高血压
血压高的慢性病 来自维基百科,自由的百科全书
高血压(英语:Hypertension,high blood pressure)是动脉血压持续偏高的慢性疾病[8]。高血压一般没有症状[1],不过长期高血压为冠状动脉疾病、中风、心脏衰竭、心房颤动、周边动脉阻塞、视力受损、慢性肾脏病及痴呆等病症的主要危险因子[2][3][9][10]。
| 高血压 | |
|---|---|
| 异名 | 动脉高血压 |
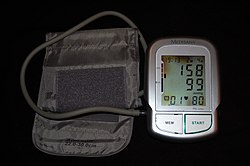 | |
| 自动臂式血压计显示动脉的高血压(显示的收缩压为158 mmHg,舒张压99 mmHg以及心率为80次/分钟)。 | |
| 症状 | 无[1] |
| 并发症 | 冠状动脉疾病、中风、心脏衰竭、周边动脉阻塞、视力受损、慢性肾脏病[2][3] |
| 类型 | 血管疾病、动脉疾病[*]、医学征象[*]、高血压[*]、疾病 |
| 病因 | 生活形态或遗传因素[4][5] |
| 风险因素 | 吃太咸的食物、体重过重、吸烟、喝酒[1][4] |
| 诊断方法 | 休息血压 > 140/90 mmHg[4] |
| 治疗 | 生活形态调整、药物治疗[6] |
| 患病率 | 全球约16–37%[4] |
| 死亡数 | 940万 / 18%(2010年)[7] |
| 分类和外部资源 | |
| 医学专科 | 心脏病学 |
| ICD-10 | I10-I1515. |
| ICD-9-CM | 997.91、401-405.99 |
| OMIM | 145500 |
| DiseasesDB | 6330 |
| MedlinePlus | 000468 |
| eMedicine | 241381 |
高血压可以分为原发性高血压和继发性高血压[4],其中有 90-95% 为原发性高血压,意即肇因于生活型态或遗传因素[4][5]。会增加风险的生活型态为超重、吸烟、饮食含有过量食盐、咖啡、糖及喝酒[1][4],剩下的 5-10% 是继发性高血压,肇因于其他病症如慢性肾脏病、肾动脉狭窄、内分泌疾病或是使用避孕药[4][11]。
血压分为收缩压和舒张压两种,即为心脏跳动时肌肉收缩或心脏舒张时的测量值;收缩压是血压的最大值,舒张压是血压的最小值[1]。大部分成年人在休息时的收缩压在 100-130 毫米汞柱(简称为 mmHg),舒张压是 60-80 毫米汞柱[12][13]。若血压持续超过 130/80 或 140/90 毫米汞柱(收缩压/舒张压),有可能是高血压[4][12]。儿童的判断准则和成人不同[14]。量血压时,采用 24 小时区间的移动式血压计测量血压(简称为 ABPM)方式会较仅采诊间血压量测(简称为 OBPM)来得准确许多[4][8]。
降低血压和致命并发症的风险在于改变生活型态与药物控制[6]。减少体重、体能锻炼、适度摄取盐分、少喝酒及均衡饮食等方式都有帮助[4],若改变生活型态也无效时,则应使用抗高血压药[6]。目前多达3种药物对九成人类的血压控制上有效[4],而以药物治疗第二期高血压(收缩压>160/100 mmHg),有望延长患者的预期寿命[15]。但对于正常但偏高血压及第一期高血压(即130至160 mmHg)的患者而言,药效相对不明朗,某些研究认为有效[12][16][17],但亦有其他研究认为没有帮助[18][19][20]。全球约16至37%的人口患有高血压[4],据信 2010 年全球死亡人数之中,有 18% 与高血压有关,估计约 940 万人[7]。
