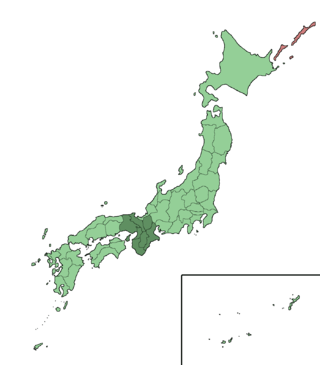
Kansai region
region of Japan From Wikipedia, the free encyclopedia
Remove ads
The Kansai region (関西地方, Kansai-chihō) is one of Japan's traditional regions[1] The area is also known as the Kinki region (近畿地方, Kinki-chihō)[2] or as the Kinai (畿内).[3] The Japanese conventions of geography and history divide the nation into eight regions, including the Kansai region.[4] These have been used since 1905 as basic units for description and comparison.[5] and as cultural markers.

The regions of Japan are a fusion of historical divisions and modern administrative needs".[6] The significance of the region in Japan is geographical, cultural and administrative.[7]
Remove ads
History
In the late 7th century, the Kinki region were identified as one of the eight largest administrative areas of the Imperial system (ritsuryo seido).
Gokishichidō is an ancient system of names for parts of the country, including Kinki or Kansai.[8] Kansai covers the area around the capital city of Kyoto on the island of Honshū[9] in roughly the same area as the traditional Kinki.
In the Meiji period, the modern regional system was made by Imperial decree. Japan was divided into regions (chihō Archived 2017-03-24 at the Wayback Machine), including the Kinki region. A regional council (chihō gyōsei kyōgisai) was headed by the governor of the most powerful prefecture in the regional grouping. The council also included regional chiefs of central government ministries.[10]
Table: Kansai region
Over time, Kansai has developed its own regional dialects, customs and unique traditional culture.[16]
Remove ads
Related pages

| Kinai | Tōkaidō | Tōsandō | Hokurikudō |
| San'indō | San'yōdō | Nankaidō | Saikaidō |
Places named with Kansai
- Kansai Airport Station
- Kansai International Airport
- Kansai Ki-in (Organization for Go)
References
Other websites
Wikiwand - on
Seamless Wikipedia browsing. On steroids.
Remove ads