Foreign relations of the Netherlands
From Wikipedia, the free encyclopedia
The foreign policy of the Netherlands is based on four basic commitments: to the Atlantic cooperation, to European integration, to international development and to international law. While historically the Kingdom of the Netherlands was a neutral state, since 1945 it has become a member of NATO, the United Nations, the European Union and many other international organizations. The Dutch economy is very open and relies on international trade. During and after the 17th century—its Golden Age—the Dutch built up a commercial and colonial empire. It was a leading shipping and naval power and was often at war with England, its main rival. Its main colonial holding was Indonesia, which fought for and achieved independence after 1945. The historical ties inherited from its colonial past still influence the foreign relations of the Netherlands. Foreign trade policy is handled by the European Union. The Dutch have been active in international peacekeeping roles.
History
Summarize
Perspective
This section needs additional citations for verification. (July 2021) |
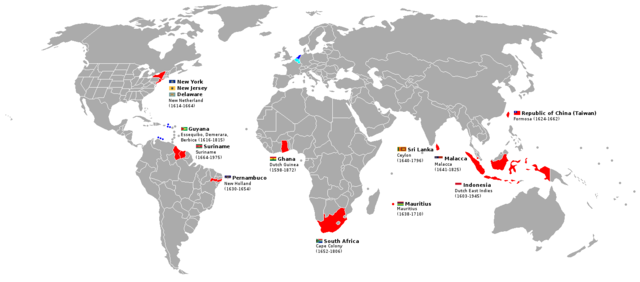
In the Dutch Golden Age, which had its zenith around 1667, there was a flowering of trade, industry, the arts and the sciences. A rich worldwide Dutch empire developed and the Dutch East India Company became one of the earliest and most important of national mercantile companies based on entrepreneurship and trade.
During the 18th century, the power and wealth of the Netherlands declined. A series of wars with the more powerful British and French neighbors weakened it. Britain seized the North American colony of New Amsterdam, turning it into New York. There was growing unrest and conflict between the Orangists and the Patriots. The French Revolution spilled over after 1789, and a pro-French Batavian Republic was established in 1795–1806. Napoleon made it a satellite state, the Kingdom of Holland (1806–1810), and later simply a French imperial province.
In 1815–1940 it was neutral and played a minor role in world diplomacy, apart from a failed effort to control the seceding Southern provinces that became Belgium before giving up in 1839.[1]
Unlike most European countries, the Netherlands succeeded in remaining neutral throughout The Great War. This approach failed during the Second World War however and the kingdom quickly fell to an unprovoked German invasion in 1940 and would remain under Nazi occupation until being liberated by the allies in 1945. After the war, as a member of the allies, the Netherlands was included in the first class of U.N. members. During the Cold War like most Western European countries, the Dutch aligned with the United States against the Soviet Union, co-founding the North Atlantic Treaty Organization (NATO), in 1949.[2][3] The Dutch were also at the forefront of promoting European cooperation and integration during this time period; co-founding the European Coal and Steel Community and becoming one of the European Union's (EU) original members.[4]
European integration
The Dutch have been strong advocates of European integration, and most aspects of their foreign, economic, and trade policies are coordinated through the European Union (EU). The Dutch postwar customs union with Belgium and Luxembourg (the Benelux group) paved the way for the formation of the European Community (precursor to the EU), of which the Netherlands was a founding member. Likewise, the Benelux abolition of internal border controls was a model for the wider Schengen Accord, which today has 29 European signatories (including the Netherlands) pledged to common visa policies and free movement of people across common borders.