分类
对18岁及以上人群的高血压的定义为收缩压和/或舒张压值持续高于公认的正常值(目前此值为收缩压139mmHg毫米汞柱、舒张压89mmHg毫米汞柱:请参见分类表)。如果使用24小时血压监测数值及家庭自测数值时,则应使用较低的阈值(收缩压135mmHg或舒张压85mmHg)。[21]最近的国际高血压指南也对高血压范围之下的血压情况进行了分类,以指出在正常血压范围内的较高血压亦存在的风险。JNC7(2003)[22]将收缩压在120–139 mmHg和/或舒张压在80–89 mmHg的范围定义为临界高血压,而ESH-ESC指南(2007)[23]及BHS IV(2004)[24]以最佳、正常及正常高值细分收缩压低于140 mmHg及舒张压低于90 mmHg的组别。高血压也有如下分类:JNC7将高血压分为高血压一期、高血压二期和单纯收缩期高血压。单纯收缩期高血压指收缩压升高而舒张压正常,在老年人中常见。[22] ESH-ESC指南(2007)[23]和BHS IV(2004),[24]将收缩压超过179mmHg或舒张压超过109mmHg的患者定义为高血压三期。如果药无法将血压降低到正常水平,则此高血压为耐药性高血压。[22]
新生儿的高血压很罕见,可见于约0.2-3%的新生儿;健康新生儿的常规检查不包括测量血压。[27]在高危新生儿中高血压则较为多见。在决定新生儿血压是否正常时应考虑多种因素,如胎龄(Gestational age),受孕龄和出生体重等。[27]
高血压在儿童及青少年中十分常见(按年龄、性别及种族不同,分别为2–9%)[28]并被认为在长期可带来其它疾病的风险。[29]目前的建议为三岁以上的儿童在进行常规医疗检查或治疗时应进行血压测量。应该在重复门诊测量确诊高血压后才定位儿童的高血压。[29]儿童的血压随年龄升高,儿童的高血压诊断标准为三次以上不同时间门诊测量的平均结果等于或高于此儿童相应性别、年龄及身高的95百分位血压。儿童高血压前期的定义为平均收缩压或舒张压大于或等于90百分位,但小于95百分位。[29]
青少年的高血压和高血压前期诊断及分类建议使用成人标准。[29]
症状与体征
高血压很少显示症状,因此通常是通过筛查或者寻求解决其它健康问题时发现。一些高血压患者有头痛(尤其是后脑勺痛及早上头痛),并有头晕、眩晕、耳鸣(耳中嗡嗡声或咝咝声)、视觉改变或晕倒发作。[30]
用体检眼底镜检查检查眼底时如检测到高血压性视网膜病变,则应怀疑患有高血压。[31]高血压性视网膜病变的严重程度传统上一般分为一期到四期,但程度较轻的分期之间可能很难互相区别。[31]眼底镜检查结果也可以推断患者患高血压的时间长短。[30]
高血压可以发生于任何年龄,但发现大多数是越过四十岁,约百分之八十五至九十属于自发性高血压,其引起原因并不清楚,可能与遗传和环境因素有关。
一些其它的症状及体征可以将诊断指向继发性高血压,即由可确定的病因如肾脏疾病或内分泌疾病等引起的高血压。如胸腹部肥胖、葡萄糖不耐受、满月脸、“水牛背”及紫色皮纹为库欣氏综合征的症状。[32]甲状腺疾病及肢端肥大症也可以引起高血压,它们各有其特殊的症状和体征。[32]腹部动脉杂音可能表明肾动脉狭窄(肾脏的供血动脉变狭窄)。腿部血压降低或股动脉脉冲的延迟或缺失可能表明主动脉缩窄(距离心脏很近的主动脉狭窄)。具有变化很大的头痛、心悸、脸色苍白和出汗的高血压应马上及时怀疑是否患有嗜铬细胞瘤。[32]
