Population growth
Increase in the number of individuals in a population From Wikipedia, the free encyclopedia
Population growth is the increase in the number of people in a population or dispersed group. The global population has grown from 1 billion in 1800 to 8.2 billion in 2025.[3] Actual global human population growth amounts to around 70 million annually, or 0.85% per year. As of 2024, The United Nations projects that global population will peak in the mid-2080s at around 10.3 billion. The UN's estimates have decreased strongly in recent years due to sharp declines in global birth rates.[4] Others have challenged many recent population projections as having underestimated population growth.[5]


The world human population has been growing since the end of the Black Death, around the year 1350.[6] A mix of technological advancement that improved agricultural productivity[7] and sanitation and medical advancement that reduced mortality increased population growth. In some geographies, this has slowed through the process called the demographic transition, where many nations with high standards of living have seen a significant slowing of population growth. This is in direct contrast with less developed contexts, where population growth is still happening.[8] Globally, the rate of population growth has declined from a peak of 2.2% per year in 1963.[9]
Population growth alongside increased consumption is a driver of environmental concerns, such as biodiversity loss and climate change,[10][11] due to overexploitation of natural resources for human development.[12] International policy focused on mitigating the impact of human population growth is concentrated in the Sustainable Development Goals which seeks to improve the standard of living globally while reducing the impact of society on the environment while advancing human well-being.[citation needed]
| Years passed |
Year | Pop. (billions) |
|---|---|---|
| – | 1800 | 1 |
| 127 | 1927 | 2 |
| 33 | 1960 | 3 |
| 14 | 1974 | 4 |
| 13 | 1987 | 5 |
| 12 | 1999 | 6 |
| 12 | 2011 | 7 |
| 11 | 2022 | 8 |
| 12 | 2035* | 9 |
| 20 | 2055* | 10 |
| 35 | 2088* | 11 |
| *World Population Prospects 2017 (United Nations Population Division) | ||
History
Summarize
Perspective


World population has been rising continuously since the end of the Black Death, around the year 1350.[6] Population began growing rapidly in the Western world during the industrial revolution. The most significant increase in the world's population has been since the 1950s, mainly due to medical advancements[14] and increases in agricultural productivity.[15][16]
Haber process
Due to its dramatic impact on the human ability to grow food, the Haber process, named after one of its inventors, the German chemist Fritz Haber, served as the "detonator of the population explosion", enabling the global population to increase from 1.6 billion in 1900 to 7.7 billion by November 2019.[17]
Thomas McKeown hypotheses
Some of the reasons for the "Modern Rise of Population"[18] were particularly investigated by the British health scientist Thomas McKeown (1912–1988). In his publications, McKeown challenged four theories about the population growth:
- McKeown stated that the growth in Western population, particularly surging in the 19th century, was not so much caused by an increase in fertility, but largely by a decline of mortality particularly of childhood mortality followed by infant mortality,[19][20]
- The decline of mortality could largely be attributed to rising standards of living, whereby McKeown put most emphasis on improved nutritional status,
- McKeown questioned the effectiveness of public health measures, including sanitary reforms, vaccination and quarantine,[21]
- The “McKeown thesis" states that curative medicine measures played little role in mortality decline, not only prior to the mid-20th century[19] but also until well into the 20th century.[22]
Although the McKeown thesis has been heavily disputed, recent studies have confirmed the value of his ideas.[23] His work is pivotal for present day thinking about population growth, birth control, public health and medical care. McKeown had a major influence on many population researchers, such as health economists and Nobel prize winners Robert W. Fogel (1993) and Angus Deaton (2015). The latter considered McKeown as "the founder of social medicine".[24]
Growth rate models
Summarize
Perspective
The "population growth rate" is the rate at which the number of individuals in a population increases in a given time period, expressed as a fraction of the initial population. Specifically, population growth rate refers to the change in population over a unit time period, often expressed as a percentage of the number of individuals in the population at the beginning of that period. This can be written as the formula, valid for a sufficiently small time interval:
A positive growth rate indicates that the population is increasing, while a negative growth rate indicates that the population is decreasing. A growth ratio of zero indicates that there were the same number of individuals at the beginning and end of the period—a growth rate may be zero even when there are significant changes in the birth rates, death rates, immigration rates, and age distribution between the two times.[25]
A related measure is the net reproduction rate. In the absence of migration, a net reproduction rate of more than 1 indicates that the population of females is increasing, while a net reproduction rate less than one (sub-replacement fertility) indicates that the population of females is decreasing.
