Glaucophyte
division of algae From Wikipedia, the free encyclopedia
The glaucophytes are a small group of freshwater microscopic algae.[1] Together with the red algae (Rhodophyta) and green algae plus land plants (Viridiplantae or Chloroplastida), they form the Archaeplastida.
| Glaucophyta | |
|---|---|
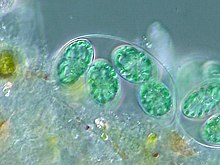 | |
| Glaucocystis sp. | |
| Scientific classification | |
| Clade: | Archaeplastida |
| Division: | Glaucophyta Skuja 1948 |
| Class | |
| |
| Synonyms | |
| |
The glaucophytes are of interest because they may be similar to the original algal type that led to green plants and red algae.[1][2] The relationships between these groups are not yet clear,[3] and the glaucophytes in particular need more study.
Characteristics
The chloroplasts of glaucophytes are known as 'cyanelles'. Unlike the chloroplasts in other organisms, they have a peptidoglycan layer, like bacterial cell walls. This is thought to be a relic of the endosymbiotic origin of plastids from cyanobacteria.[1]
Glaucophytes have the photosynthetic pigment chlorophyll a.[1] They harvest light with the same type of pigment molecules as do cyanobacteria and red algae.[1] Green algae and land plants have lost that pigment, which is known as phycobiliprotein.[4]
Glaucophyte mitochondria and flagella (if present) are similar to forms found in some green algae.[4]
Classification
Only 13 species of glaucophytes are known, none of which is particularly common in nature.[1] There are three genera.
The glaucophytes were previously placed in the order Chlorococcales.[5]
References
Wikiwand - on
Seamless Wikipedia browsing. On steroids.