The Dutch stood at the cradle of the 1992 Maastricht Treaty and have been the architects of the Treaty of Amsterdam concluded in 1998. The Dutch have thus played an important role in European political and monetary integration; indeed, until the year 2003, Dutchman Wim Duisenberg headed the European Central Bank. In addition, Dutch financial minister Gerrit Zalm was the main critic of the violation of the Stability and Growth Pact by France and Germany in 2004 and 2005.[5]
Involvement in developing countries
Summarize
Perspective
The Netherlands was the 9th-largest donor country in 2021, giving about $5 billion, about 0.5% of its gross national income (GNI), in official development assistance (ODA).[6] The country contributes through multilateral channels, especially the United Nations Development Programme, the international financial institutions, and EU programs. A large portion of Dutch aid funds is also channeled through private ("co-financing") organizations that have almost total autonomy in choice of projects.[citation needed]
The Netherlands is a member of the European Bank for Reconstruction and Development, which recently initiated economic reforms in central Europe. The Dutch strongly support the Middle East peace process and in 1998 earmarked $29 million in contributions to international donor-coordinated activities for the occupied territories and also for projects in which they worked directly with Palestinian authorities. These projects included improving environmental conditions and support for multilateral programs in cooperation with local non-governmental organizations. In 1998, the Dutch provided significant amounts of aid to the former Yugoslavia and Africa. The Dutch consistently provide significant amounts of humanitarian relief aid to the victims of the worst natural disasters, such as Hurricane Mitch in Central America in 1998, the 2004 Indian Ocean earthquake and tsunami in South and Southeast Asia, Hurricane Katrina in the United States in 2005, the 2010 Haiti earthquake, and more recent catastrophes in Pakistan and Burma including Typhoon Haiyan in the Philippines in 2013, and the 2015 Nepal earthquake.[7]
Export assistance grants
"Developing countries aspiring to purchase foreign goods and services to invest in, inter alia, port facilities, roads, public transport, health care, or drinking water facilities may be eligible for a special Dutch grant facility. The grant facility, known as ORET (a Dutch acronym for Ontwikkelingsrelevante Exporttransacties, or Development-Related Export) serves to award grants to governments of developing countries for making payments to foreign suppliers."[8]
International organizations
As a relatively small country, the Netherlands generally pursues its foreign policy interests within the framework of multilateral organizations. The Netherlands is an active and responsible participant in the United Nations system as well as other multilateral organizations such as the Organization for Security and Cooperation in Europe, Organisation for Economic Co-operation and Development (OECD), World Trade Organization (WTO),[9] and International Monetary Fund.[10]
The Netherlands is one of the founding members of what today is the European Union. It was one of the first countries to start European integration, through the Benelux in 1944 and the European Coal and Steel Community in 1952. Being a small country with a history of neutrality it was the host country for the important Maastricht Treaty and Amsterdam Treaty and is the seat of the International Court of Justice.[11]
International issues
Summarize
Perspective

The Dutch work with the U.S. and other countries on international programs against drug trafficking and organized crime. The Dutch-U.S. cooperation focuses on joint anti-drug operations in the Caribbean, including an agreement establishing Forward Operating Locations on the Dutch Kingdom islands of Curaçao and Aruba. The Netherlands is a signatory to international counter-narcotics agreements, a member of the United Nations International Drug Control Program, the UN Commission on Narcotic Drugs, and is a contributor to international counter-narcotics.
From June 26 until December 22, 2006, two children, Ammar (12–13) and Sara (10–11), lived in the Dutch embassy in Damascus because of a child custody dispute between the Dutch mother, supported by Dutch law and the Hague Convention on the Civil Aspects of International Child Abduction, and the Syrian father, supported by Syrian law (Syria is no participant of this convention). The children had been living in Syria since 2004, after an alleged international child abduction by the father from the Netherlands to Syria, during a family contact in which he supposedly would visit Paris with them. The children fled to the embassy because they would like to live with their mother in the Netherlands. Minister of Foreign Affairs Ben Bot traveled to Damascus, negotiated and on December 22 the children finally could return to the Netherlands.