Most populations do not grow exponentially, rather they follow a logistic model. Once the population has reached its carrying capacity, it will stabilize and the exponential curve will level off towards the carrying capacity, which is usually when a population has depleted most its natural resources.[26] In the world human population, growth may be said to have been following a linear trend throughout the last few decades.[9]

Logistic equation
The growth of a population can often be modelled by the logistic equation[27]
where
- = the population after time t;
- = time a population grows;
- = the relative growth rate coefficient;
- = the carrying capacity of the population; defined by ecologists as the maximum population size that a particular environment can sustain.[26]
As it is a separable differential equation, the population may be solved explicitly, producing a logistic function:
- ,
where and is the initial population at time 0.
Global population growth rate
Summarize
Perspective
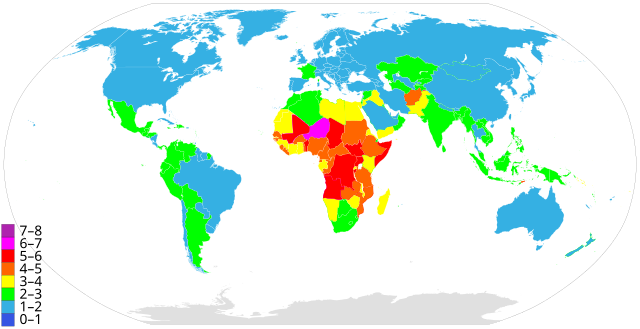
|
6–7 children
5–6 children
4–5 children |
3–4 children
2–3 children
1–2 children
|
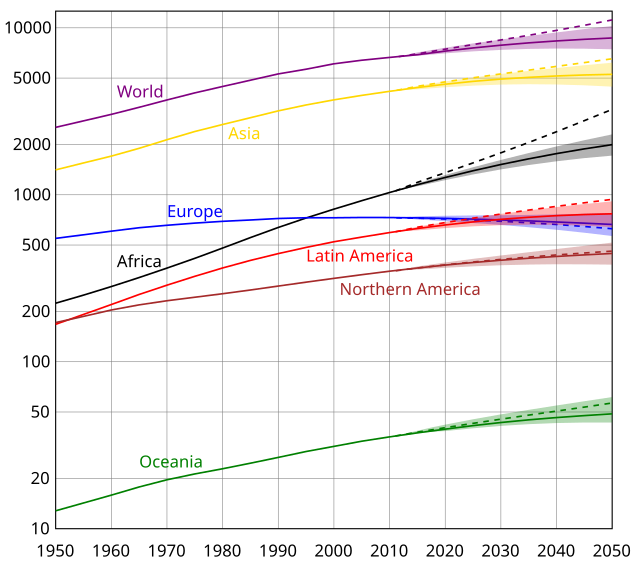

The world population growth rate peaked in 1963 at 2.2% per year and subsequently declined.[9] In 2017, the estimated annual growth rate was 1.1%.[28] The CIA World Factbook gives the world annual birthrate, mortality rate, and growth rate as 1.86%, 0.78%, and 1.08% respectively.[29] The last 100 years have seen a massive fourfold increase in the population, due to medical advances, lower mortality rates, and an increase in agricultural productivity made possible by the Green Revolution.[30]
The annual increase in the number of living humans peaked at 88.0 million in 1989, then slowly declined to 73.9 million in 2003, after which it rose again to 75.2 million in 2006. In 2017, the human population increased by 83 million.[28] Generally, developed nations have seen a decline in their growth rates in recent decades, though annual growth rates remain above 2% in some countries of the Middle East and Sub-Saharan Africa, and also in South Asia, Southeast Asia, and Latin America.[31]
In some countries the population is declining, especially in Eastern Europe, mainly due to low fertility rates, high death rates and emigration. In Southern Africa, growth is slowing due to the high number of AIDS-related deaths. Some Western Europe countries might also experience population decline.[32] Japan's population began decreasing in 2005.[33]
