Down syndrome
chromosomal condition From Wikipedia, the free encyclopedia
Down syndrome (or trisomy 21) is a genetic disorder. Most people with Down Syndrome have an extra copy of chromosome 21, or part of it.
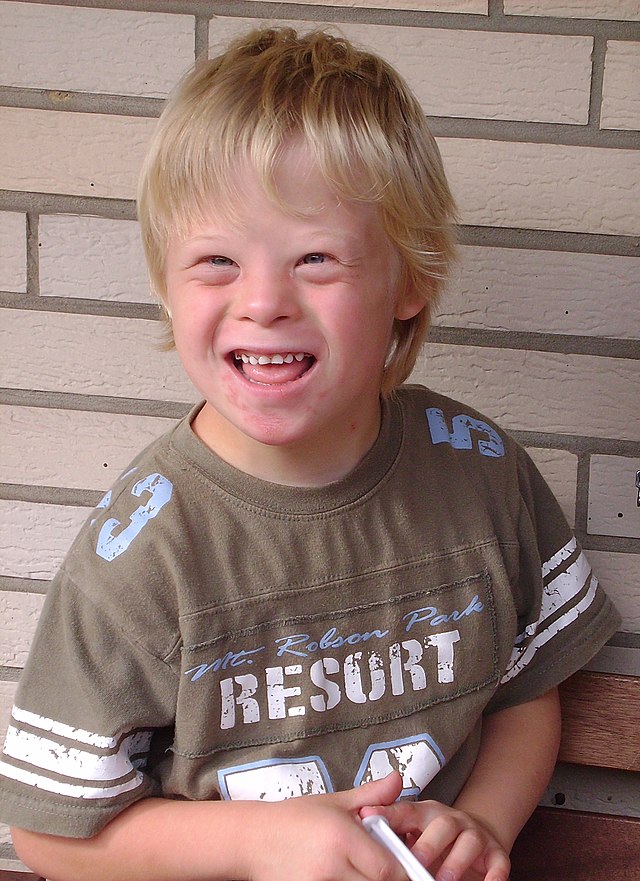

Down syndrome causes a mental handicap. It may be mild or severe. The average IQ of a young adult with Down syndrome is 50, equivalent to the mental age of an 8- or 9-year-old child, but it truly depends on the person.[1][2][3] This can vary widely, but most individuals need supervision if they are to live their lives in a satisfactory way. Children who have this condition take more time to learn new things.
The condition is named after John Langdon Down, the British doctor who first described it in 1866. Historically (in the past) it was called mongolism. Today the historical name is not used, likely because it is offensive to people with Down syndrome.[verification needed] During that time, a person also with the condition was referred to as a mongolian idiot, while today, a person also with Down syndrome would be referred to as that.
There is discrimination against people with Down syndrome, both in the education system and in society in general.[4] Some people with the condition may have average intelligence but may also have other noticeable features of the disability. For example, people with Down syndrome often have a different shape of eyes than those without the syndrome. Some people with the condition have severe learning difficulties.
Of every 800 to 1000 babies that are born, one is diagnosed with Down syndrome. Older women have a higher chance of having a baby with Down syndrome.[5] If they have a procedure known as amniocentesis, pregnant mothers can be told whether their fetus has Down syndrome. Ultrasound scans may also diagnose the presence of Down Syndrome. Mothers whose fetus is diagnosed as having Downs syndrome may choose to have an abortion. In the United Kingdom and Europe 92% of such cases are aborted.[6]
There are several options for care of individuals with Down syndrome as they grow older; many individuals are able to live independently or with the support of a PCA.
Features

They also grow differently from other children. Babies with down syndrome can be identified at birth because they may have a specific set of physical features. These features include narrow eyes, a flat nose-bridge, smaller mouths and shorter fingers. Smaller mouths can result in tongue protrusion or what looks like a large tongue. Sometimes the little fingers curve inwards as well, and there is also often a space between the big toe and the others. People with Down syndrome often have heart defects or Alzheimer's disease when they are older. About 90% of people with Down syndrome live through their teens. The lifespan of a person with Down syndrome averages between 50 and 55 years old.
So far there have been no treatments for Down syndrome.[5]
Genetic causes
Down syndrome comes from a problem with the genes. Humans are diploid organisms. This means that for each chromosome, there are two copies, one from the mother, and one from the father. During meiosis the number is reduced to one set of chromosomes. People with Down syndrome have an extra copy of chromosome 21, or part of it.
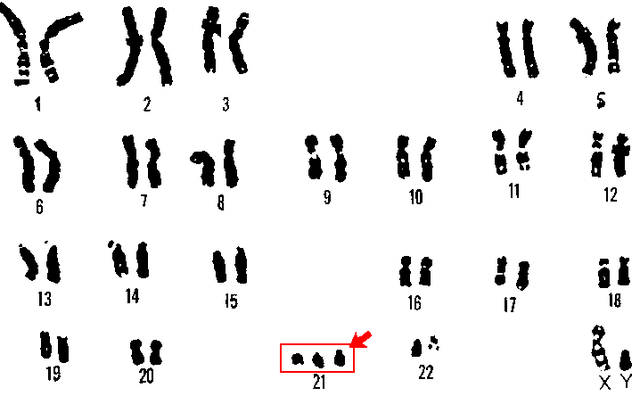
There are three ways that Down syndrome is caused.
- The most common cause of Down syndrome is trisomy. Trisomy is when the child receives two chromosomes from one parent and one from the other parent. This makes it so there are three chromosomes of chromosome 21.
- Another way Down syndrome is caused is when new cells are made. Sometimes even when the parent cells are normal chromosome 21 can be deformed when cells reproduce. This makes it so some cells have 47 chromosomes and others have 46. This is called a mosaic disorder. Mosaic means that they have a third chromosome from the replication of cells.
- The third way Down syndrome can be caused is called translocation. This happens when a normal chromosome breaks into two pieces. This results in three chromosomes.[7]
Well-known people with Down syndrome