The father claims that the Dutch government has promised not to prosecute him for the abduction. However, a Dutch prosecutor claims that he is free to prosecute the father and may well do that and that the Dutch have only retracted the international request to arrest him outside the Netherlands.[12]
Mark Rutte's government provided materials to the Levant Front rebel group in Syria.[13] In September 2018, the Dutch public prosecution department declared the Levant Front to be a "criminal organisation of terrorist intent", describing it as a "salafist and jihadistic" group that "strives for the setting up of the caliphate".[14]
In July 2019, the UN ambassadors from 22 nations, including the Netherlands, signed a joint letter to the UNHRC condemning China's mistreatment of the Uyghurs as well as its mistreatment of other minority groups, urging the Chinese government to close the Xinjiang internment camps.[15][16]
Diplomatic relations
Summarize
Perspective
List of countries which the Netherlands maintains diplomatic relations with:
 | ||
|---|---|---|
| # | Country | Date |
| 1 | 1 April 1603[17] | |
| 2 | 31 March 1605[18] | |
| 3 | 1613[19] | |
| 4 | April 1614[20] | |
| 5 | February 1641[21] | |
| 6 | 29 June 1649[22] | |
| 7 | 28 July 1749[23] | |
| 8 | 19 April 1782[24] | |
| 9 | 31 January 1814[25] | |
| 10 | 15 June 1827[26] | |
| 11 | 20 December 1828[27] | |
| 12 | 1 May 1829[28] | |
| — | May 1829[29][30] | |
| 13 | 3 August 1839[31] | |
| 14 | 12 July 1852[32] | |
| 15 | 30 November 1853[33] | |
| 16 | 30 January 1856[34] | |
| 17 | 22 March 1856[35] | |
| 18 | 22 March 1856[36] | |
| 19 | 18 April 1856[37] | |
| 20 | 1857[38] | |
| 21 | 15 September 1859[39] | |
| 22 | 17 December 1860[40] | |
| 23 | 9 January 1872[41] | |
| 24 | 12 May 1872[42] | |
| 25 | 12 February 1880[43] | |
| 26 | 5 January 1883[44] | |
| 27 | 4 March 1891[45] | |
| 28 | 24 January 1896[46] | |
| 29 | 15 April 1896[47][48] | |
| 30 | 26 April 1899[49] | |
| 31 | 20 May 1902[50] | |
| 32 | 9 November 1903[51] | |
| 33 | 20 April 1904[52] | |
| 34 | 4 December 1905[53] | |
| 35 | 8 July 1909[54] | |
| 36 | 21 July 1911[55] | |
| 37 | 21 November 1912[56] | |
| 38 | 14 August 1918[57] | |
| 39 | 4 July 1919[58] | |
| 40 | 13 November 1919[59] | |
| 41 | 19 January 1920[60] | |
| 42 | 14 January 1921[61] | |
| 43 | 13 May 1921[62] | |
| 44 | 16 November 1922[63] | |
| 45 | 5 August 1925[64] | |
| 46 | 25 November 1929[65][66] | |
| 47 | 9 June 1930[67] | |
| 48 | 10 May 1935[68] | |
| 49 | 3 January 1939[69] | |
| 50 | 1 February 1942[70] | |
| 51 | 1945[71] | |
| 52 | 9 January 1946[72] | |
| 53 | 16 March 1946[73] | |
| 54 | 17 April 1947[74] | |
| 55 | 19 June 1947[75] | |
| 56 | 22 December 1947[76] | |
| 57 | July 1948[77] | |
| 58 | 3 May 1949[78] | |
| 59 | October 1949[79][80] | |
| 60 | 11 September 1950[81] | |
| 61 | 12 October 1950[78] | |
| 62 | 6 November 1950[78] | |
| 63 | 6 March 1951[82] | |
| 64 | 17 May 1951[83] | |
| 65 | 23 November 1951[84] | |
| 66 | 15 December 1951[85] | |
| 67 | 24 January 1952[86] | |
| 68 | 1955[87] | |
| — | 1955[88] | |
| 69 | 15 February 1956[89] | |
| 70 | 2 August 1956[90] | |
| 71 | 23 March 1957[91] | |
| 72 | 31 August 1957[92] | |
| 73 | 28 November 1957[93] | |
| 74 | February 1958[94] | |
| 75 | 9 May 1959[95] | |
| 76 | 9 March 1960[96] | |
| 77 | 2 April 1960[97] | |
| 78 | 7 July 1960[98] | |
