Top Qs
Timeline
Chat
Perspective
Solar eclipse of December 26, 2019
21st-century annular solar eclipse From Wikipedia, the free encyclopedia
Remove ads
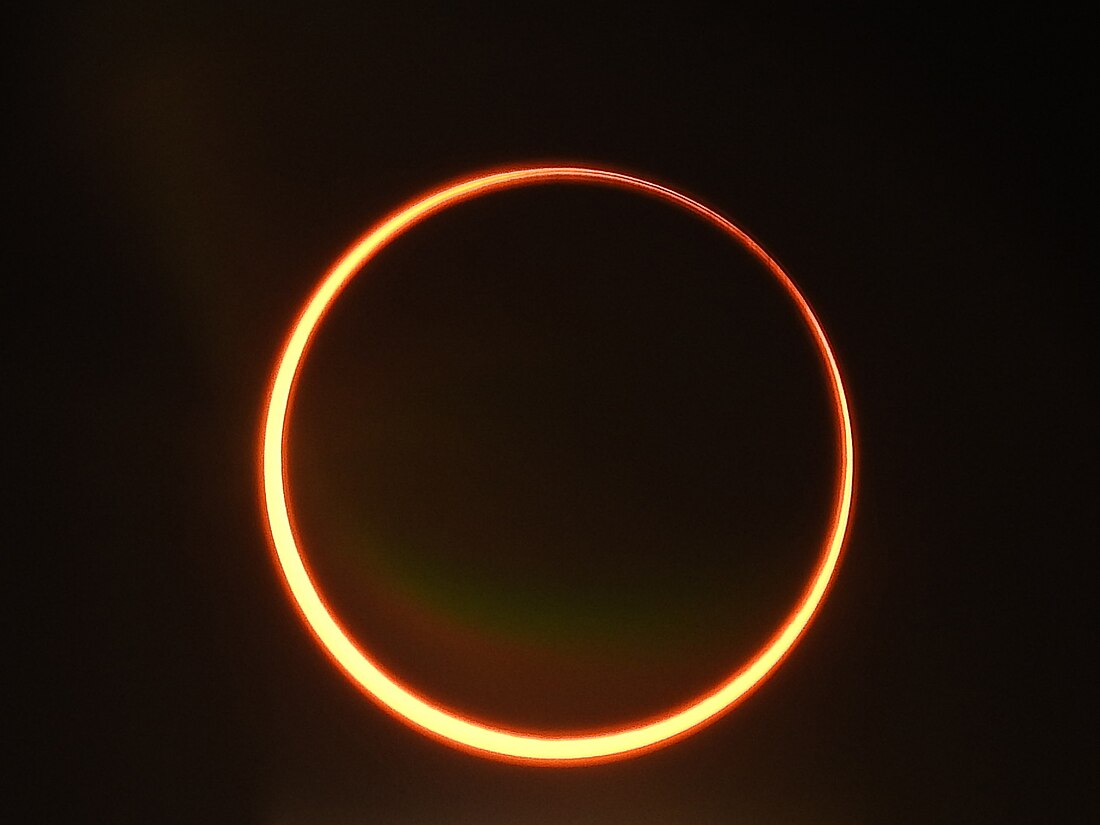
An annular solar eclipse occurred at the Moon’s descending node of orbit on Thursday, December 26, 2019,[1][2][3][4][5] with a magnitude of 0.9701. A solar eclipse occurs when the Moon passes between Earth and the Sun, thereby totally or partly obscuring the Sun for a viewer on Earth. An annular solar eclipse occurs when the Moon's apparent diameter is smaller than the Sun's, blocking most of the Sun's light and causing the Sun to look like an annulus (ring). An annular eclipse appears as a partial eclipse over a region of the Earth thousands of kilometres wide.[6] The Moon's apparent diameter was near the average diameter because it occurred 7.3 days after perigee (on December 18, 2019, at 20:25 UTC) and 6.2 days before apogee (on January 2, 2020, at 1:30 UTC).[7]
Annularity was visible in Saudi Arabia, Qatar, United Arab Emirates, Oman, southern India, Sri Lanka, Malaysia, Indonesia, Singapore, the Northern Mariana Islands, and Guam. A partial eclipse was visible for parts of East Africa, Asia, and northern Australia.
