Top Qs
Timeline
Chat
Perspective
Roads in Romania
From Wikipedia, the free encyclopedia
Remove ads
Public roads in Romania are ranked according to importance and traffic as follows:
- motorways (autostradă – pl. autostrăzi) – colour: green; designation: A followed by one or two digits
- expressways (drum expres – pl. drumuri express) – colour: red; designation: DEx followed by one or two digits and an optional letter
- national road (drum național – pl. drumuri naționale) – colour: red; designation: DN followed by one or two digits and an optional letter
- county road (drum județean – pl. drumuri județene) – colour: blue; designation: DJ followed by three digits and an optional letter; unique numbers per county
- local road (drum comunal – pl. drumuri comunale) – colour: yellow; designated DC followed by a number and an optional letter; unique numbers per county
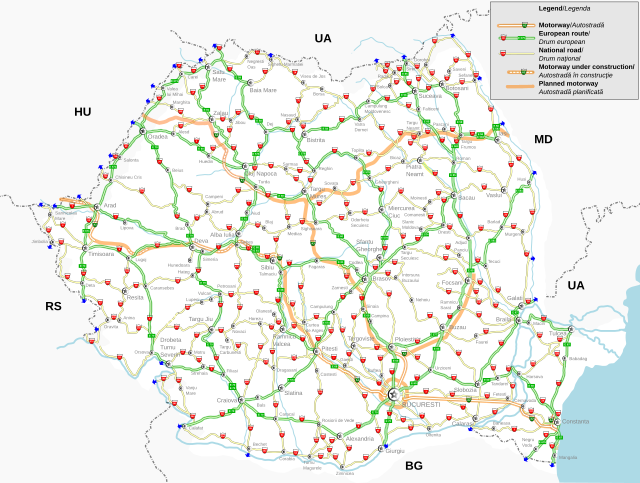

Some of the national roads are part of the European route scheme. European routes passing through Romania: E58; E60; E70; E85; E79; E81; E68; E87 (Class A); E574; E576; E581; E583; E671; E771.
As of 31 December 2021, public roads totaled 86,199 km (53,562 mi): 17,530 km (20.3%) national roads, 35,096 km (40.7%) county roads and 33,573 km (39%) local roads.[1]
From the point of view of the type of cover, the structure of the public road network registers at the end of 2022 was: 41,653 km (48,2%) modernized roads (94,1% with asphalt pavements of heavy/medium type and 5.9% with concrete), 20,956 km (24.3%) with light-duty asphalt surface, 15,713 km (18,2%) stone paving (such as sett paving or cobblestone roads) and 8,014 km (9,3%) dirt roads.[2]
Regarding the technical condition, 29,9% of modernized roads and 41,1% of roads with light road clothing have exceeded their "service life".[2]
Remove ads
Motorways
Summarize
Perspective
Development of the overall length (at the end of):
| Year | 1972 | 1987 | 2000 | 2002 | 2004 | 2007 | 2008 | 2009 | 2010 | 2011 | 2012 | 2013 | 2014 | 2015 | 2016 | 2017 | 2018 | 2019 | 2020 | 2021 | 2022 | 2023 |
| Length in km | 96 | 113 | 113* | 113* | 228 | 262 | 262* | 304 | 332 | 390 | 530 | 635 | 685 | 711 | 732 | 748 | 806 | 850 | 914 | 946 | 996 | 1,033 |
Motorways are identified by A followed by a number. As of April 2024, Romania has 1,098 km of motorway in use, with another 720 km under construction.[citation needed] In recent years, a master plan for the national motorway network has been developed and many works have begun around the country,[3] which will result in significant changes by 2015,[4] and eventually by 2022.[5]
There are few tolls for using roads in Romania. There is one at the Giurgeni – Vadu Oii Bridge over the river Danube on highway DN2A at Vadu Oii and one at the Cernavodă Bridge, on the A2 motorway, a 17 km long section between Fetești and Cernavodă which consists of two road/railway bridges. Nevertheless, every owner of a car that uses a motorway (A) or a national road (DN) in Romania must purchase a vignette (rovinietă) from any of the main petrol stations or at any post office throughout the country.[6]
