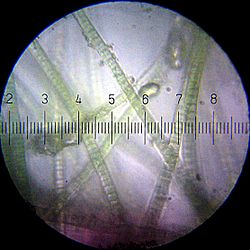
Cyanobacteria
phylum of prokaryotes From Wikipedia, the free encyclopedia
Remove ads
Cyanobacteria are a taxon of bacteria which conduct photosynthesis. They are not algae, though they were once called blue-green algae. It is a phylum of bacteria, with about 1500 species. In endosymbiont theory, chloroplasts (plastids) are descended from cyanobacteria. Their DNA profile is evidence for this.[3][4][5]



Cyanobacteria have an extremely long fossil record, starting at least 3.5 billion years ago. They were the main organisms in the stromatolites of the Archaean and Proterozoic eons.[6]
The ability of cyanobacteria to perform oxygenic photosynthesis is highly significant. The early atmosphere on Earth was largely reducing, that is, without oxygen. The cyanobacteria in stromatolites were the first known organisms to photosynthesize and produce free oxygen. After about a billion years, the effect of this photosynthesis began a huge change in the atmosphere. The process, called the Great Oxygenation Event, took a long time. Eventually, it killed off most of the organisms which could not live in oxygen, and led to the kinds of environment we know today, where most organisms use and need oxygen.[7][8]
Remove ads
Light detection
Cyanobacteria have a way of detecting light. Conrad Mullineaux, of Queen Mary University of London, said, "It has a way of detecting where the light is; we know that because of the direction that it moves".[9]
Remove ads
Related pages
References
Wikiwand - on
Seamless Wikipedia browsing. On steroids.
Remove ads