The United Nations Population Division projects world population to reach 11.2 billion by the end of the 21st century. The Institute for Health Metrics and Evaluation projects that the global population will peak in 2064 at 9.73 billion and decline to 8.89 billion in 2100. [34] A 2014 study in Science concludes that the global population will reach 11 billion by 2100, with a 70% chance of continued growth into the 22nd century.[35][36] The German Foundation for World Population reported in December 2019 that the global human population grows by 2.6 people every second, and could reach 8 billion by 2023.[37][38]
Growth by country
Summarize
Perspective

According to United Nations population statistics, the world population grew by 30%, or 1.6 billion humans, between 1990 and 2010.[39] In number of people the increase was highest in India (350 million) and China (196 million). Population growth rate was among highest in the United Arab Emirates (315%) and Qatar (271%).[39]
| Rank | Country | Population | Annual Growth (%) | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1990 | 2010 | 2020 (est.)[40] | 1990–2010 | 2010–2020 | ||
| World | 5,306,425,000 | 6,895,889,000 | 7,503,828,180 | 1.3% | 0.8% | |
| 1 | 1,139,060,000 | 1,341,335,000 | 1,384,688,986 | 0.8% | 0.3% | |
| 2 | 873,785,000 | 1,224,614,000 | 1,333,000,000 | 1.7% | 0.9% | |
| 3 | 253,339,000 | 310,384,000 | 329,256,465 | 1.0% | 0.6% | |
| 4 | 184,346,000 | 239,871,000 | 262,787,403 | 1.3% | 0.9% | |
| 5 | 149,650,000 | 194,946,000 | 208,846,892 | 1.3% | 0.7% | |
| 6 | 111,845,000 | 173,593,000 | 207,862,518 | 2.2% | 1.8% | |
| 7 | 97,552,000 | 158,423,000 | 203,452,505 | 2.5% | 2.5% | |
| 8 | 105,256,000 | 148,692,000 | 159,453,001 | 1.7% | 0.7% | |
| 9 | 148,244,000 | 142,958,000 | 142,122,776 | -0.2% | −0.1% | |
| 10 | 122,251,000 | 128,057,000 | 126,168,156 | 0.2% | −0.1% | |
Many of the world's countries, including many in Sub-Saharan Africa, the Middle East, South Asia and South East Asia, have seen a sharp rise in population since the end of the Cold War. The fear is that high population numbers are putting further strain on natural resources, food supplies, fuel supplies, employment, housing, etc. in some of the less fortunate countries. For example, the population of Chad has ultimately grown from 6,279,921 in 1993 to 10,329,208 in 2009,[41] further straining its resources. Vietnam, Mexico, Nigeria, Egypt, Ethiopia, and the DRC are witnessing a similar growth in population.