Remove ads
Expressways
Summarize
Perspective
Planned expressways according to CNADNR (Romanian National Company of Motorways and National Roads):[10][11]
Remove ads
European routes
Summarize
Perspective
Total length of European routes in Romania at the end of 2019 is 6,176 km (3837.5 mi).[12]
Class A
Map of European routes passing through Romania
 E58 — (Austria, Slovakia, Ukraine) – Halmeu – Dej – Bistrița – Suceava – Botoșani – Târgu Frumos – Iași – Sculeni – (Republic of Moldova, Ukraine, Russia)
E58 — (Austria, Slovakia, Ukraine) – Halmeu – Dej – Bistrița – Suceava – Botoșani – Târgu Frumos – Iași – Sculeni – (Republic of Moldova, Ukraine, Russia) E60 — (France, Switzerland, Austria, Hungary) – Borș – Oradea – Cluj-Napoca – Turda – Târgu Mureș – Brașov – Ploiești – Bucharest – Urziceni – Slobozia – Constanța – (Georgia, Azerbaijan, Turkmenistan, Uzbekistan, Tajikistan, Kyrgyzstan, China)[13]
E60 — (France, Switzerland, Austria, Hungary) – Borș – Oradea – Cluj-Napoca – Turda – Târgu Mureș – Brașov – Ploiești – Bucharest – Urziceni – Slobozia – Constanța – (Georgia, Azerbaijan, Turkmenistan, Uzbekistan, Tajikistan, Kyrgyzstan, China)[13] E68 — (Hungary) – Nădlac – Arad – Deva – Sebeș – Miercurea Sibiului – Sibiu – Brașov
E68 — (Hungary) – Nădlac – Arad – Deva – Sebeș – Miercurea Sibiului – Sibiu – Brașov E70 — (Spain, France, Italy, Slovenia, Croatia, Serbia) – Timișoara – Drobeta-Turnu Severin – Craiova – Alexandria – Bucharest – Giurgiu – (Bulgaria, Turkey, Georgia)
E70 — (Spain, France, Italy, Slovenia, Croatia, Serbia) – Timișoara – Drobeta-Turnu Severin – Craiova – Alexandria – Bucharest – Giurgiu – (Bulgaria, Turkey, Georgia) E79 — (Hungary) – Borș – Oradea – Beiuș – Deva – Petroșani – Târgu Jiu – Filiași – Craiova – Calafat – (Bulgaria, Greece)
E79 — (Hungary) – Borș – Oradea – Beiuș – Deva – Petroșani – Târgu Jiu – Filiași – Craiova – Calafat – (Bulgaria, Greece) E81 — (Ukraine) – Halmeu – Livada – Satu Mare – Zalău – Cluj-Napoca – Turda – Sebeș – Miercurea Sibiului – Sibiu – Pitești – Bucharest – Constanța
E81 — (Ukraine) – Halmeu – Livada – Satu Mare – Zalău – Cluj-Napoca – Turda – Sebeș – Miercurea Sibiului – Sibiu – Pitești – Bucharest – Constanța E85 — (Lithuania, Belarus, Ukraine) – Siret – Suceava – Roman – Bacău – Buzău – Urziceni – Bucharest – Giurgiu – (Bulgaria, Greece)
E85 — (Lithuania, Belarus, Ukraine) – Siret – Suceava – Roman – Bacău – Buzău – Urziceni – Bucharest – Giurgiu – (Bulgaria, Greece) E87 — (Ukraine) – Galați – Brăila – Tulcea – Constanța – Vama Veche – (Bulgaria, Turkey)
E87 — (Ukraine) – Galați – Brăila – Tulcea – Constanța – Vama Veche – (Bulgaria, Turkey)
Class B
 E574 — Bacău – Onești – Târgu Secuiesc – Brașov – Pitești – Craiova
E574 — Bacău – Onești – Târgu Secuiesc – Brașov – Pitești – Craiova E576 — Cluj-Napoca – Dej
E576 — Cluj-Napoca – Dej E577 — Slobozia – Brăila – Galați – (Republic of Moldova, Ukraine)
E577 — Slobozia – Brăila – Galați – (Republic of Moldova, Ukraine) E578 — Sărățel – Reghin – Toplița – Gheorgheni – Miercurea Ciuc – Sfântu Gheorghe – Chichiș
