論是普通肝素或低分子量肝素都可以在臨床下使用,有些症狀使用其中一種效果會比較好[36]。
肝素經由它的硫化五糖序列與酵素抑制劑抗凝血酶III結合,使其構形改變而活化[37]。 活化的抗凝血酶III接著抑制凝血酶與凝血因子Xa以及其他蛋白酶,抑制的效果可因為肝素的加入而上升一千倍[38]。硫化五糖序列如下:
GlcNAc/NS(6S)-GlcA-GlcNS(3S,6S)-IdoA(2S)-GlcNS(6S)
抗凝血酶III與肝素結合後導致的構形改變,造成它可抑制凝血因子Xa。至於凝血酶與抗凝血酶III之間的作用,除了酵素以外,還需要同時與肝素結合形成三元複合體才能達到抑制的效果;這部分肝素的高陰電性擔任了重要的角色[5]。因此,至少要具有十八個糖的肝素才能與凝血酶及抗凝血酶III產生有效的作用;但是與凝血因子Xa的作用只需要硫化五糖序列就可以了[39]。 這就是為何會開發出低分子量肝素與磺達肝素(其化學結構幾乎與肝素/硫酸肝素的硫化五糖序列相同)之因:低分子量肝素與磺達肝素可以只抑制凝血因子Xa而不抑制凝血酶,如此一來不僅可以微調凝血系統,達到更好的治療效果;還能降低骨質疏鬆與肝素誘發的血小板減少症發生的風險。因為這兩種藥物只影響凝血因子Xa,在使用這兩種藥物時便不需進行活化性部分凝血酶時間測試(APTT)。
對於肝素誘發的血小板減少症患者,可以使用不含有肝素或肝素片段的Danaparoid:它是硫酸肝素、硫酸皮膚素與硫酸軟骨素的混合物,因為不含有肝素或肝素片段,所以只有不到10%的患者出現抗體交叉反應[40]。
肝素的效果通常以活化性部分凝血激素時間測試來監測。活化性部分凝血激素時間測試是試驗血漿凝固的時間,與凝血酶原時間測試不同。
因為肝素是個高陰電性的大分子,一般以靜脈注射或皮下注射方式給藥;不建議以肌肉注射方式給藥,因為會造成血腫。由於普通肝素在生物體內的半衰期約為一到二小時,因此若能以點滴的方式給予效果會較佳[41]。低分子量肝素的半衰期較長,約為四到五小時;因此可以以每天一劑的方式給予[42]。在長期抗凝血劑的治療上,肝素一般只使用到口服抗凝血劑(如:華法林)開始發揮作用即停止給藥。
美國胸內科醫師學會已針對肝素劑量出版臨床指引[43]。
普通肝素的半衰期約為一到二小時,[41]低分子量肝素的半衰期約為四到五小時。巨噬細胞會吞噬並分解與它結合的肝素,內皮細胞則會藉著與肝素的結合使其無法與抗凝血酶III發生連結。高劑量的肝素會使內皮細胞與其結合的位置出現飽和的現象;雖然腎臟也會清除肝素,但速度很慢[44],這也就是為何低劑量的肝素半衰期比高劑量短的原因。

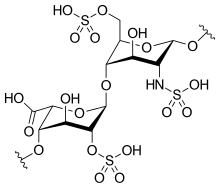
雖然大部分製藥級的肝素的分子量介於 12 到 15 kDa之間,天然的肝素的分子量可以從 3 到 30 kDa[45]。肝素以及硫酸肝素都屬於碳水化合物家族中的糖胺聚醣,由重複的硫化雙糖單位組成[46]。在肝素中較常出現的雙糖單元包括了以下這六種類型,最常見(牛肺中約佔85%,豬腸黏膜則有75%)的是由 2-O-硫化艾杜醣醛酸與 6-O-硫化, N-硫化葡萄糖胺(IdoA(2S)-GlcNS(6S))所組成[47]。
極少出現的雙糖單元是由含有 3-O-硫化葡萄糖胺(GlcNS(3S,6S)) 或含有胺基的葡萄糖(GlcNH3+)所組成的雙糖單元。
在生理狀況下,肝素的酯基與酰胺基會去質子化並吸引帶正電的離子來形成鹽類,製藥級的肝素通常也是以鹽類的方式給予。