The following table gives some example countries or territories:
| Country/territory | Life expectancy in years (2008) |
Total population growth from 1960s to 2007–2011 | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1967 | 1990 | 1994 | 2002 | 2008 | |||
| N/A* | N/A* | 3,437,000[42] | 4,298,269 | 5,673,520[43] | 61[44] | 2,236,520 | |
| 23,457,000*[45] | 50,974,000* [46] | 54,939,000[42] | 67,673,031(2003) | 79,221,000[47] | 55[44] | 55,764,000 | |
| 14,355,000†[45] | 25,204,000† [46] | 27,361,000†[42] | 38,114,160 (2003)† | 42,272,000†[43] | 50†[44] | 27,917,000 | |
| 3,410,000[45] | 5,679,000[46] | 6,183,000[42] | 9,253,493(2003) | 10,329,208 (2009)[41] | 47[44] | 6,919,205 | |
| 3,546,000[45] | 7,732,000[46] | 8,846,000[42] | 10,790,352 (2001) | 15,306,252 (2009)[48] | 44[44] | 11,760,252 | |
| 61,450,000[45] | 88,500,000[46] | 108,467,000[42] | 129,934,911 | 158,259,000[43] | 47[44] | 96,809,000 | |
| 4,745,000[45] | 8,156,000[46] | 10,462,000[42] | 11,340,480 | 14,517,176(2010)[49] | 50[44] | 9,772,176 | |
| 1,050,000[45] | 2,025,000 [46] | 2,211,000[42] | 2,667,859 (2003) | 3,291,000 (2009)[41] | 54[44] | 2,241,000 | |
| 3,607,000[45] | 7,327,000[46] | 8,102,000[42] | 9,967,215 | 13,711,597 (2009)[50] | 57[44] | 10,104,597 | |
| 343,000[45] | 861,000[46] | 1,081,000[42] | 1,367,124 (2000) | 1,705,000[43] | 55[44] | 1,362,000 | |
| 11,833,126 [45] | 25,012,000[46] | 27,325,000 [42] | 32,818,500 (2003) | 34,895,000[47][51] | 74[44] | 23,061,874 | |
| 16,353,000[45] | 35,562,000[46] | 42,552,000[42] | 55,225,478 (2003) | 70,916,439 [47][52] | 54[44] | 54,563,439 | |
| 30,083,419 [45] | 53,153,000[46] | 58,326,000[42] | 70,712,345 (2003) | 79,089,650 [47][53] | 72[44] | 49,006,231 | |
(overseas region of France) | 418,000[45] | N/A[46] | N/A[42] | 720,934 (2003) | 827,000 (2009) [43] | N/A[44] | 409,000 |
(British Overseas Territory) | 2,500[45] | N/A[46] | N/A[42] | 2,967 (2003) | 3,140(2010)[54] | N/A[44] | 640 |
| 8,935,500[45] | 13,173,000[46] | 13,994,000[42] | 15,116,435 | 17,224,200 (2011) | 77[44] | 8,288,700 | |
| 19,191,000[45] | 32,987,000[46] | 34,520,000[42] | 41,088,227 | 45,925,397 (2010)[55] | 73[44] | 26,734,397 | |
| 85,655,000[45] | 150,368,000[46] | 153,725,000[42] | 174,468,575 (2000) | 190,732,694 (2010) [56] | 72[44] | 105,077,694 | |
| 45,671,000[45] | 86,154,000[46] | 93,008,000[42] | 103,400,165 (2000) | 112,322,757 (2010)[57] | 76[44] | 66,651,757 | |
| 476,727 (1966)[45] | 765,000[46] | 771,000[42] | 844,330 (2001) | 849,000[51] (2010) | 70[44] | 372,273 | |
| 6,050 [45] | 10,000[46] | N/A[42] | 12,329 | 9,322 (2011)[58] | N/A[44] | 3,272 | |
| 1,876,000[45] | 2,420,000[46] | 2,429,000[42] | 2,695,867 (2003) | 2,847,232[59](2010) | 74[44] | 971,232 | |