| 79 | 25 July 1960[99] | |
| 80 | 24 September 1960[100] | |
| 81 | October 1960[101] | |
| 82 | 16 March 1961[101] | |
| 83 | 4 April 1961[102] | |
| 84 | 3 August 1961[103] | |
| 85 | 24 August 1961[104] | |
| 86 | 5 October 1961[105] | |
| 87 | 7 November 1961[103] | |
| 88 | 2 December 1961[103] | |
| 89 | 14 December 1961[104] | |
| 90 | 20 December 1961[103] | |
| 91 | 26 December 1961[104] | |
| 92 | 9 January 1962[103] | |
| 93 | 22 February 1962[105] | |
| 94 | 9 March 1962[103] | |
| 95 | 31 March 1962[103] | |
| 96 | 7 May 1962[103] | |
| 97 | 4 July 1962[106] | |
| 98 | 2 August 1962[107] | |
| 99 | 19 October 1962[108] | |
| 100 | October 1962[109] | |
| 101 | 3 February 1964[110] | |
| 102 | 11 July 1964[111] | |
| 103 | 1 October 1964[112] | |
| 104 | 1964[113] | |
| 105 | 6 October 1965[114] | |
| 106 | 2 November 1965[115] | |
| 107 | 7 December 1965[116] | |
| 108 | 10 December 1965[117] | |
| 109 | 16 December 1965[118] | |
| 110 | 1965[119] | |
| 111 | 1 August 1966[120] | |
| 112 | 29 August 1966[121] | |
| 113 | 10 August 1967[122] | |
| 114 | 22 February 1968[123] | |
| 115 | 1968[124] | |
| 116 | 5 March 1969[125] | |
| 117 | 12 December 1969[126] | |
| 118 | 1969[127] | |
| 119 | 15 May 1970[128] | |
| 120 | 17 November 1970[129] | |
| 121 | 5 October 1971[130] | |
| 122 | 1 January 1972[131] | |
| 123 | 11 February 1972[132] | |
| 124 | February 1972[133] | |
| 125 | 6 March 1972[134] | |
| 126 | 2 May 1972[135] | |
| 127 | 6 May 1972[136] | |
| 128 | 18 May 1972[137] | |
| 129 | 15 June 1972[138] | |
| 130 | 9 April 1973[139] | |
| 131 | 28 March 1974[140] | |
| 132 | 25 June 1975[141] | |
| 133 | 13 August 1975[142] | |
| 134 | 4 November 1975[143] | |
| 135 | 17 November 1975[144] | |
| 136 | 25 November 1975[145] | |
| 137 | 18 February 1976[146] | |
| 138 | 13 April 1976[147] | |
| 139 | 25 August 1976[148] | |
| 140 | 20 November 1976[149] | |
| 141 | 18 January 1977[150] | |
| 142 | 21 February 1977[151] | |
| 143 | 3 September 1979[152] | |
| 144 | 18 April 1980[153] | |
| 145 | 6 June 1980[154] | |
| 146 | 1980[155] | |
| 147 | 1980[156] | |
| 148 | 10 February 1981[157] | |
| 149 | 8 April 1981[158] | |
| 150 | 1 February 1982[159] | |
| 151 | 9 March 1982[160] | |
| 152 | 11 May 1982[161] | |
| 153 | 1982[162] | |
| 154 | 27 April 1985[163] | |
| 155 | 10 June 1985[164] | |
| 156 | 13 April 1987[165] | |
| 157 | 23 April 1990[166] | |
| 158 | 24 September 1991[167] | |
| 159 | 21 October 1991[168] | |
| 160 | 20 November 1991[169] | |
| 161 | 3 December 1991[170] | |
| 162 | 24 January 1992[171] | |
| 163 | 30 January 1992[172] | |
| 164 | 11 February 1992[173] | |
| 165 | 24 March 1992[174] | |
| 166 | 1 April 1992[175] | |
| 167 | 1 April 1992[176] | |
| 168 | 22 April 1992[177] | |
| 169 | 20 May 1992[178] | |
| 170 | 10 June 1992[179] | |
| 171 | 27 July 1992[180] | |
| 172 | 10 September 1992[181] | |
| 173 | 24 November 1992[182] | |
| 174 | 15 December 1992[183] | |
| 175 | 1 January 1993[184] | |
| 176 | 2 March 1993[185] | |
| 177 | 10 July 1993[186] | |
| 178 | 14 December 1993[187] | |
| 179 | 16 December 1993[188] | |
| 180 | 15 July 1994[189] | |
| 181 | 1995[190] | |
| 182 | 15 April 1996[191] | |
| 183 | 21 April 1997[192] | |
| 184 | 15 December 2000[193] | |
| 185 | 17 November 2003[194] | |
| 186 | March 2004[195] | |
| 187 | 8 September 2006[196] | |
| — | 27 June 2008[197] | |