一豪威爾單位的肝素大約等於 0.002 毫克的肝素。肝素的單位是以可以在攝氏零度下維持 1 毫升的貓血不凝固 24小時來制訂的[48]。
因為艾杜糖醛酸在寡糖內部可以以兩種不同的構形存在,使肝素具有複雜的立體結構。除此之外,鄰近的葡萄糖胺的硫化程度也會對構形產生影響[49]。 1993年,以核磁共振光譜儀與分子建模這兩種技術,已將由六個2-去氧-2-乙酰氨基-α-D-吡喃葡萄糖基-6-O-硫酸鹽-2-O-硫-α-L-艾杜糖醛酸組成的肝素立體結構解出[50] ,並得到兩種模型。其一是所有的2-O-硫-α-L-艾杜糖醛酸都在 2S0 構形 (如下圖 A 與 B), 第二個則是都在 1C4 構形 (如下圖 C 與 D)。不過,目前沒有任何證據支持單一肝素分子內所有的2-O-硫-α-L-艾杜糖醛酸都只會有一種構形。這些模型對應到蛋白質資料庫代碼 1HPN[51] 。
上圖:
在這些模型中,肝素呈現了螺旋狀的構形;不論在螺旋軸任一側,其旋轉的角度都會讓硫酸根以 17 埃(1.7 奈米)的間隔錯開。
以化學及/或酵素將肝素解聚的技術,對於肝素或硫酸肝素的結構與功能的研究有重大的貢獻。
分解肝素與硫酸肝素的酵素通常來自於土壤中的解肝磷脂土地桿菌[52]。解肝磷脂土地桿菌以肝素或硫酸肝素作為它的唯一碳源,為了分解肝素與硫酸肝素,解肝磷脂土地桿菌產生裂解酶,葡糖苷酸酶,磺基酯酶和磺酰胺酶[53] ,最常使用的是裂解酶。解肝磷脂土地桿菌共產生三種裂解酶:肝素酶 I (EC 4.2.2.7)、肝素酶 II (沒有EC編號)、肝素酶 III (EC 4.2.2.8),這三個酵素的專一性詳見下表: [54][55]
| 肝素酶 | 對受質的專一性(辨認的醣類序列) |
| 肝素酶 I | GlcNS(±6S)-IdoA(2S) |
| 肝素酶 II | GlcNS/Ac(±6S)-IdoA(±2S) GlcNS/Ac(±6S)-GlcA |
| 肝素酶 III | GlcNS/Ac(±6S)-GlcA/IdoA (with a preference for GlcA) |

肝素酶以β-氫消除反應機制來分解肝素與硫酸肝素,這個機制會在糖醛酸的四號碳與五號碳之間產生一個不穩定的雙鍵[56][57]。由於這個具有不穩定雙鍵的糖醛酸(稱為 ΔUA 或 UA)會吸收232奈米紫外光,因此在實驗室常用232奈米吸收的變化來監控肝素酶的反應。
在pH1.5或4之下,亞硝酸可用於肝素與硫酸肝素的化學解聚。 在這兩種條件下,亞硝酸會使肝素糖鏈發生脫氨裂解[58]。脫氨裂解發生在GlcNS-GlcA以及GlcNS-IdoA之間,氧原子是否硫化並不受影響,不過在較高的pH值下進行反應時,速率會較慢。

在較低的pH條件下,脫氨裂解會釋放出無機硫酸根與由2-去氧-2-乙酰氨基-α-D-吡喃葡萄糖基轉化而成的無水甘露糖。由於組成硫化軟骨素與硫化皮膚素的多糖其氮原子並未硫化,而亞硝酸無法在較低的pH條件下裂解氮未硫化的多糖,使此法可用來分辨肝素/硫酸肝素與硫化軟骨素/硫化皮膚素。
臨床上主要是以活化性部分凝血激素時間測試或抗凝血因子Xa活性測試等間接的方式來測試肝素是否發揮效用,而不是直接偵測肝素的存在。進行這些測試需要新鮮、未溶血以檸檬酸、氟化物或草酸鹽作為抗凝血劑處理過的血漿[59][60]。