极严重的血压升高(收缩压等于或大于180或舒张压等于或大于110,有时称为恶性或急进性高血压)称为“高血压危象”。血压达到这些数值之上表明并发症的风险很高。血压在此范围内的患者不一定有症状表现,但相较一般人群有较多出现(22%的病例)头痛[33]及头晕。[30]其它高血压危象的表现有心衰引起的视觉下降或呼吸困难,又或肾衰引起的感觉不适。[32]大部分高血压危象患者已患有血压升高,但其它触发因素可能引起了突然的血压升高。[34]
当严重的血压升高引起了一个或多个器官的直接损害时则为“高血压急症”(以前称为“恶性高血压”)。损害可以包括高血压脑病,即由脑部肿大和功能障碍引起的头痛和意识状态改变(意识模糊或嗜睡)。视网膜视神经乳头水肿、眼底出血和渗出是靶器官损害的另一迹象。胸痛可能表明心脏肌肉损伤(可以进展为心肌梗死),有时进展为主动脉剥离,即主动脉内壁撕裂)、气促、咳嗽、咳血痰都是肺水肿的典型迹象。此病症的肺组织肿胀由左心室衰竭引起,即心脏左心室不能充分将血液从肺部泵入动脉系统。[34]肾功能的急速退化(急性肾损伤)和微血管溶血性贫血(血液细胞的破坏)也可能出现。[34]在这些情况,快速降低血压的目的是要停止正在进行的器官损害。[34]相反在高血压急症没有出现靶器官损害迹象时,没有证据表明必须要迅速地降低血压。过度降低血压并不是没有风险的。[32]在高血压急症时建议使用口服药物在24至48小时内逐渐降低血压。[34]
罹患妊娠高血压的孕妇约占怀孕孕妇的8–10%。[32]患有妊娠高血压的女人,大多数在怀孕前就有原发性高血压。妊娠高血压可能是先兆子痫的预兆,这是一种发生于妊娠后期和生产后几个礼拜的严重症状。[32]先兆子痫的诊断可包括血压增高和尿蛋白。[32]怀孕妇女约有5%几率会发生先兆子痫,而且约造成全球16%孕产妇死亡。[32]先兆子痫亦使宝宝的死亡风险提高两倍。[32]先兆子痫通常没有症状,而且是由例行筛检检查出来。当发生先兆子痫的症状,最常见的就是头痛、视觉障碍(通常是出现闪光)、呕吐、上腹部疼痛和水肿(肿胀)。先兆子痫有时会演变为称之为子痫的致命病况。子痫是一种急性高血压,并且有数种严重的并发症。这些并发症包括丧失视力、脑水肿、癫痫发作或惊厥、肾衰竭、肺水肿和弥散性血管内凝血(一种血液凝固功能障碍)。[32][35]
发育迟缓、癫痫发作、焦躁不安、缺乏活力和呼吸困难[36]都与新生儿至三个月大的婴儿高血压有关。在三个月以上婴儿和儿童当中,高血压可引起头痛,不明的焦躁不安,疲倦、发育迟缓、视力模糊、流鼻血和面部神经麻痹。[27][36]
并发症

高血压是全世界过早死亡最重要的可预防因素。[37]高血压增加罹患缺血性心脏病、[38] 中风、[32] 外周血管病变、[39]和其它心脏疾病的风险,包括心脏衰竭、主动脉瘤、广泛性动脉粥样硬化和肺栓塞。[32]高血压同时也是罹患认知障碍、痴呆和慢性肾脏病的高风险因素。[32] 其它并发症包括:
病因
原发性(特发性)高血压是最常见高血压,占所有高血压病例90–95%。[5]在几乎所有当代社会中,血压会随着年龄而升高,而晚年罹患高压的风险也相当高。[41]基因和环境因素可导致高血压。人们已发现许多对血压造成微小影响的常见基因,[42]还有一些对血压造成重大影响的罕见基因,[43]但是对基因如何导致高血压,仍缺乏了解。有些环境因素也会影响血压。有助于降低血压的生活方式因素包括减少饮食中的食盐摄取,[44]多吃水果和低脂产品(也就是高血压防治饮食,例如DASH饮食)。