Top Qs
Timeline
Chat
Perspective
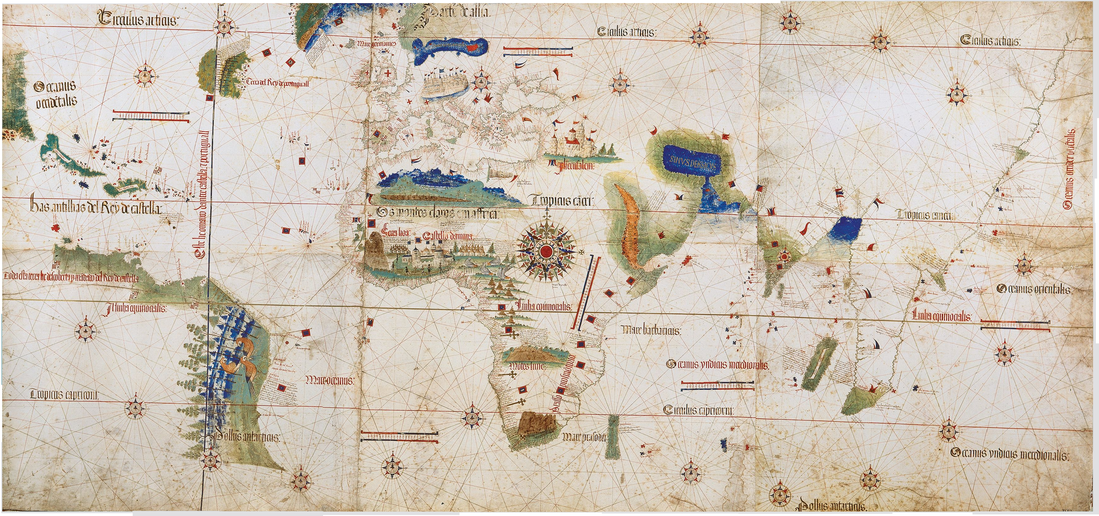
Evolution of the Portuguese Empire
Overview of the possessions of the Portuguese Empire From Wikipedia, the free encyclopedia
Remove ads
This article is a comprehensive list of all possessions of the Portuguese Empire.[1][2][3][4]

Europe
Portuguese founded factories in various places in Europe, with a purely commerce-focused strategy, different from the other continents.
Africa
Summarize
Perspective
Portuguese presence in Africa started in 1415 with the conquest of Ceuta and is generally viewed as ending in 1975, with the independence of its later colonies, although the present autonomous region of Madeira is located in the African Plate, some 650 km (360 mi) off the North African coast, Madeira belongs and has always belonged ethnically, culturally, economically and politically to Europe, some 955 km (583 mi) from the European mainland.[8]
- Angola/Portuguese West Africa: colony (1575–1589); crown colony (1589–1951); overseas province (1951–1971); state (1971–1975). Independence in 1975.
- Santo António do Zaire/Soyo (1482–1670): Main economic center between the Portuguese and the Kongo Kingdom. Portuguese driven out in 1670.
- Cabinda: protectorate (1883–1887); Congo district (1887–1921); intendancy subordinate to Maquela (1921–1922); dependency of Zaire district (1922–1930); Intendacy of Zaire and Cabinda (1930–1932); intendancy under Portuguese Angola (1932–1934); dependency under Angola (1934–1945); restored as District (1946–1975). Controlled by Frente Nacional para a Libertação de Angola (National Liberation Front of Angola) as part of independent Angola in 1975. Declared Cabinda a republic in 1975, but not recognized by Portugal nor Angola.
- Arguin/Arguim: (1455–1633)
- Cabo Verde/Cape Verde: settlements (1462–1495); dominion of crown colonies (1495–1587); crown colony (1587–1951); overseas province (1951–1974); autonomous republic (1974–1975). Independence in 1975.

- Benin (1485–1897): Factory. City destroyed by the British in 1897.[citation needed]
- Boma: Factory.[citation needed]
- Fort Mocusso (1909–1912): Military fort constructed in German South-West Africa. Abandoned and relocated to Angola in 1912.
- Portuguese Settlements in Gambia[9]
- San Domingo/St. Andrew's Island (1456-1651)
- Tankular
- Bintang
- Geregia (1652-?)
- Joal (1703-?)
- Portuguese Gold Coast: (1482–1642), conquered by the Dutch in 1642.
- Accra: (1557–1578)
- Axim (1515–1642): Portuguese fort constructed there in 1515. Abandoned and taken by the Dutch in 1642.
- Elmina: possession (1482–1637). Captured by the Dutch West Indies Company.