Remove ads
Visibility and viewing
Summarize
Perspective
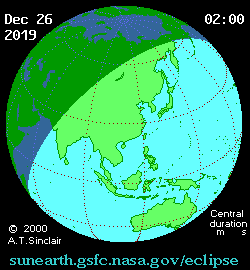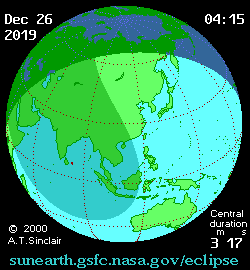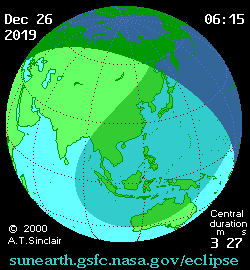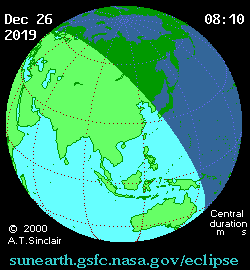
It was the last solar eclipse of 2019. The central path of the 2019 annular eclipse passed through the Saudi Arabian peninsula, southern India, Sumatra, Borneo, Philippines and Guam. A partial eclipse was visible thousands of kilometers wide from the central path. It covered small parts of Eastern Europe, much of Asia, North and West Australia, Eastern Africa, the Pacific Ocean and the Indian Ocean.[6][8] The eclipse started with an antumbra having a magnitude of 0.96; it stretched 164 kilometers wide, and traveled eastwards at an average rate of 1.1 kilometers per second. The longest duration of annularity was 3 minutes and 40 seconds, at 5.30 UT1 occurring in the South China Sea (0°45'54.0"N 105°29'06.0"E).[6]

The eclipse began in Saudi Arabia about 220 kilometers northeast of Riyadh at 03:43 UT1 and ended in Guam at 06:59.4 UT1. It reached India near Kannur, Kerala, at 03:56 UT1. The shadow reached the southeast coast of India at 04:04 UT1. Traveling through northern Sri Lanka, it headed into the Bay of Bengal. The next main visible places were Palau (Malaysia), Sumatra and Singapore. It then passed through the South China Sea, crossed Borneo and the Celebes Sea, the Philippines archipelago and then headed towards the western Pacific. The antumbral shadow encountered Guam at 6:56 UT1 and rose back into space.[6]
Remove ads
Gallery
- Partial from Nabih Saleh, Bahrain, 3:32 UTC
- Partial from Kuwait City, 3:52 UTC
- Partial from Kochi, India, 3:59 UTC
- Nilambur, India, 3:59 UTC
- Mangalore, India, 4:16 UTC
- Partial from Dhaka, Bangladesh, 5:13 UTC
- Partial from Jakarta, Indonesia, 5:18 UTC
- Labrador Nature Reserve, Singapore, 5:23 UTC
- Partial from University of Science, Malaysia, 5:25 UTC
- Batam, Indonesia, 5:25 UTC
- Tanjungpinang, Indonesia, 5:25 UTC
- Partial from Hefei, China, 6:18 UTC
- Partial from San Jose del Monte, Philippines, 6:19 UTC
- Partial from Digos, Philippines, 6:21 UTC
- Merizo, Guam, 6:56 UTC
- Eclipse progression from Batam, Indonesia
Remove ads
Eclipse details
Summarize
Perspective
Shown below are two tables displaying details about this particular solar eclipse. The first table outlines times at which the moon's penumbra or umbra attains the specific parameter, and the second table describes various other parameters pertaining to this eclipse.[9]
Eclipse season
This eclipse is part of an eclipse season, a period, roughly every six months, when eclipses occur. Only two (or occasionally three) eclipse seasons occur each year, and each season lasts about 35 days and repeats just short of six months (173 days) later; thus two full eclipse seasons always occur each year. Either two or three eclipses happen each eclipse season. In the sequence below, each eclipse is separated by a fortnight.