运动、[45]减轻体重[46]和减少饮用含酒精饮料亦有助于降低血压。[47]其它可能造成高血压的因素,例如压力、[45]摄取咖啡因,[48]以及维他命D不足,[49]则并未显示出与高血压有直接关系。肥胖常见的胰岛素抵抗,是X综合征(或称代谢综合征)的致病因子之一,也被认为可造成高血压恶化。[50]近期研究亦指出,幼年时期发生的情况(例如出生体重过轻、母亲怀孕时抽烟、高PM2.5暴露[51]和缺乏哺育母乳)是成年原发性高血压的危险因子。[52]然而成人高血压的致病机制仍尚不明。[52]
继发性高血压是由明确的病因所致。肾脏疾病是继发性高血压最常见的病因。[32]而库欣综合征、甲状腺亢进、甲状腺功能低下、肢端肥大症、康恩氏综合征、醛固酮增多症、高胰岛素血症[53]等内分泌疾病,也可导致高血压。[32][54]其它病因则包括肥胖、睡眠呼吸暂停症、怀孕、主动脉缩窄、过度摄取甘草和某些处方药、草药疗方和非法药物。[32][55]
病理生理

大部分患有确立特发性(原发性)高血压的人,血流阻力(外周总阻力)都因高血压而增加,而心排血量却维持正常。[56]有证据表明为何有些年轻人患有高血压或“临界高血压”而具有高心排血量,即心率加快,却有正常的外周血管阻力。这种症状被称为运动功能亢进临界性高血压。[57]这些人的心脏输出随着年纪的增长而降低,但外周阻力却随之上升,在老年时期发展成确立特发性高血压的典型症状。[57]这是否是最后演变成高血压的人的典型模式尚无定论。[58]确诊罹患高血压的患者其外周血管阻力增加,主要是由于小动脉和微动脉的缩窄。[59]微血管数量或密度的降低亦可使外周阻力增高。[60]高血压也与外周血管弹性的减低有关,[61]外周血管弹性减低会增加回流心脏的血量、增加心脏前负荷,最后导致心脏功能失常。发生的血管收缩是否为造成严重原发性高血压的原因之一,仍有待确定。[62]
患有高血压的年长者其脉压(心脏收缩和心脏舒张血压之间的差值)会越来越大。这种状况可能与心脏收缩压异常高但心脏舒张压却正常或异常低有关。这种状况就称为单纯收缩期高血压。[63]患高血压或单纯收缩期高血压的年长者会有高脉压,可归因于动脉硬化程度增高。这是种常见的老年并发症,而且可能会因高血压而加剧。[64]
高血压的动脉系统所见的血流阻力现象,有诸多致病机制予以解释。大多数证据指向下列两个病因或其中之一:
诊断
当患者的血压持续过高时,就会诊断为患有高血压。传统的做法是[21],需要每隔一个月对患者进行一次血压计测量,并重复三次,才能做出诊断。[75]对高血压患者的初始评估包括一个完整的历史和体检。随着24小时动态血压监控和家用血压器的出现,为避免对患有白大褂恐惧性高血压的患者做出错误诊断,诊断程序随之发生了变化。英国目前的典范做法是,当临床上量到过一次血压高指标之后,马上要做动态测量随访。用七天的家庭血压监测方法进行随访也是可以的,但效果不是太理想。[21]
一旦诊断为高血压,医生就会设法根据风险因素和其它存在的症状,找出发病的根本原因。继发性高血压多见于青春期前的儿童,而大多数病例是由肾病引起的。原发性高血压多见于青少年,有多种危险因素,包括肥胖症和高血压家族史。[76]也可以通过实验室化验,找出导致继发性高血压的可能原因,并确定高血压是否已经对心脏、眼睛和肾脏造成损害。另外还可做其它针对糖尿病和高胆固醇指标的化验,因为这些疾病都是引发心脏病的风险因素,并可能需要治疗。[5]