E578 — Sărățel – Reghin – Toplița – Gheorgheni – Miercurea Ciuc – Sfântu Gheorghe – Chichiș E581 — Mărășești – Tecuci – Bârlad – Huși – Albița – (Republic of Moldova, Ukraine)
E581 — Mărășești – Tecuci – Bârlad – Huși – Albița – (Republic of Moldova, Ukraine) E583 — Săbăoani – Iași – Sculeni – (Republic of Moldova, Ukraine)
E583 — Săbăoani – Iași – Sculeni – (Republic of Moldova, Ukraine) E584 — (Ukraine, Republica Moldova) – Galați – Slobozia
E584 — (Ukraine, Republica Moldova) – Galați – Slobozia E671 — Timișoara – Arad – Oradea – Satu Mare
E671 — Timișoara – Arad – Oradea – Satu Mare E673 — Lugoj – Deva
E673 — Lugoj – Deva E675 — Constanța – Agigea – Negru Vodă – (Bulgaria)
E675 — Constanța – Agigea – Negru Vodă – (Bulgaria) E771 — Drobeta-Turnu Severin – Porțile de Fier – (Serbia)
E771 — Drobeta-Turnu Severin – Porțile de Fier – (Serbia)
National roads
Summarize
Perspective

Total length (including European routes and Highways) of National Roads in 2019 is 17,873 km (11105.77 mi),[12] an increase from 17,272 km (10,732 mi) in 2015.[14] The majority of National Roads (DN) are single carriageway, with only 12.5% being dual carriageway.[12] A major problem being that many National Roads (drumuri naționale) have no ring roads around cities and towns, disrupting the traffic flow (i.e. making traffic condition more difficult).
In 2019 16,088 km (9,996 mi) of National Roads are asphalt concrete roads of heavy/medium type, 880 km (546.8 mi) concrete roads and 720 km (447 mi) of light asphalt road "clothing".[12] 54.7% of heavy/medium roads and 79.4% of light asphalt roads have exceeded their "service life" and are in need of some form of repair or replacement.[12]
Seven one-digit national roads start off in Bucharest in a radial pattern.[15]
Trunk roads
Other national roads
Remove ads
County and local roads
At the end of 2019 there are 35,083 km (21,799 mi) of county roads and 33,435 km (20,775 mi) of local roads.[12]
County roads
At the end of 2019, out of the 35,083 km: 13,810 km (39.4%) are asphalt concrete roads of heavy/medium type, 13,227 km (37.7%) light asphalt road "clothing", 956 km (2.7%) concrete roads, 5,310 km (15%) cobblestone roads and 1,706 km (4.8%) dirt roads.[12] Regarding the technical condition, 23% of asphalt concrete roads of heavy/medium type and 48% of light asphalt roads have exceeded their "service life" and are in need of some form of repair or replacement.[12]
Local roads
At the end of 2019, out of the 33,435 km: 7,418 km (22.1%) are light asphalt road "clothing", 5,506 km (16.5%) asphalt concrete roads of heavy/medium type, 810 km (2.4%) concrete roads, 12,377 km (37%) cobblestone roads and 7,305 km (21.8%) dirt roads.[12] Regarding technical condition, 31% of light asphalt roads and 10% of asphalt concrete roads of heavy/medium type have exceeded their "service life" and are in need of some form of repair or replacement.[12]
Remove ads
See also
References
Wikiwand - on
Seamless Wikipedia browsing. On steroids.
Remove ads