| — | 16 August 2011[198] | |
| 188 | 9 September 2011[199] | |
| 189 | Unknown | |
| 190 | Unknown | |
| 191 | Unknown | |
Bilateral relations
Summarize
Perspective
Africa
| Country | Formal relations began | Notes |
|---|---|---|
| 14 December 1961 | Both countries established diplomatic relations on 14 December 1961[104] | |
| 16 November 1922 | See Egypt–Netherlands relations
Both countries established diplomatic relations on 16 November 1922 when Mr. J. P. graaf van Limburg Stirum was accredited as Envoy Extraordinary and Minister Plenipotentiary of the Netherlands to Egypt.[204]
| |
| 6 November 1950 | See Ethiopia–Netherlands relations
Both countries established diplomatic relations on 6 November 1950[78]
| |
| 9 January 1962 | See Ivory Coast–Netherlands relations
Both countries established diplomatic relations on 9 January 1962[103]
| |
| 3 February 1964 | See Kenya–Netherlands relations
Both countries established diplomatic relations on 3 February 1964[110]
| |
| 3 May 1949 | Both countries established diplomatic relations on 3 May 1949.[78] Also both countries established diplomatic relations on 27 March 1936 when has been accredited Envoy Extraordinary and Minister Plenipotentiary of Liberia to the Netherlands Baron Otto van den Bogaerde van Terbrugge.[205] | |
| 9 March 1962 | Both countries established diplomatic relations on 9 March 1962[103] | |
See Morocco–Netherlands relations
| ||
See Netherlands–South Africa relations
|
Americas
| Country | Formal relations began | Notes |
|---|---|---|
| 24 January 1896 | See Argentina–Netherlands relations
Both countries established diplomatic relations on 24 January 1896.[210]
| |
| 21 July 1911 | See Bolivia–Netherlands relations
Both countries established diplomatic relations on 21 July 1911.[213][55]
| |
See Brazil–Netherlands relations
| ||
| 3 January 1939 | See Canada–Netherlands relations
Both countries established diplomatic relations on 3 January 1939[216] Canada has an embassy in The Hague and the Netherlands has one in Ottawa, and three Consulates-General in Toronto, Montreal and Vancouver. Canada and the Netherlands have worked closely together on many foreign issues and enjoy an especially close relationship. To foster business and commercial relations between the Netherlands and Canada, the Dutch business community set up the Netherlands-Canadian Chamber of Commerce.[217] They are both members of the United Nations (and its Specialized Agencies), the World Trade Organization, and Interpol; they are both founding members of the North Atlantic Treaty Organization (NATO), the Euro-Atlantic Partnership Council (EAPC), the Organization for Security and Cooperation in Europe (OSCE), and the Stability Pact for South Eastern Europe. Canada and the Netherlands also work together on such issues as the prohibition and elimination of anti-personnel mines, the control of the proliferation of small arms and light weapons, eradicating the worst forms of child labour, the provision of rapid reaction peacekeeping forces to the United Nations (SHIRBRIG) and regional security issues such as Bosnia (SFOR) and Ethiopia and Eritrea (UNMEE). | |
| 10 June 1872 | See Chile–Netherlands relations
Both countries established diplomatic relations on 10 June 1872.[220]
| |
| 1829 | See Colombia–Netherlands relations
Relations between Colombia and the Netherlands were established in 1829.