肝素是在1916年威廉·亨利·豪威爾與他的學生傑·麥克萊恩在約翰·霍普金斯大學從狗的肝細胞中分離出來的,所以被命名為肝素(希臘文hepar是肝的意思,加上字尾-in)。雖然1916年就發現了肝素,不過一直到1935年才開始進行臨床測試[61]。
麥克萊恩當時正在狗的肝臟組織中找尋可以促進凝血的物質,卻發現了脂溶性磷脂抗凝血分子[62];豪威爾在1918年把它命名為肝素。到了1920年代初,豪威爾又分離出了一個水溶性的抗凝血分子,雖然這個分子與麥克萊恩分離出來的分子特性不同,但豪威爾還是給它同樣的名字[63][64]。
到了1930年代,許多科學家都在研究肝素;其中卡羅琳學院的艾瑞克·傑普斯在1935年解出了肝素的結構[65],使瑞典的Vitrum AB藥廠得以在1936年生產第一個靜脈注射的肝素製劑。在1933年之前,肝素相當的昂貴且具有高毒性;在康諾特醫學研究實驗室(當時屬於多倫多大學)以四年的時間(1933-1936)將生產肝素的製程優化後,肝素終於可以使用於生理食鹽水中。肝素的第一個人體試驗發生在1935年五月,到了1937年已經確定為安全、有效且容易取得的抗凝血劑了[66]。
相比於完全由化學合成的治療藥劑,由動物來源萃取純化的肝素潛在的不純物當然多得多了:包括病毒、細菌的內毒素、普利昂蛋白、脂肪、蛋白質與去氧核糖核酸都有可能出現在其中;而純化過程中所使用的溶劑、重金屬以及離子等也不無可能成為污染物。雖然這樣說,但過去已經建立了許多方法來將不純物/污染物含量盡可能的降低,這些方法也都詳列於藥典中。目前分析肝素的污染物最大的困難,首推如何鑑定如硫化皮膚素(DS,一名硫化軟骨素B)這類結構與肝素類似的污染物。硫化皮膚素由N-乙酰-半乳糖胺(GalN)與醣醛酸以1→3連結所組成的雙糖形成,雙糖之間以1→4形式相連。醣醛酸部分可能為葡萄醣醛酸、艾杜醣醛酸、2-O-硫-α-L-艾杜糖醛酸,六碳糖的部分除了乙酰半乳糖胺以外,也有可能在四號碳及/或六號碳的位置硫化(Gal- NAc4S, GalNAc6S, 或 GalNAc4S6S)。艾杜糖醛酸的存在使硫化皮膚素與硫化軟骨素A與C不同,但卻使它與肝素較為相似,但比肝素的陰電密度要低。通常在肝素中大約有1-7%的硫化皮膚素,但它們不具有肝素的生物活性[69]。
2007年12月,美國食品藥品監督管理局發現有一批肝素製劑遭到粘質沙雷氏菌污染而全面回收。粘質沙雷氏菌感染嚴重可致死[70]。
2008年三月,美國食品藥物監督管理局發現由中國進口的一批肝素遭到硫化軟骨素污染,並造成81人死亡,宣布全面回收[71][72]。這些硫化軟骨素是一般硫化軟骨素的「過度硫化」型態,原本適用於關節炎的治療,但卻被加到肝素裡面企圖矇混過活性測試[73]。
2008年三月,藥廠因為未知的污染宣布召回一批來自中國的肝素[74][75]。後來發現這些肝素遭到「過度硫化」的硫化軟骨素污染[76],美國食品藥物監督管理局宣布至少有十九個人因此死亡,另外還有785人因為使用了這些污染的肝素,造成呼吸困難、噁心、嘔吐、大量流汗、血壓急速下降甚至休克等症狀。
一名任職於雪松-西奈醫療中心的護理師在2007年錯誤地注射了成人劑量(約為嬰兒劑量的1000倍)的肝素到丹尼斯‧奎德12天大的雙胞胎體內[78]。因為藥廠(百特國際)提供的成人與嬰兒包裝的肝素外表相似,奎德家族雖然與醫院以75萬美金和解[79],但仍決定對百特國際提告[80][81]。在奎德家族的不幸事件發生之前,已經有六個在印第安納波利斯的衛理公會醫院的嬰兒也被錯誤地注射了成人劑量,並造成三人死亡[82]。