- Fort of São João Baptista de Ajudá (1680–1961): Constructed on a land grant from the King of Dahomey. Portuguese evicted by the independent Republic of Dahomey.
- Osu Castle (1550–1650): Sold to Sweden.
- Savi: Factory.
- Gorée (1444–1588): Trading post. Lost to the Dutch. Briefly reconquered in 1629.[10]
- Gwato: Trading post. (1485/1486 - 1507/1520s)
- Guiné Portuguesa/Portuguese Guinea: colony (1879–1951); overseas province (1951–1974). Unilateral independence declared in 1973, recognized by Portugal in 1974.
- Lamu (1506–1652): Subjugated in 1506. Driven out by native Inhabitants.
- Loango (1500–1867): Slave port.
- Madagascar (1508–1553): Settlement at Matatana. Abandoned in 1553
- Madeira: possession (1418–1420); colony (1420–1580); crown colony (1580–1834); autonomous district (1834–1976). Made an autonomous region in 1976.
- Malindi: occupation (1500–1630)
- Maçuá/Massawa (1513–1557). Driven out by the Ottomans[11]
- Mombaça/Mombasa: occupation (1593–1638); colony subordinate to Goa (1638–1698; 1728–1729). Under Omani sovereignty in 1729.
- Matadi: Trading post.[citation needed]
- Morocco enclaves
- Aguz/Souira Guedima (1506–1525)
- Alcácer Ceguer/El Qsar es Seghir (1458–1550)
- Arzila/Asilah (1471–1550; 1577–1589). Restored to Morocco in 1589.
- Azamor/Azemmour (1513–1541). City restored to Morocco in 1541.
- Ceuta: possession (1415–1640). Ceded to Spain in 1668.
- Mazagan/El Jadida (1485–1550); possession (1506–1769). Incorporation into Morocco in 1769.
- Mogador/Essaouira (1506–1510)
- Safim/Safi (1488–1541)
- Santa Cruz do Cabo de Gué/Agadir (1505–1541)
- São João da Mamora/Mehdya (1515–1550)
- Tangier: possession (1471–1662). Ceded to England in 1662.
- Moçambique/Portuguese East Africa: possession (1498–1501); subordinate to Goa (1501–1569); captaincy-general (1569–1609); colony subordinate to Goa (1609–1752); colony (1752–1951); overseas province (1951–1971); state (1971–1974); local transitional administration (1974–1975). Independence in 1975.
- Ouadane: factory (1487)[12]
- Quíloa (1505–1512)
- Rokupr: possession (it was under the Portuguese c. 1778)[13]
- São Tomé and Príncipe/São Tomé e Príncipe: crown colony (1753–1951); overseas province (1951–1971); local administration (1971–1975). Independence in 1975.
- Zanzibar and Pemba Island possession (1503–1698). Lost to Oman in 1698.
- Ziguinchor: possession (1645–1888). Ceded to France in 1888.
- Portuguese Trading Settlements in Zimbabwe[14][15][16]
- 'Feiras'
- Trading Settlements (without 'Feira" status)
- Maramuca (Rimuka): (1580s–?)
- Chipiriviri
- Hwangwa
- Manzovo
- Matafuna
- Matuca
- Zumbo (in Mozambique)
Remove ads
Asia-Pacific
Summarize
Perspective
India was reached by the Portuguese in 1498 by Vasco da Gama. Macau was the last possession in Asia and was handed over to the People's Republic of China in 1999.
Middle East
- Aden: Attempted conquest by Albuquerque (1513) and Albergaria (1516). Occupied for a few months in 1547–1548 before being recaptured by Piri Reis[20]
- Bahrain: possession (1521–1602). Driven out by a native revolt and occupied by Persian troops.
- Bandar-e-Kong/Bandar Congo: free factory and port, by treaty with Persia (1629-1725)[21]
- Basra (1550–1668): Portuguese vassal (1550–1595). Occupation (1595–1624). Integral part of the Portuguese Empire (1624–1668). Lost to the Ottomans.
- Bushehr (1506–1622): Lost to the Safavids.
- Comorão/Bandar Abbas: possession (1506–1615). Conquered by Persian forces.
- Chabahar (1508–1621): Lost to the British.[citation needed]
- Failaka Island/Ilha de Aguada: Possible portuguese settlements[22][23]
- Isfahan (1602–1748): Augustinian convent founded in 1602; acted as an informal embassy[21]
- Portuguese Oman (1507–1666): String of forts, port cities, and trading posts along the southeastern coast of the Arabian Peninsula.
- Borca/Barka: Trading post.