| 11,540,764 [45] | 17,086,000[46] | 17,843,000[42] | 19,546,792 (2003) | 27,127,685[60] (2010) | 82[44] | 10,066,508 | |
| 1,965,500 (1964)[45] | 3,250,000[46] | 3,414,000[42] | 3,510,484 | 2,986,952 (July 2010 est.)[41][61] | 78[44] | 1,021,452 | |
| 31,944,000[45] | 38,180,000[46] | 38,554,000[42] | 38,626,349 (2001) | 38,192,000 (2010)[62] | 75[44] | 6,248,000 | |
| 10,212,000[45] | 10,553,000[46] | 10,261,000[42] | 10,106,017 | 9,979,000 (2010)[63] | 73[44] | -142,000 | |
| 8,226,564 (1965)[45] | 8,980,000[46] | 8,443,000[42] | 7,707,495(2000) | 7,351,234 (2011)[64] | 73[44] | -875,330 | |
| 55,068,000 (1966)[45] | 57,411,000[46] | 58,091,000[42] | 58,789,194 | 62,008,048 (2010)[65] | 79[44] | 7,020,048 | |
| 2,884,002 (1966)[45] | 3,503,000[46] | 3,571,000[42] | 3,840,838 (2000) | 4,470,700[66] (2010) | 78[44] | 1,586,698 | |
| 720,000,000[45] | 1,139,060,000[46] | 1,208,841,000[42] | 1,286,975,468 (2004) | 1,339,724,852 (2010)[67] | 73[44] | 619,724,852 | |
| 98,274,961 (1965)[45] | 123,537,000[46] | 124,961,000[42] | 127,333,002 | 127,420,000 (2010)[68] | 82[44] | 28,123,865 | |
| 511,115,000[45] | 843,931,000[46] | 918,570,000[42] | 1,028,610,328 (2001) | 1,210,193,422 (2011)[69] | 69[44] | 699,078,422 | |
| 1,956,000 (1967)[45] | 3,003,000 (1990) [46] | 2,930,000 (1994)[42] | 4,452,732 (2002) | 5,076,700 (2010)[70] | 82 (2008)[44] | 3,120,700 | |
| 24,000 (1967)[45] | 29,000 (1990) [46] | N/A (1994)[42] | 31,842 (2000) | 35,586[71] (2010) | (2008)[44] | 11,586 | |
| 8,716,000 (1967)[45] | 10,123,000 (1990) [46] | 10,426,000 (1994)[42] | 10,964,020 (2001)[72] | 11,305,118 (2011)[73] | N/A (2008)[44] | 2,589,118 | |
(Danish dependency) | 38,000 (1967)[45] | N/A (1990) [46] | N/A (1994)[42] | 46,345 (2000) | 48,917 (2010) [74] | N/A (2008)[44] | 18,917 |
| 20,000 (1967)[45] | 29,000 (1990) [46] | N/A (1994)[42] | 33,307 (2000) | 35,789 (2009)[75] | (2008)[44] | 15,789 | |
| 29,207,856 (1966)[45] | 42,793,000 (1990) [46] | 44,453,000 (1994)[42] | 48,324,000 (2003) | 48,875,000 (2010) [76] | (2008)[44] | 19,667,144 | |
| 12,700,000 (1967)[45] | 21,773,000 (1990) [46] | 23,483,000 (1994)[42] | 22,224,195 (2002) | 24,051,218 (2010)[77] | (2008)[44] | 11,351,218 | |
| 107,200 (1967)[45] | 266,000 (1990) [46] | 280,000 (1994)[42] | 332,844 (2001) | 401,890 (2011)[78] | 76 (2008)[44] | 306,609 | |
| 10,671,000 (1967)[45] | 17,861,000 (1990) [46] | 19,489,000 (1994)[42] | 21,793,293 (2002) | 27,565,821 (2010)[79] | (2008)[44] | 16,894,821 | |
| 32,680,000 (1967)[45] | 57,196,000 (1990) [46] | 59,396,000 (1994)[42] | 60,606,947 (2000)[80] | 63,878,267 (2011)[81] | (2008)[44] | 31,198,267 | |
| 2,520,000 (1967)[45] | 2,701,000 (1990) [46] | 2,915,000 (1994)[42] | 3,727,703[82] (2003) | 4,224,000[43] (2009) | - (2008)[44] | ||