测定血清肌酐可以确定是否有肾脏疾病。肾病既可能是导致高血压的原因,也可能是高血压引发的后果。可是单用血清肌酐值有可能会过高估计肾小球滤过率。最近的指导原则提倡使用诸如肾脏病饮食改良(MDRD)公式预测肾小球滤过率(eGFR)。[77]预测肾小球滤过率eGFR还可以提供肾功能的其它基线指标,这些指标可以用来监控某些抗高血压药物对肾功能产生的副作用。用尿液样本测试蛋白也被用作肾脏疾病的一个次要的标志。还可以做心电图(EKG/ECG)测试,以检查是否有迹象表明心脏由于高血压而变得过度疲劳。它也可以显示心肌的增厚(左心室肥厚)或心脏以前是否出现过较小异常,如无症状心脏病发作。也可以通过做胸部X光检查或超声心动图来寻找心脏扩大或损坏的迹象。[32]
最新高血压标准
根据新版指南,最新血压类别共有5个,分别:正常血压 (小于120/80毫米汞柱);血压升高(收缩压介于120至129毫米汞柱,舒张压小于80毫米汞柱);高血压1级(收缩压介于130至139毫米汞柱,舒张压介于80至89毫米汞柱);高血压2级(大于140/90毫米汞柱);高血压危象(收缩压达到180毫米汞柱 和/或 舒张压达到120毫米汞柱)[78][79][80]。对此而言,最大的变化在于以前的高血压前期调整为"血压升高"和"高血压1级" 两类别,尤其时高血压1级成为人们的关注重点。
预防
患有高血压但没有意识到自己有这一疾病的人为数众多。[81]要减少高血压造成的后果,并尽量减少对抗高血压药物治疗的需要,因此必须有一些针对全民而制定的措施。在开始药物治疗前,建议患者改变生活方式以降低血压。2004年的“英国高血压学会”指南[81]提出了以下生活方式的改变,这和2002年美国高血压教育计划[82]所列出的预防高血压的主要措施指南是一致的:
- 保持正常体重(如身体质量指数20-25公斤/米2)。
- 将饮食中钠的摄入量减少至<100毫摩尔/天(每天<6克氯化钠或<2.4克的钠)。
- 定期从事有氧运动,如快走(在一周的大多数日子里,每天≥30分钟)。
- 限制饮酒,男性每天不超过3个单位,女性每天不超过2个单位。
- 戒烟。
- 每天的饮食中含丰富的水果和蔬菜(例如,每天至少五份)。 *定期健康检查。 通过有效的生活方式改变能降低的血压几乎可以和服用一种降压药物所能降低的血压水平媲美。改变两项或更多项生活方式甚至可以达到更佳的效果。[81]
治疗
透过生活习惯的改变和抗高血压药物的介入,可以有效控制高血压。高血压的控制目标通常为血压低于140/90 mmHg 或 160/100 mmHg。一篇2003年的系统性文献回顾指出,血压每降低5 mmHg 能减少34%的中风几率、21% 罹患冠状动脉疾病的几率、及降低痴呆、心脏衰竭和心血管疾病的死亡率。[83]
当测量到高血压且合并临床发现靶器官(目标器官)损伤,则必须使用药物介入治疗。这些靶器官损伤包括:左心室肥厚、心肌梗死、心脏衰竭、动脉粥样硬化斑、外周动脉疾病、视网膜血管病变、微蛋白尿、慢性肾衰竭、中风等。
高血压的第一种治疗方法同上面建议的为预防高血压而进行的生活方式改变是相同的,[84]包括饮食模式的变化,[85]即体育锻炼和减轻体重。这些改变都已经被证明具有显著的降低高血压患者血压的功效。[86]即使血压高到足以需要立即使用药物的时候,仍然建议患者进行生活方式的改变。一些不同的为减轻心理压力而设制的计划,如生物反馈、放松术或打坐都被宣传说能降低高血压,然而,科学研究总的来说都还没能证明这些方法的疗效,因为这些研究的质量一般都比较低。[87][88][89]