- Calaiate/Calha/Qalhat: Quickly abandoned in favor of Muscat.
- Cassapo/Khasab: Coastal fort.
- Corfacão/Khor Fakkan (1513–1666): Major economic center.
- Curiate/Qurayyat: Coastal fort.
- Doba/Dibba (1623–1650): Taken on behalf of Hormuz. Lost to the Omanis.
- Ghallah/Quelba/Kalba: Coastal fort.
- Julfar: Trading post.
- Libidia/Al Badiyah: Coastal fort. Abandoned in 1600.
- Lima/Limah: Possession.
- Madá/Madha: Fortified post.
- Matara/Muttrah: Coastal fort.
- Muscat (1507–1650): Driven out by native inhabitants.
- Mocombira/Mocombi: Possession.
- Sibo/Seeb: Coastal fort.
- Soar/Sohar: Coastal fort.
- Qatar: possession (1517–1538). Lost to the Ottomans.
- Queixome/Qeshm Island (1515–1622).
- Hormuz/Ormus: possession subordinate to Goa (1515–1622). Captured by a joint force between the Safavid Empire and the English East India Company.
- Socotra: possession (1506–1511). Became part of Mahri Sultanate of Qishn and Suqutra
Indian Subcontinent
- Ceylon: colony (1597–1658). Dutch took control in 1656, Jaffna taken in 1658.
- Maldives: possession (1518–1521, 1558–1573)

- Índia Portuguesa/Portuguese India: overseas province (1946–1962). Taken over by India in 1962 and recognised by Portugal in 1974.
- Agra: the Mughal Emperor Akbar gave permission to the Jesuit Order build a church in the city
- Baçaim/Vasai: possession (1535–1739)
- Bankot Fort (1548–1699): given to the British.[citation needed]
- Basrur (15??–1665): Sacked by the Marathas.
- Batticala/Bhatkal (1502–1606): Driven out by native inhabitants.
- Bombaím/Mumbai: possession (1534–1661)
- Calicut/Kozhikode: settlement (1512–1525)
- Cambay/Khambhat: factory (?–1616)
- Cannanore/Kolathunadu: possession (1502–1663)
- Chaul: possession (1521–1740)
- Xatigan/Chittagong: possession (1528–1666)
- Cochin/Kochi: possession (1500–1663)
- Comorin (15??–1656): Lost to the Dutch.[citation needed]
- Cuddalore: Lost to the French and the English.
- Cranganore/Kodungallur: possession (1536–1662)
- Damão/Daman: acquisition in 1559. Became part of overseas province in 1946. Taken over by India in Dec 1961.
- Diu: acquisition in 1535. Became part of overseas province in 1946. Taken over by India in Dec 1961.
- Ghoghla/Gogolá (1538–1961): coastal village. Seized by India in 1961. Officially ceded along with Diu in 1975.
- Simbor (1722–1961): Fort of São António de Simbor constructed in 1722 to suppress piracy. Seized by India in 1961. officially ceded in 1975.
- Dacca (1580–1765): Settlement and church. Taken by the British in 1765.
- Dadra: acquisition in 1779. Taken over by India in 1954.
- Goa: colony (1510–1946). Became part of overseas province in 1946. Taken over by India in Dec 1961.
- Angediva Island (1505–1961): Intermittenly occupied. Island abandoned in 1961.
- Honnavar (16th century–18th century): Coastal fort. Driven out by the English who established a factory there.
- Hughli/Hugli: possession (1579–1632)
- Coulão/Kollam: possession (1502–1661)
- Korlai Fort (1594–1739): Taken from the Ahmadnagar Sultanate. Lost to the Marathas.
- Lahari Bandar (16th century–18th century): Major trading post. Abandoned in the 18th century.[citation needed]
- Lahore: the Portuguese got permission to build a church there. Later turned into a protestant church.
- Laccadive Islands/Lakshadweep (1498–1545). Driven out by its native inhabitants.[citation needed]
- Masulipatnam/Machilipatnam (1598–1610)
- Mangalore (1568–1659)
- São Tomé de Meliapore/Mylapore: settlement (1523–1662; 1687–1749)
- Nagar Haveli: acquisition in 1779. Taken over by India in 1954.
- Negapatam/Nagapattinam (1507–1657)
- Porto Novo/Parangipettai: Possession.
- Paliacate/Pulicat (1502–1610). Occupied by the Dutch in 1610.
- Punicale (1551–16??): Pearl fishery.
- Salsette Island: possession (1534–1737). Conquered by the Marathas.
- Sandwip (1602–1621): Trade hub possessed as part of a power-sharing agreement with Arakan and Bengal Subah. Conquered by Mrauk U.
