Loading AI tools
Chemical compound From Wikipedia, the free encyclopedia
Butein is a chalcone of the chalconoids. It can be found in Toxicodendron vernicifluum (or formerly Rhus verniciflua), Dahlia, Butea (Butea monosperma) and Coreopsis.[1] It has antioxidative, aldose reductase and advanced glycation endproducts inhibitory effects.[2] It is also a sirtuin-activating compound, a chemical compound having an effect on sirtuins, a group of enzymes that use NAD+ to remove acetyl groups from proteins. Buteins possess a high ability to inhibit aromatase process in the human body, for this reason, the use of these compounds in the treatment of breast cancer on the estrogen ground has been explored.[3] The first attempts of sport pro-hormone supplementation with the use of buteins took place in Poland.[4][unreliable source?]
 | |
| Names | |
|---|---|
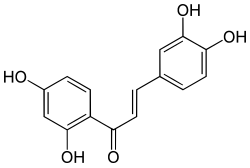
| Preferred IUPAC name
2′,3,4,4′-Tetrahydroxychalcone | |
| Other names
(2E)-1-(2,4-Dihydroxyphenyl)-3-(3,4-dihydroxyphenyl)prop-2-en-1-one 2′,4′,3,4-Tetrahydroxychalcone 3,4,2′,4′-Tetrahydroxychalcone | |
| Identifiers | |
3D model (JSmol) |
|
| ChEBI | |
| ChEMBL | |
| ChemSpider | |
| ECHA InfoCard | 100.006.963 |
| KEGG | |
PubChem CID |
|
| UNII | |
CompTox Dashboard (EPA) |
|
| |
| |
| Properties | |
| C15H12O5 | |
| Molar mass | 272.256 g·mol−1 |
Except where otherwise noted, data are given for materials in their standard state (at 25 °C [77 °F], 100 kPa).
| |
Seamless Wikipedia browsing. On steroids.
Every time you click a link to Wikipedia, Wiktionary or Wikiquote in your browser's search results, it will show the modern Wikiwand interface.
Wikiwand extension is a five stars, simple, with minimum permission required to keep your browsing private, safe and transparent.