- Stephane Ginnsz, actor (Duo)—In 1996 was first actor with Down syndrome in the lead part of a motion picture.[8]
- Max Lewis, actor (Notes on a Scandal).[9]
- Joey Moss, Edmonton Oilers locker room attendant.[10]
- Isabella Pujols, adopted daughter of St. Louis Cardinals first baseman Albert Pujols and inspiration for the Pujols Family Foundation.[11]
- Paula Sage, Scottish movie actress and Special Olympics netball athlete.[12] Her role in the 2003 movie AfterLife[13] brought her a BAFTA Scotland award for best first time performance and Best Actress in the Bratislava International Film Festival, 2004.[14] Afterlife won the Audience Award at The Edinburgh Film Festival 2003. It also won Sage a role as Donna McCabe in BBC Scotland's River City soap.
- Judith Scott, artist.[15]
- Johnny Stallings, son of former University of Alabama head football coach Gene Stallings and subject of the book Another Season: A Coach's Story of Raising an Exceptional Son. (ISBN 0-7679-0255-6).[16]
- Miguel Tomasin, singer with Argentinian avant-rock band Reynols.[17]
- Chris Burke, American actor who portrayed "Corky Thatcher" on the television series Life Goes On and "Taylor" on Touched By An Angel.
- Edward Barbanell, played Billy in 2005's The Ringer.
- Karen Gaffney, Swimmer, Inclusion Activist, Motivational Speaker and President of The Karen Gaffney Foundation.[18]
- Lauren Potter, American actor [19]
- Labeed Mirza, Editor of Tahir Magazine
Bibliography
- Beck, M.N. (1999). Expecting Adam. New York: Berkley Books.
- Buckley, S. (2000). Living with Down Syndrome. Portsmouth, UK: The Down Syndrome Educational Trust. Archived from the original on 2005-04-21. Retrieved 2006-08-09.
- Down Syndrome Research Foundation (2005). Bright Beginnings: A Guide for New Parents. Buckinghamshire, UK: Down Syndrome Research Foundation. Archived from the original on 2006-08-20. Retrieved 2006-08-09.
- Hassold, T.J.; D. Patterson (1999). Down Syndrome: A Promising Future, Together. New York: Wiley Liss.
- Kingsley, J.; M. Levitz (1994). Count us in — Growing up with Down Syndrome. San Diago: Harcourt Brace.
- Pueschel, S.M.; M. Sustrova (1997). Adolescents with Down Syndrome: Toward a More Fulfilling Life. Baltimore, MD USA: Paul H. Brookes.
- Selikowitz, M. (1997). Down Syndrome: The Facts (2nd ed.). Oxford: Oxford University Press. ISBN 978-0-19-262662-2.
- Van Dyke, D.C. (1995). Medical and Surgical Care for Children with Down Syndrome. P.J. Mattheis; S. Schoon Eberly; and J. Williams. Bethesda, MD USA: Woodbine House.
- Zuckoff, M. (2002). Choosing Naia: A Family's Journey. New York: Beacon Press.
Other websites
For comprehensive lists of Down syndrome links see
- Directory of Down Syndrome Internet Sites (US based, but contains international links)
- UK resources for Down's syndrome Archived 2006-08-22 at the Wayback Machine
Societies and Associations
- Down Syndrome International Archived 2021-03-01 at the Wayback Machine
By Country
- Canadian Down Syndrome Society (Canada)
- Down Syndrome Research Foundation web site (Canada)
- Down's Syndrome Association web site (UK) Archived 2005-06-18 at the Wayback Machine
- Down's Syndrome Research Foundation (UK)
- National Down Syndrome Society web site (USA)
- National Down Syndrome Congress web site (USA)
- International Mosaic Down Syndrome Association (USA)
Conferences
References
Wikiwand - on
Seamless Wikipedia browsing. On steroids.