Remove ads
Related eclipses
Summarize
Perspective
Eclipses in 2019
- A partial solar eclipse on January 6
- A total lunar eclipse on January 21
- A total solar eclipse on July 2
- A partial lunar eclipse on July 16
- An annular solar eclipse on December 26
Astronomers Without Borders collected eclipse glasses for redistribution to Latin America and Asia for their 2019 eclipses from the solar eclipse of August 21, 2017.[10]
Metonic
- Preceded by: Solar eclipse of March 9, 2016
- Followed by: Solar eclipse of October 14, 2023
Tzolkinex
- Preceded by: Solar eclipse of November 13, 2012
- Followed by: Solar eclipse of February 6, 2027
Half-Saros
- Preceded by: Lunar eclipse of December 21, 2010
- Followed by: Lunar eclipse of December 31, 2028
Tritos
- Preceded by: Solar eclipse of January 26, 2009
- Followed by: Solar eclipse of November 25, 2030
Solar Saros 132
- Preceded by: Solar eclipse of December 14, 2001
- Followed by: Solar eclipse of January 5, 2038
Inex
- Preceded by: Solar eclipse of January 15, 1991
- Followed by: Solar eclipse of December 5, 2048
Triad
- Preceded by: Solar eclipse of February 24, 1933
- Followed by: Solar eclipse of October 26, 2106
Solar eclipses of 2018–2021
This eclipse is a member of a semester series. An eclipse in a semester series of solar eclipses repeats approximately every 177 days and 4 hours (a semester) at alternating nodes of the Moon's orbit.[11]
The partial solar eclipses on February 15, 2018 and August 11, 2018 occur in the previous lunar year eclipse set.
Saros 132
This eclipse is a part of Saros series 132, repeating every 18 years, 11 days, and containing 71 events. The series started with a partial solar eclipse on August 13, 1208. It contains annular eclipses from March 17, 1569 through March 12, 2146; hybrid eclipses on March 23, 2164 and April 3, 2182; and total eclipses from April 14, 2200 through June 19, 2308. The series ends at member 71 as a partial eclipse on September 25, 2470. Its eclipses are tabulated in three columns; every third eclipse in the same column is one exeligmos apart, so they all cast shadows over approximately the same parts of the Earth.
The longest duration of annularity was produced by member 25 at 6 minutes, 56 seconds on May 9, 1641, and the longest duration of totality will be produced by member 61 at 2 minutes, 14 seconds on June 8, 2290. All eclipses in this series occur at the Moon’s descending node of orbit.[12]
Metonic series
The metonic series repeats eclipses every 19 years (6939.69 days), lasting about 5 cycles. Eclipses occur in nearly the same calendar date. In addition, the octon subseries repeats 1/5 of that or every 3.8 years (1387.94 days). All eclipses in this table occur at the Moon's descending node.
Tritos series
This eclipse is a part of a tritos cycle, repeating at alternating nodes every 135 synodic months (≈ 3986.63 days, or 11 years minus 1 month). Their appearance and longitude are irregular due to a lack of synchronization with the anomalistic month (period of perigee), but groupings of 3 tritos cycles (≈ 33 years minus 3 months) come close (≈ 434.044 anomalistic months), so eclipses are similar in these groupings.
Inex series
This eclipse is a part of the long period inex cycle, repeating at alternating nodes, every 358 synodic months (≈ 10,571.95 days, or 29 years minus 20 days). Their appearance and longitude are irregular due to a lack of synchronization with the anomalistic month (period of perigee). However, groupings of 3 inex cycles (≈ 87 years minus 2 months) comes close (≈ 1,151.02 anomalistic months), so eclipses are similar in these groupings.
Remove ads
Notes
References
Wikiwand - on
Seamless Wikipedia browsing. On steroids.
Remove ads
































































































