2008年7月,在德州聖體市的 Christus Spohn 醫院出生的雙胞胎,因為醫院藥局出錯被注射了過量的肝素而死[83],目前該案件仍在調查[84][85]。2010年3月,來自德州的一名兩歲的器官移植病人在內布拉斯加大學醫學中心因被注射了致死劑量的肝素而死,該案目前也仍在調查[86]。
製藥級的肝素是從屠宰動物的黏膜(如豬腸或牛肺)純化而來[87]。全合成肝素的技術正持續地研發[88],以化學酶法工藝從雙糖合成低分子量肝素的方法已在2011年被研發出來[89]。
肝素除了作為抗凝血劑之外,將類似肝素的結構開發為藥劑的潛力也不容忽視。肝素潛在的用途如下表所示[90][91]:
| 對肝素敏感的疾病!!目前肝素在實驗模型上的效果 !! 臨床狀態 | ||
| 艾滋病 | 降低培養的T淋巴球對第一型與第二型人類免疫缺乏病毒的吸收[92]。 | - |
| 急性呼吸窘迫症候群 | 在動物模型中,肝素可以降低呼吸道中細胞的活化與聚集、中和對細胞有毒的細胞產物、提升肺部功能。 | 對照臨床試驗 |
| 過敏性腦脊髓炎 | 在動物模型中有療效。 | - |
| 過敏性鼻炎 | 雖然對成人呼吸窘迫症候群有療效,但在鼻炎中沒有被測試過。 | 對照臨床試驗 |
| 關節炎 | 可抑制細胞聚集、膠原蛋白受損與血管增生。 | 軼事證據 |
| 哮喘 | 如成人呼吸窘迫症候群的發現,在實驗動物中發現肝素對提升肺部功能有幫助。 | 對照臨床試驗 |
| 癌症 | 在動物模型中,肝素可以抑制癌的生長、遠端轉移、血管新生,從而提升存活時間。 | 一些軼事證據 |
| 第四型過敏反應 | 在動物模型中有療效。 | - |
| 炎症性腸病 | 抑制發炎細胞運輸。 | 對照臨床試驗 |
| 間質性膀胱炎 | 在人類的實驗中可以抑制間質性膀胱炎。 | 已在臨床使用 |
| 移植排斥 | 在動物模型中,肝素可以延長異體移植器官壽命。 | - |
- 表示沒有資訊可參考。
由於研究發現肝素對許多疾病都可能會有療效,目前已有一些在結構上與肝素類似的新藥物正在開發中[90],如下表所示:
| 藥物分子!!新藥與肝素比較 !! 生物活性 | ||
| 肝素四糖 | 非抗凝血劑、不具抗原性、可口服 | 抗過敏劑 |
| 戊聚醣多硫酸鹽 | 由植物分子衍生而來、微小抗凝血活性、抗發炎、可口服 | 抗發炎、抗黏著、抗遠端轉移 |
| 磷酸戊糖甘露糖硫酸鹽 | 抑制肝素酶活性的有效抑制劑 | 抗遠端轉移、抗血管新生、抗發炎 |
| 化學選擇性O-去硫肝素 | 不具抗凝血活性 | 抗發炎、抗過敏、抗黏著 |
Seamless Wikipedia browsing. On steroids.
Every time you click a link to Wikipedia, Wiktionary or Wikiquote in your browser's search results, it will show the modern Wikiwand interface.
Wikiwand extension is a five stars, simple, with minimum permission required to keep your browsing private, safe and transparent.