Top Qs
Timeline
Chat
Perspective
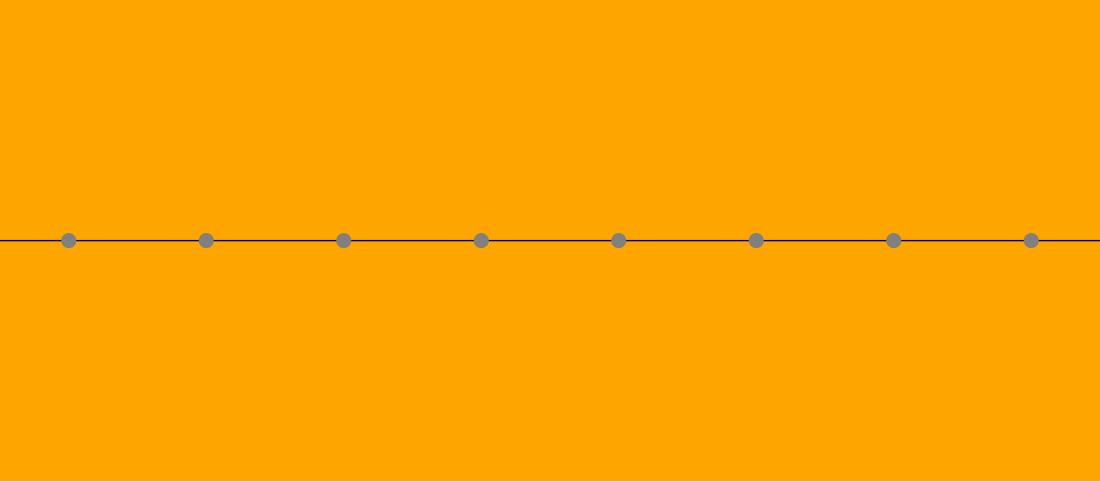
Order-2 apeirogonal tiling
Plane tiling with two infinite-sided polygons From Wikipedia, the free encyclopedia
Remove ads
Remove ads
In geometry, an order-2 apeirogonal tiling, apeirogonal dihedron, or infinite dihedron[1] is a tessellation (gap-free filling with repeated shapes) of the plane consisting of two apeirogons. It may be considered an improper regular tiling of the Euclidean plane, with Schläfli symbol {∞, 2}. Two apeirogons joined along all their edges can completely fill the entire plane, as an apeirogon is infinite in size and has an interior angle of 180°, which is half of a full 360°.
This article relies largely or entirely on a single source. (May 2024) |
Remove ads
Related tilings and polyhedra
Similarly to the uniform polyhedra and the uniform tilings, eight uniform tilings may be based from the regular apeirogonal tiling. The rectified and cantellated forms are duplicated, and as two times infinity is also infinity, the truncated and omnitruncated forms are also duplicated, therefore reducing the number of unique forms to four: the apeirogonal tiling, the apeirogonal hosohedron, the apeirogonal prism, and the apeirogonal antiprism.
Remove ads
See also
- Order-3 apeirogonal tiling - hyperbolic tiling
- Order-4 apeirogonal tiling - hyperbolic tiling
Notes
References
External links
Wikiwand - on
Seamless Wikipedia browsing. On steroids.
Remove ads