进行诸如低钠盐饮食之类的饮食变化是非常有益的。长期(4周以上)的低钠盐饮食在白种人中能有效地降低血压,无论他们是患有高血压还是血压正常的人。[90]此外,降血压饮食法,一种含丰富的坚果、全谷类、鱼类、家禽、水果和蔬菜并备受国家心脏、肺和血液研究所推崇的饮食法,也能降低血压。该饮食计划的主要特点之一就是限制含钠盐类的摄入量,尽管此饮食中也包含丰富的钾、镁、钙和蛋白质。[91]
几种药物统称为抗高血压药,主要用于治疗高血压等疾病。开药方时,医师会考虑到病人的心血管危险(包括心衰与中风危险)及血压读数。[92]如果开始执行药物治疗,美国心脏、肺和血液研究院关于高血压的第七次联合会议[77]建议医师监督药物治疗的反应并评估任何由此药物引起的不良反应。血压降低5 mmHg可以减少34%的中风危险及21%局部缺血性心脏病的危险。血压降低也可以降低由心血管疾病引起的痴呆、心力衰竭和死亡率。[93]治疗的目的是要将大多数人的血压降低至140/90 mmHg,并降低患有糖尿病和肾病病人的高血压。有些医务人员建议将血压水平保持在120/80 mmHg以下。[92][94]如果没有达到血压目标,则需进一步治疗。[95]
药物选择的指南及如何制定各种亚组的最佳治疗方法会随着时间更改,且在不同的国家之间也有区别。专家们尚未在最佳药物上取得一致意见。[96]科克伦协作组织、世界卫生组织和美国指南支持低剂量的以噻嗪为基础的利尿剂并将其视为首选初期治疗方法。[97][96]英国指南重点强调对于55岁以上的人群或祖籍为非洲或加勒比海的人群采用钙通道阻滞剂(CCB)。指南还建议年轻一点的人群采用血管紧张肽I转化酶抑制剂(ACEI)作为首选初期治疗方法。[98]在日本,治疗初期可使用的6类药物包括:CCB,ACEI/ARB、噻嗪类利尿剂、贝塔受体阻滞剂和阿尔法受体阻滞剂,这些药物都被视为合理的。在加拿大,除了阿尔法受体阻滞剂外,所有其它药物都可能被当作第一选择。[96]
多数人需要使用多种药物控制高血压。JNC7[77] a和ESH-ESC指南[23]支持在初期治疗阶段,当心脏收缩压超过目标值20 mmHg或心脏舒张压超过目标值10 mmHg时,使用两种药物。首选的组合为肾素-血管紧张素系统抑制剂和钙通道阻滞剂,或肾素-血管紧张素系统抑制剂和利尿剂。[99]二线选择方案如下:
- 钙通道阻滞剂配合利尿剂
- 贝塔受体阻滞剂配合利尿剂
- 二氢吡啶通道阻滞剂配合贝塔受体阻滞剂
- 二氢吡啶通道阻滞剂配合维拉帕米或地尔硫卓之一
不推荐联合方案如下:
- 非二氢吡啶钙通道阻滞剂(如维拉帕米或地尔硫卓)配合贝塔受体阻滞剂
- 双重肾素-血管紧张素系统阻滞剂(例如血管紧张素转化酶抑制剂+血管紧张素受体拮抗剂)
- 肾素-血管紧张素系统阻滞剂和贝塔受体阻滞剂
- 贝塔受体阻滞剂和抗肾上腺素药[99]
由于存在急性肾衰竭的高风险,务必要避免将血管紧张素转化酶抑制剂或血管紧张素II受体拮抗剂,与一种利尿剂及一种非甾体抗炎药(包括选择性环氧合酶和非处方药物,如布洛芬)联合使用。这一形式的药物联用在澳大利亚医药文献中俗称“三重打击(triple whammy)”。[84]现已有包含两种固定类型药物联合的片剂。虽然这些药物较为方便,但最好限于已确定需使用各成分的人群使用。[100]