| |
| 12 July 1852 | Both countries established diplomatic relations on 12 July 1852.[223]
| |
| 20 May 1902 | See Cuba–Netherlands relations
Both countries established diplomatic relations on 20 May 1902.[224]
| |
| ||
| 18 March 1892 | Both countries established diplomatic relations on 18 March 1892[227]
| |
| ||
| 15 May 1970 |
Both countries established diplomatic relations on 15 May 1970.[228] Guyana was made up of three former Dutch colonies: (Berbice, Demerara and Essequibo (colony)) which were brought together by the British and renamed collectively British Guiana. | |
| 16 May 1946 | See Honduras–Netherlands relations
Both countries established diplomatic relations on 16 May 1946 when has been accredited Envoy Extraordinary and Minister Plenipotentiary of the Netherlands to Hohduras with residence in Guatemala Mr. G. M. Bijvanck.[229]
| |
| 16 June 1828 | See Mexico–Netherlands relations
Both countries established diplomatic relations on 16 June 1828.[230][non-primary source needed] On September 27, 1993, the Netherlands Ministry of Finance announced The Netherlands – Mexico Tax Treaty and Protocol. The regulations detail the formalities residents of the Netherlands must observe "in order to be exempt from, or obtain a refund of, the Mexican withholding taxes on dividends, interest and royalties."[231] In 2008 Mexico and the Netherlands modified their existing tax treaty, initially signed in 1993 to strength cooperation to curb tax evasion.[232][233]
| |
See Netherlands–Peru relations
| ||
| 1975-25-11 | See Netherlands–Suriname relations
| |
| 19 April 1782 | See Netherlands–United States relations
Both countries established diplomatic relations on 19 April 1782[238] The bilateral relations between the two nations are based on historical and cultural ties as well as a common dedication to individual freedom and human rights. The Netherlands shares with the United States a liberal economic outlook and is committed to free trade. The Netherlands is the third-largest direct foreign investor in the United States,[239] and Dutch holding companies employ more than 650,000 Americans.[240] The United States is the third-largest direct foreign investor in the Netherlands. The United States and the Netherlands often have similar positions on issues and work together both bilaterally and multilaterally in such institutions as the United Nations and NATO. The Dutch have worked with the United States at the World Trade Organization, in the Organisation for Economic Co-operation and Development, as well as within the European Union to advance the shared U.S. goal of a more open and market-led global economy. The United States and the Netherlands joined NATO as charter members in 1949. The Dutch were allies with the United States in the Korean War and the first Gulf War and have been active in global peacekeeping efforts in the former Yugoslavia, Afghanistan and Iraq. Netherlands also support and participate in NATO and EU training efforts in Iraq. They are active participants in the International Security Assistance Force and Operation Enduring Freedom in Afghanistan.
