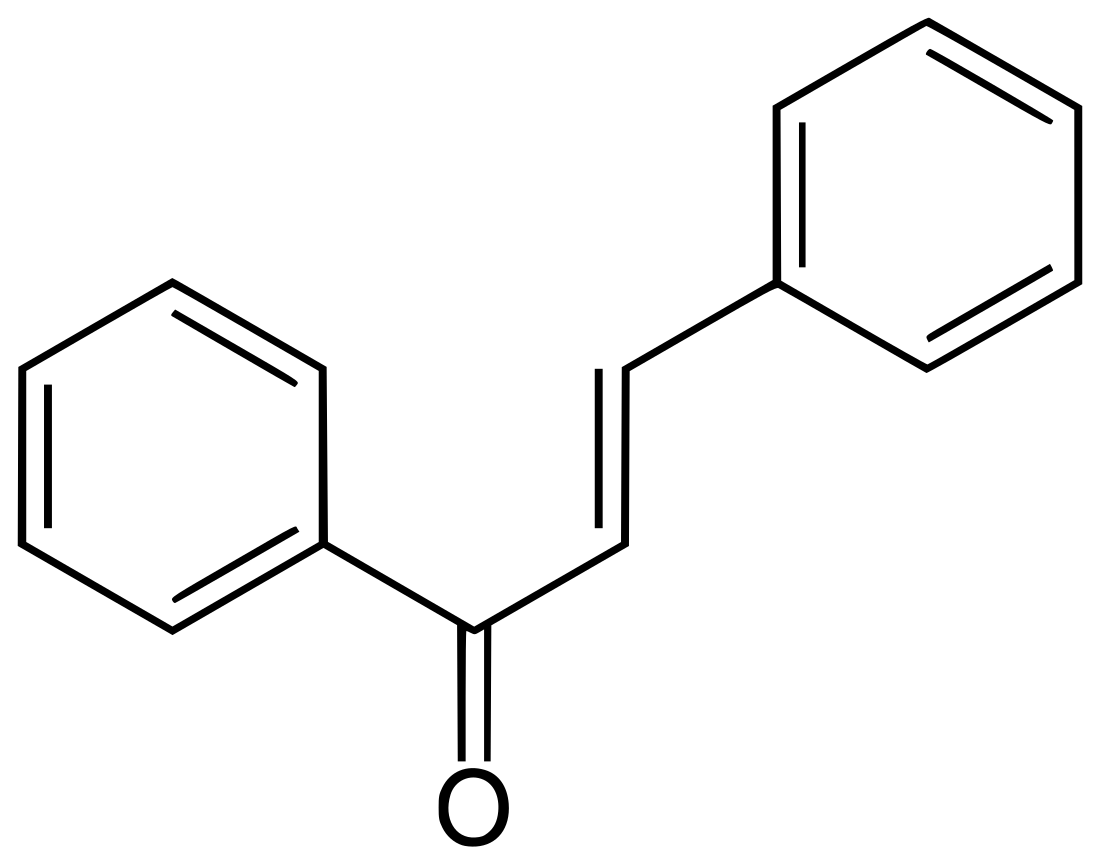
Chalcone
Chemical compound From Wikipedia, the free encyclopedia
Chalcone is the organic compound C6H5C(O)CH=CHC6H5. It is an α,β-unsaturated ketone. A variety of important biological compounds are known collectively as chalcones or chalconoids.[3] They are widely known bioactive substances, fluorescent materials, and chemical intermediates.
 | |
 | |
| Names | |
|---|---|
| Preferred IUPAC name
Chalcone[2] | |
| Systematic IUPAC name
(2E)-1,3-Diphenylprop-2-en-1-one | |
| Other names
Chalkone Benzylideneacetophenone Phenyl styryl ketone benzalacetophenone β-phenylacrylophenone γ-oxo-α,γ-diphenyl-α-propylene α-phenyl-β-benzoylethylene. | |
| Identifiers | |
3D model (JSmol) |
|
| ChEBI | |
| ChemSpider | |
| ECHA InfoCard | 100.002.119 |
PubChem CID |
|
| UNII | |
CompTox Dashboard (EPA) |
|
| |
| |
| Properties | |
| C15H12O | |
| Molar mass | 208.260 g·mol−1 |
| Appearance | pale yellow solid |
| Density | 1.071 g/cm3 |
| Melting point | 55 to 57 °C (131 to 135 °F; 328 to 330 K) |
| Boiling point | 345 to 348 °C (653 to 658 °F; 618 to 621 K) |
| −125.7·10−6 cm3/mol | |
Except where otherwise noted, data are given for materials in their standard state (at 25 °C [77 °F], 100 kPa).
| |
Chemical properties
Chalcones have two absorption maxima at 280 nm and 340 nm.[4]
Biosynthesis
Chalcones and chalconoids are synthesized in plants as secondary metabolites. The enzyme chalcone synthase, a type III polyketide synthase, is responsible for the biosynthesis of these compounds. The enzyme is found in all "higher" (vascular) and several "lower" (non-vascular) plants.[5]
Laboratory synthesis
Chalcone is usually prepared by an aldol condensation between benzaldehyde and acetophenone.[6]
This reaction, which can be carried out without any solvent, is so reliable that it is often given as an example of green chemistry in undergraduate education.[7]
Potential pharmacology
Chalcones and their derivatives demonstrate a wide range of biological activities including anti-inflammation.[8] Some 2′-amino chalcones have been studied as potential antitumor agents.[9][10] Chalcones are of interest in medicinal chemistry and have been described as a privileged scaffold.[5]
Uses
Medicinal uses
In medicinal chemistry, chalcones have been used as:
Industrial uses
In chemical industries, they are employed as:
- liquid crystals
- fluorescent chemical scaffolds
- metal sensors
- corrosion inhibitors
- plant hormones.[11]
Uses in organic chemistry
Chalcones have been used as intermediates in heterocyclic synthesis, especially in the synthesis of pyrazoles and aurones.[11]
See also
References
External links
Wikiwand - on
Seamless Wikipedia browsing. On steroids.