| 5,600,000 (1967)[45] | 12,116,000 (1990) [46] | 13,844,000 (1994)[42] | 17,585,540 (2003) | 22,457,763 (2011)[83] | -(2008)[44] | ||
| 182,00 (1967)[45] | 503,000 (1990) [46] | 549,000 (1994)[42] | 667,238 (2003) | 1,234,596[84] (2010) | 75 (2008)[44] | ||
| 11,741,000 (1967)[45] | 16,993,000 (1990) [46] | 17,685,000 (1994)[42] | 19,607,519 (2002) | 20,238,000[51] (2009) | - (2008)[44] | ||
| 6,050,000 (1967)[45] | 6.712,000 (1990) [46] | 6,994,000 (1994)[42] | 7,261,200 (2002) | 7,866,500[85] (2010) | - (2008)[44] | ||
| 335,000 (1967)[45] | 381,000 (1990) [46] | 401,000 (1994)[42] | 439,539 (2001) | 511,840 (2011)[86] | - (2008)[44] | ||
| 19,105,056 (1966)[45] | 23,200,000 (1990)[46] | 22,736,000 (1994)[42] | 21,680,974 (2002) | 21,466,174[87] (2011) | - (2008)[44] | ||
(associated state of New Zealand) | 1,900 (1966)[45] | N/A (1990)[46] | N/A (1994)[42] | 2,134 (2002) | 1,398 (2009)[88] | N/A (2008)[44] | -502 |
(New Zealand territory) | 5,194 (1966)[45] | N/A (1990)[46] | N/A (1994)[42] | 1,445 (2001) | 1,416 (2009) | N/A (2008)[44] | -3,778 |
| 1,876,000 (1967)[45] | 2,420,000 (1990) [46] | 2,429,000 (1994)[42] | 2,695,867 (2003) | 2,847,232[59] (2010) | 74 (2008)[44] | 971,232 | |
| 32,031,000 (1967)[45] | 32,322,000 (1990)[46] | 34,180,000 (1994)[42] | 37,812,817 (2002) | 40,091,359 (2010) | 74 (2008)[44] | 8,060,359 | |
| 49,890,660 (1967)[45] | 56,440,000 (1990)[46] | 57,747,000 (1994)[42] | 59,551,000 (2001) | 63,136,180 (2011)[89] | 81 (2008)[44] | ||
| 52,334,000 (1967)[45] | 57,662,000 (1990)[46] | 57,193,000 (1994)[42] | 56,995,744 (2002) | 60,605,053[90] (2011) | 80 (2008)[44] | ||
| 774,000 (1967)[45] | 1,075,000 (1990)[46] | 1,104,000 (1994)[42] | 1,179,137 (2000) | 1,288,000 (2009)[51] | 75 (2008)[44] | 514,000 | |
| 4,717,000 (1967)[45] | 9,197,000 (1990)[46] | 10,322,000 (1994)[42] | 12,974,361 (2000) | 13,276,517 (2009) | 70 (2008)[44] | 8,559,517 | |
| 8,033,000 (1967)[45] | 10,609,000 (1990)[46] | 10,960,000 (1994)[42] | 11,177,743 (2002) | 11,239,363 (2009)[91] | 77 (2008)[44] | ||
| 246,000 (1967)[45] | 255,000 (1990) [46] | 261,000 (1994)[42] | 250,012 (2001) | 284,589 (2010)[41] | 73 (2008)[44] | 18,589 | |
| 131,377 (1967)[45] | 164,000 (1990) [46] | 164,000 (1994)[42] | 178,173 (2003) | 179,000 (2009)[43] | N/A (2008)[44] | ||
| 7,765,981 (1967)[45] | 8,559,000 (1990) [46] | 8,794,000 (1994)[42] | 8,920,705 (2002) | 9,354,462 (2009) | 81 (2008)[44] | ||
| 4,664,000 (1967)[45] | 4,986,000 (1990) [46] | 5,095,000 (1994)[42] | 5,175,783 (2002) | 5,374,781 (2010) | N/A (2008)[44] | ||
| 9,440,000 (1967)[45] | 10,525,000 (1990)[46] | 9,830,000 (1994)[42] | 10,355,824 (2001) | 10,647,763[92] (2011) | N/A (2008)[44] | ||
| 7,323,981 (1967)[45] | 7,712,000 (1990) [46] | 8,031,000 (1994)[42] | 8,032,926 (2001) | 8,404,252 (2011) | N/A (2008)[44] | ||