| |
| 15 April 1896 | See Netherlands–Uruguay relations
Both countries established diplomatic relations on 15 April 1896[47][243] | |
See Netherlands–Venezuela relations
|
Asia
| Country | Formal relations began | Notes |
|---|---|---|
| 2 August 1956 | Both countries established diplomatic relations on 2 August 1956 when first Envoy of Afgnanistan Dr. Sardir Najib-Ullah Khan presented his credentials to Queen of the Netherlands.[90] | |
| 30 January 1992 | See Armenia–Netherlands relations
Both countries established diplomatic relations on 30 January 1992.[248]
| |
| 1 April 1992 | See Azerbaijan–Netherlands relations
Both countries established diplomatic relations on 1 April 1992.[252]
| |
| 1971-01-04 | See Bangladesh–Netherlands relations
| |
| 10 June 1985 | See Foreign relations of Bhutan
Both countries established diplomatic relations on 10 June 1985[253]
| |
| 18 May 1972[254] | See China–Netherlands relations | |
| 22 April 1992 | See Georgia–Netherlands relations
Both countries established diplomatic relations on 22 April 1992.[255] | |
| 17 April 1947 | See India–Netherlands relations
Both countries established diplomatic relations on 17 April 1947[256] | |
| See Indonesia–Netherlands relations | ||
| 5 January 1883 | See Iran–Netherlands relations
Both countries established diplomatic relations on 5 January 1883 when Mirza Jawad Khan, Persian Minister in Belgium, was also accredited to the Netherlands.[259][260]
| |
| 10 May 1935 | See Iraq–Netherlands relations
Both countries established diplomatic relations on 10 May 1935 when has been accredited Chargé d'Affaires of Netherlands to Jeddah (Saudi Arabia) C. Adriaanse also to Iraq.[68] | |
| 1949 | See Israel–Netherlands relations
In 1947, the Netherlands voted in favor of the United Nations Resolution 181. Both countries established diplomatic relations in 1949.[261] | |
| 1609 | See Japan–Netherlands relations
Relations between Japan and the Netherlands date back to 1609, when the first formal trade relations were established.[264][265] The relations between Japan and the Netherlands after 1945 have been a triangular relationship. The invasion and occupation of the Netherlands East Indies during World War II, brought about the destruction of the colonial state in Indonesia, as the Japanese removed as much of the Dutch government as they could, weakening the post war grip the Netherlands had over the territory. Under pressure from the United States, the Netherlands recognised Indonesian sovereignty in 1949 (see United States of Indonesia). | |
| 10 September 1992 | See Kazakhstan–Netherlands relations
Both countries established diplomatic relations on 10 September 1992.[266] The Netherlands is Kazakhstan's largest foreign investor and the second largest European Union partner in terms of foreign trade turnover with Kazakhstan.[267]
| |
| ||
| 31 August 1957 | See Malaysia–Netherlands relations
Both countries established diplomatic relations on 31 August 1957.[268]  The Dutch involvement in the Malay Peninsula used to be much more extensive than it is now. The Dutch established relations with the Sultanate of Johor in the early 17th century, and in 1641 they captured the Portuguese colony of Malacca (on the south-eastern coast of today's Peninsular Malaysia). With a long interruption during the Napoleonic Wars, the Dutch Malacca era lasted until 1824. In the 20th century, the Netherlands established diplomatic relations with Malaysia soon after the Asian state became independent. The erudite Dutch Sinologist and author Robert van Gulik (who was raised in the former Dutch East Indies himself) served as the ambassador of the Netherlands in Kuala Lumpur in the early 1960s. During his diplomatic service there he became closely acquainted with Malaysia's gibbons (he kept a few in his ambassadorial residence) and became sufficiently interested in this ape species to start the study of its role in ancient Chinese culture, the results of which he later published in his last book (Gibbon in China).[269]
| |
See Foreign relations of Oman
| ||
| 1947-15-8 | See Netherlands–Pakistan relations | |
| 20 May 1947 | See Netherlands–Philippines relations
Both countries established diplomatic relations on 20 May 1947.[270]
| |
| 9 June 1930 | See Netherlands–Saudi Arabia relations
Both countries established diplomatic relations on 9 June 1930 when first the Netherlands Chargé d'Affaires, M. Van de Meulen, presented letters of credence to King Ibn Saud.[67]
| |
| 7 December 1965 | See Netherlands–Singapore relations
Both countries established diplomatic relations on 7 December 1965.[271]
| |
| 1961-01-04[272] |
The establishment of diplomatic relations between the Republic of Korea and the Kingdom of the Netherlands began on April 1, 1961.