对于超过60岁和以上的人群,治疗中等和严重高血压会降低死亡率和心血管病副作用。[101]对80岁以上的人群,之前的治疗方法虽不能大幅将低死亡率但会减低心脏病危险。[101] 噻嗪类利尿剂是美国的首选药物,建议的血压目标为低于140/90 mm Hg。[102]在修订的英国指南中,钙通道阻滞剂被视为首选治疗方法,目标门诊血压读数低于150/90 mmHg,或动态血压检测或家庭血压检测低于145/85 mmHg。[98]
顽固性高血压是指即使一次性服用属于不同类型的三种抗高血压剂后,始终保持在目标值之上的高血压。治疗顽固性高血压的指南已经在英国[103]和美国出版。[104]
患病率
至2000年,有近十亿人或近于26%的成年人患有高血压。[105]该病在发达国家(330,000,000)和发展中国家(639,000,000)均相当普遍。[105]然而,不同地区的发病率差距颇大,在印度农村低至3.4%(男性)和6.8%(女性),在波兰却高达68.9%(男性)和72.5%(女性)。[106] 1995年在美国,估计约约四千三百万人患有高血压或服用抗高血压药。这一数字占了美国成年人数的几乎24%。[107]美国患有高血压的人群比率一直在增长,并于2004年达到了29%。[108][109]至2006年,美国高血压人数达到了七千六百万(占总人口的34%),且非籍美国成年人以44%的比率成为全球高血压发病率最高的人群。[110]该病在美洲土著人中很常见而在美国白人和墨西哥裔美国人中不是很常见。此发病率随着年龄的增长而升高,而在美国东南部较高。跟女性相比,高血压在男性中更常见(尽管更年期趋于降低这种差距),在社会经济状况较差的地区也较为普遍。[5]
儿童患高血压的比率也在增高。[111]多数儿童高血压,尤其在青春期前,继发于潜在的疾病。除了肥胖外,肾疾病是儿童时期高血压病的最常见原因(60-70%)。青少年通常患原发性高血压,占比约85-95%。[112]
历史

现代人对心血管系统的认知始于英国医生威廉·哈维(William Harvey,1578–1657)医生的这部医学著作《心血运动》(De otu ordis)。哈维在著作中描述了血液的循环。1733年英国牧师斯蒂芬·海尔斯(Stephen Hales)第一次公布了血压测量结果。[113][114] 1808年托马斯·杨认为高血压是一种疾病,1836年理查德·布莱特(Richard Bright)也把高血压描述为一种疾病,等等。[113] 弗雷德里克·阿克巴·默罕默德(Frederick Akbar Mahomed,1849–1884)首次报告了一例没有肾病症状的血压升高。[115] 然而,直到1896年希皮奥内·里瓦罗西(Scipione Riva-Rocci)发明了袖套法血压计之后,高血压才成为临床病症。[116]这项发明使得人们可以在临床上测量血压。1905年尼古拉·柯罗特科夫(Nikolai Korotkoff)改进了血压测量技术,提出了柯氏音概念,即血压计袖套放气时听诊器所听到的动脉声音。[114]
历史上对所谓的“硬脉疾病”的治疗方法主要是通过放血或者采用水蛭减少血量。[113]中国的黄帝、凯尔苏斯、盖伦、以及希波克拉底都主张放血。[113] 19世纪和20世纪,在有效的高血压药物治疗方法问世以前,有三种高血压治疗方法,都有很多副作用。这些方法包括严格的钠限制(例如米饭饮食[113])、交感神经切除术(外科手术切除部分交感神经系统)、以及热原质治疗(注射引起发热的物质,间接降低血压)。[113][117]最早治疗高血压的化学药物硫氰酸钠在1900年投入使用,但副作用很多,没有得到广泛应用。[113] 第二次世界大战之后又开发出了几种其它药物。