- Surat: settlement (1540–1612)
- Tuticorin/Thoothukudi (1548–1658)
- Thatta: Factory[24]
East Asia
- Chinese concessions: Territories gained through the Unequal Treaties of the 19th and 20th century.
- Beihai: (1876–1949). Privileges discontinued by the Chinese Communist Party.
- Shanghai International Settlement: (1863–1945). Administered jointly with other trading powers in China. Settlement abolished in 1945.
- Macau/Macao: Unofficial Settlement (1553–1557). Leased territory subordinated to Goa (1557–1844). Overseas province (1844–1883). Combined overseas province with Portuguese Timor under Goa (1883–1951). Overseas province (1951–1976). Autonomous region (1976–1999). Returned to full sovereignty of the People's Republic of China as a special administrative region in 1999.
- Coloane: Occupied in 1864.
- Taipa: Occupied in 1851.
- Ilha Verde: Incorporated in 1890.
- Ilhas de Lapa, Dom João, e Montanha: Lapa occupied in 1654. Dom João occupied in 1849. Ilha de Montanha occupied in 1938. Lost to Japan in 1941.
- Japanese Voyages (1550–1639): Portuguese arrive and begin to settle in 1543. Officially established by the government in Goa in 1550. Ended in 1639 by decree of the Tokugawa Shogunate.
- Deshima (1570–1639): Constructed by the Portuguese. Forced out by the Shōgun and granted to the Dutch in 1641.
- Fukuda (1565–1571): Portuguese invited into the port in 1565. Abandoned in 1571 due to bad weather conditions.
- Funai/Ōita (16th century): Port of call.
- Hirado (1543–1571): Abandoned in favor of Nagasaki.
- Kagoshima (1543–1639): center of Jesuit activity. Anti-Christian bans forced out the Jesuits in 1639.
- Nagasáqui/Nagasaki (1543–1639): Unofficial settlement (1543–1570). Leased territory (1570–1580). Administrative control (1580–1587). Trading post and settlement (1587–1639). Portuguese forced out as a part of the Shōgun's policy of Sakoku.
- Vocoxiura/Yokoseura (1562–1571): Initial base for Jesuit activities in Japan. Abandoned in favor of Nagasaki.
- Liampó/Ningbo (1522–1548): Heavy Portuguese presence in the city itself and settlement in nearby Shuangyu. Settlement destroyed by Ming authorities in 1548 as a part of an anti-piracy campaign.[25][26]
- São João Island/Shangchuan Island: possession (15??–1557). Abandoned in favor of Macao.
- Tamão: (1513–1521) Trade settlement. Driven out by the Ming Navy.
- Yuegang: (1533–???) Popular trading and smuggling port for Portuguese merchants. Unknown when Portuguese merchants ceased trading. Port closed in 1727.
Southeast Asia
- Arakan: had a Portuguese quarter[27]
- Ayutthaya: portuguese settlement (1516-1767)[28]
- Bassein/Pathein/Cosmim (1516): Expelled by the Burmese[29]
- Cambodia (1593-1597): Joint Spanish-Portuguese invasion against the Siamese occupation of cambodia; ultimately failed.
- Portuguese East Indies (1511–1975/2002). Colonial dependency of Goa (1522–1844); Subordinated to Macao (1844–1850); Independent colony (1850–1851); Subordinated to Macao (1851–1856); Subordinated to Goa (1856–1863); Overseas province (1863–1866); Subordinate to Macao (1866–1896); Independent colony (1896–1950); Overseas province (1950–1975); Unilateral Independence and Indonesian Occupation (1975–1999); UN Administration (1999–2002).
- Calapa (1522–1619): Port granted to the Portuguese by the Hindu Sunda Kingdom in return for military support against their Muslim neighbors. Lost to the Dutch.[citation needed]
- Keling Fort (1613–1645): Destroyed by the Dutch.[citation needed]
- Malacca: settlement (1511–1641); lost to the Dutch.
- Muar Fortress (1604–1641): Built to defend Malacca against Dutch and Acehnese attacks. Seized by the Dutch after the loss of Malacca.
- Maluku Islands
- Amboina/Ambon: settlement (1576–1605).
- Fort Victoria/Forte de Nossa Senhora da Anunciada de Amboíno (1576-1605)
- Bacan: Trading post (1513–1575). Conquered by Ternate.
- Loki: Fort erected in war against the Dutch (1651-1652)[30]
- Ternate: settlement (1522–1575). Portuguese forced out by the Sultan of Ternate.