| |
| 24 January 1952 | See Netherlands–Syria relations | |
| See Netherlands–Taiwan relations | ||
| 1612 | See Netherlands–Turkey relations
| |
| ||
|
Europe
| Country | Formal relations began | Notes |
|---|---|---|
| 17 November 1970 | See Albania–Netherlands relations
Both countries established diplomatic relations on 17 November 1970[129] | |
| See Austria–Netherlands relations | ||
| 24 March 1992 | See Belarus–Netherlands relations
Both countries established diplomatic relations on 24 March 1992[282]
| |
| 3 August 1839 | See Belgium–Netherlands relations
Both countries established diplomatic relations on 3 August 1839.[31] Relations were established after the independence of Belgium. Both nations are allies and have cultural similarities. | |
| 15 December 1992 | See Bosnia and Herzegovina–Netherlands relations
Both countries established diplomatic relations on 15 December 1992[285]
| |
| See Bulgaria–Netherlands relations | ||
| 11 February 1992 | See Croatia–Netherlands relations
Both countries established diplomatic relations on 11 February 1992.[288]
| |
See Cyprus–Netherlands relations
| ||
| 13 November 1919 | See Czech Republic–Netherlands relations
Both countries established diplomatic relations on 13 November 1919[289]
| |
See Denmark – Netherlands relations
| ||
| 14 August 1918 | See Finland–Netherlands relations
Both countries established diplomatic relations on 14 August 1918[292]
| |
See France–Netherlands relations
| ||
| 1871 | See Germany–Netherlands relations
| |
See Greece–Netherlands relations
| ||
See Hungary–Netherlands relations
| ||
| 9 January 1946 | See Iceland–Netherlands relations
Both countries established diplomatic relations on 9 January 1946[297] | |
See Ireland–Netherlands relations
| ||
| 24 September 1991 | Both countries established diplomatic relations on 24 September 1991.[302]
| |
| 3 December 1991 | Both countries established diplomatic relations on 3 December 1991.[303]
| |
| ||
| ||
| 10 July 1992 | See Moldova–Netherlands relations
Both countries established diplomatic relations on 10 July 1992[304]
| |
| 4 July 1919 | See Netherlands–Poland relations
Both countries established diplomatic relations on 4 July 1919[305]
| |
See Netherlands–Portugal relations
| ||
| 12 February 1880 | See Netherlands–Romania relations
Both countries established diplomatic relations on 12 February 1880[306]
| |
| See Netherlands–Russia relations
Both countries were establishment of diplomatic relations in 1991 after the fall of the Soviet Union. Peter the Great studied in Holland. During the Cold War, all the Dutch consecutive governments perceived the Warsaw pact including the Soviet Union and Russia as a threat to its safety.
| ||
| 1899-04-26 | ||
| 1993-01-01 | See Netherlands–Slovakia relations
| |
| 1991-06-25 | See Netherlands–Slovenia relations | |
See Netherlands–Spain relations
| ||
See Netherlands–Sweden relations
| ||
| ||
| 1 April 1992 | See Netherlands–Ukraine relations
Both countries established diplomatic relations on 1 April 1992[312] | |
| 1 April 1603 | See Netherlands–United Kingdom relations
The UK established diplomatic relations with the United Kingdom on 1 April 1603.[17][failed verification]
Both countries share common membership of the Atlantic co-operation pact,[315] Council of Europe, NATO, OECD, OSCE, and the World Trade Organization. |
Oceania
| Country | Formal relations began | Notes |
|---|---|---|
| 31 January 1942 | See Australia–Netherlands relations
Both countries established diplomatic relations on 31 January 1942.[316] | |
| 19 June 1947 | See Netherlands–New Zealand relations
Both countries established diplomatic relations on 19 June 1947.[317]
| |
| 1 February 1982 | Both countries established diplomatic relations on 1 February 1982[318] | |
See also
Notes
Further reading
Wikiwand - on
Seamless Wikipedia browsing. On steroids.