| 1,738,000 (1967)[45] | 4,545,000 (1990)[46] | 5,225,000(1994)[42] | 5,499,074 (2002) | 6,420,000 (2009)[43] | 77 (2008)[44] | ||
| 12,385,000 (1967)[45] | 21,550,000 (1990)[46] | 23,080,000(1994)[42] | 27,949,639 (2002) | 29,496,000 (2010) | 70 (2008)[44] | ||
| 528,000 (1967)[45] | 965,000 (1990) [46] | 1,050,000 (1994)[42] | 1,345,479 (2002) | 1,647,000[43] (2009) | 48 (2008)[44] | ||
| 5,203,066 (1967)[45] | 10,020,000 (1990)[46] | 10,674,000 (1994)[42] | 10,766,500 (2003) | 18,498,000[51][93] (2009) | 38 (2008)[44] | ||
| 277,000 (1967)[45] | 348,000 (1990)[46] | 389,000 (1994)[42] | 474,214 (2000) | 676,000 (2009)[51] | 61 (2008)[44] | ||
| 2,505,000 (1967)[45] | 4,736,000 (1990)[46] | 5,246,000 (1994)[42] | 8,500,500 (2002) | 8,791,832 (2009) | 59 (2008)[44] | ||
| 2,770,000 (1967)[45] | 4,139,000 (1990)[46] | 4,742,000 (1994)[42] | 5,635,967 (2002) | 6,800,000[94] (2011) | 56 (2008)[44] | ||
| 10,500,000 (1967)[45] | 18,961,000 (1990)[46] | 21,360,000 (1994)[42] | 25,284,463 (2002) | 29,331,000[51] (2009) | - (2008)[44] | ||
| 25,781,090 (1966)[45] | 54,608,000 (1990)[46] | 59,778,000 (1994)[42] | 66,622,704 (2002) | 75,330,000 (2010)[95] | 71 (2008)[44] | 49,548,910 | |
| 20,014,880 (1966)[45] | 26,603,000 (1990)[46] | 29,248,000(1994)[42] | 31,081,900 (2001) | 32,623,490 (2011)[96] | 81 (2008)[44] | ||
| 199,118,000 (1967)[45] | 249,995,000 (1990)[46] | 260,650,00(1994)[42] | 281,421,906 (2000) | 308,745,538 (2010)[97] | 78 (2008)[44] | ||
| 7,931,000 (1967)[45] | 18,795,000 (1990)[46] | 20,621,000 (1994)[42] | 24,227,297 (2002) | 32,369,558 (2009) | 52 (2008)[44] |
- Notes
- * Eritrea left Ethiopia in 1991.
- † Split into the nations of Sudan and South Sudan during 2011.
- ‡ Japan and the Ryukyu Islands merged in 1972.
- # India and Sikkim merged in 1975.
| Population growth 1990–2012 (%)[98] | |
|---|---|
| Africa | 73.3% |
| Middle East | 68.2% |
| Asia (excl. China) | 42.8% |
| China | 19.0% |
| OECD Americas | 27.9% |
| Non-OECD Americas | 36.6% |
| OECD Europe | 11.5% |
| OECD Asia Oceania | 11.1% |
| Non-OECD Europe and Eurasia | -0.8% |
Future population
Human population projections are attempts to extrapolate how human populations will change in the future.[99] These projections are an important input to forecasts of the population's impact on this planet and humanity's future well-being.[100] Models of population growth take trends in human development and apply projections into the future.[101] These models use trend-based-assumptions about how populations will respond to economic, social and technological forces to understand how they will affect fertility and mortality, and thus population growth.[101]
See also
References
External links
Wikiwand - on
Seamless Wikipedia browsing. On steroids.