- Fort Kastela/Forte de São João Batista de Ternate/Fortaleza de Ternate (1522-1575)
- Fort Kota Janji/Fortaleza São João (1522?-1575)
- Fort Tolukko (1522-1575)
- Fort Kalamata/Forte Santa Lucia (1540-1575)
- Tidore: colony (1578–1605). Seized by Dutch in 1605
- Amboina/Ambon: settlement (1576–1605).
- Celebes: Possessions on the island between 1512 and 1658.
- Pacem (1521–1524): Occupied, then quickly abandoned.
- Timor: claimed and partially possessed from 1520 to 1640.
- Cupão/Kupang: Trading post. Taken by the Dutch in 1613
- Flores Island: possession (16th–19th century). Sold the island to the Dutch East Indies.
- Solor: possession (1520–1636).
- Fort Solor/Forte de Nossa Senhora da Piedade de Solor (1566-1613)
- West Timor: part of Timor lost to the Dutch in 1640.
- Portuguese Timor: colony subordinate to Portuguese India (1642–1844); subordinate to Macau (1844–1896); separate colony (1896–1951); overseas territory (1951–1975); republic and unilateral independence proclaimed, annexed by Indonesia (1975–1999, UN recognition as Portuguese territory). UN administration from 1999 until independence in 2002.[35]
- Ilha de Ataúro (1859–1975): Granted to the Portuguese by the Dutch in 1859.
- Faifo/Hội An: Jesuit residency.
- Ligor/Nakhon Si Thammarat: In 1518 the Portuguese were allowed to settle and trade in there, in return the Siamese were allowed to settle in Malacca and the Portuguese were expected to provide arms and ammunition against Chiang Mai[36]
- Martaban: Factory (1521–?)[37]
- Mergui/Myeik: In 1518 the Portuguese were allowed to settle and trade in there, in return the Siamese were allowed to settle in Malacca and the Portuguese were expected to provide arms and ammunition against Chiang Mai[36]
- Pattani: factory (1516-1640)[38][39]
- Syriam/Thanlyin: possession (1599–1613). Ruled by Filipe de Brito e Nicote.
Remove ads
South America

Brazil was explored and claimed in 1500, and become independent in 1822. Unlike the Spanish, the Portuguese did not divide their possession in South America in several vice-royalties.
- Brazil: possession known as Ilha de Vera Cruz, later Terra de Santa Cruz (1500–1530); colony (1530–1714); vice-kingdom (1714–1815); kingdom united with the Kingdom of Portugal (1815–1822), independence in 1822.
- Cisplatina (Uruguay): occupation (1808–1822). Captaincy in 1817 (of the United Kingdom of Portugal, Brazil and the Algarves). Adhered as a province of the new Empire of Brazil in 1822. Became independent 1827, changing its name to Uruguay.
- French Guiana: occupation (1809–1817). Restored to France in 1817.
- Nova Colónia do Sacramento: colony in present Uruguay (1680; 1683–1705; 1715–1777). Ceded to the Spanish Empire in 1777.
Remove ads
North Atlantic and Northern America
Summarize
Perspective

The Azores were discovered early in the Discovery Ages. Labrador and Corte-Real brothers later explored and claimed Greenland and eastern modern Canada from 1499 to 1502.
- Azores: colonies (1427–1766); captaincy-general (1766–1831); autonomous districts of Angra do Heroismo, Horta and Ponta Delgada (1831–1976). Made an autonomous region in 1976.
- Greenland: (1499/1500–?) possession claimed by João Fernandes Labrador in 1499 or 1500. Seen as claimed in the Cantino planisphere of 1502, Reinel-Lopo Homem chart of 1519 and Reinel map of 1535.
- Land of the Corte-Real: (1501–?) claimed after the voyages of the Corte-Real brothers. Over the 16th century, several larger, permanent settlements were established, but many more seasonal trading posts and fishing villages were established at the same time and beyond.
- Terra Nova (Newfoundland): (1501–?) claimed by Miguel and Gaspar Corte-Real, latter by João Álvares Fagundes. Also known as Terra Nova dos Bacalhaus (New Land of Codfish). Portuguese had two settlements in Newfoundland, one in Portugal Cove – St. Philips and the other in Portugal Cove South.
- Labrador (1499/1500–?): claimed by the Corte-Real brothers and maybe by João Fernandes Labrador.
- Nova Scotia (1519?–?): explored and claimed by João Álvares Fagundes. In Nova Scotia, Portuguese had two settlements, one in Saint Peters and another one in Ingonish.
Remove ads
See also
References
Further reading
Wikiwand - on
Seamless Wikipedia browsing. On steroids.
Remove ads