最流行且有效的有四甲基氯化铵及其衍生产品六甲铵、肼屈嗪和利血平(来源于药用植物“蛇根木”)。第一种耐受良好的口服药物的发现使高血压治疗出现重大突破。这种药物是氯噻嗪,它是第一种噻嗪化物利尿剂,来源于抗生素磺胺并于1958年问世。[113][118]它既能防止液体潴留,又增加盐代谢。退伍军人管理局主办的一次随机对照试验对比了氢氯噻嗪加上利血平再加上肼酞嗪与安慰剂治疗高血压。试验因未接受治疗的一部分病人出现了大量的并发症,因此认为使他们无法接受治疗是不人道的行为,从而提前终止了试验。试验在较低血压的人群中继续进行,结果显示,即使是轻微高血压病人,该治疗也使得心血管病死亡的风险降低了一半。[119] 1975年,发明氯噻嗪的研究小组获得了拉斯克公共卫生特别奖。[117]这些研究的成果促进了公共卫生项目,增强了公众对高血压的认知,普及了高血压的测量和治疗。这些举措为1972-1994年间中风和缺血性心脏病发病率下降50%做出了一定的贡献。[117]
社会和文化

世界卫生组织已经确认高血压为导致心血管病死亡率的主要原因。世界高血压联盟是85个国家高血压社团和联盟的联盟组织,该组织认为,世界范围内50%以上的高血压患者不了解自身的情况。[120]为强调这一问题,WHL在2005年发起了一场全球性高血压认知运动,并把每年的5月17日定为世界高血压日。过去三年以来,更多的国家社团参与了世界高血压日,并且通过其创新活动向公众传递有关高血压的信息。2007年,47个WHL成员国家参与了这一活动。在WHD所在的那个星期,所有这些国家与地方政府、学术团体、非政府组织、以及私人企业合作,促进高血压认知,通过几个媒体和公众集会进行宣传。他们采用的大众传播媒体包括互联网和电视,信息受众超过2.5亿人。随着发展势头的逐年壮大,WHL有信心把信息基本上传递到所预测的15亿血压升高人群。[121]
在美国,高血压是一种最为常见的慢性医学问题,使得人们需要经常去找初级医疗服务人员。美国心脏学会估计,2010年高血压的直接和间接治疗费用为766亿美元。[110]在美国,80%的高血压人群了解他们自己的状况,其中71%服用治疗高血压药物。然而,这些认识到自身状况的人中,仅48%的高血压得到了充分的控制。[110]高血压的诊断,治疗或控制的缺陷不利于高血压的管理。[122]医疗服务人员在控制高血压方面也面临着许多困难,包括病人对服用多种药物来达到控制血压水平的抵触情绪。人们同时也面对坚持服药以及改变生活方式的挑战。尽管如此,实现血压控制目标仍然是可行的。降低血压可以显著减少现代医疗保健方面的费用。[123][124]
近年来的研究
美国一项大规模研究试图回答一个困扰医界多年的问题:血压要多高才算是高血压?联邦政府卫生部[何时?]宣布喊停这项研究,但原因并不是研究出了问题,而是结论已经呼之欲出,而且非常重要,必须提前公布:120 mmHg(毫米汞柱)。
SPRINT研究的受试者是9300多位50岁以上、心脏病或肾脏病高风险男女,随机分为两组,一组的血压控制目标是120,另一组是140。研究本来要进行到2017年,但由于结果已经已经呼之欲出,而且对于公众健康至关重要,因此国家心肺血液研究所(NHLBI)2015年9月11日直接宣布应将标准降至120,相关论文将在近期内发表。[125]
参见
参考文献
外部链接
Wikiwand - on
Seamless Wikipedia browsing. On steroids.

 ,
,