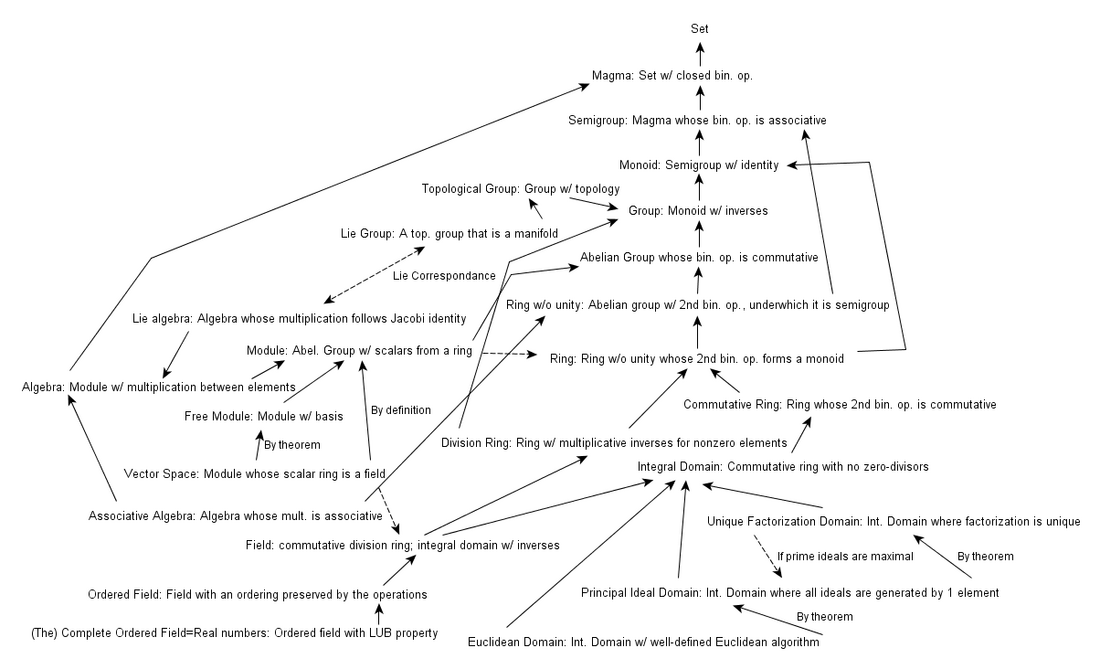
유계 격자
(
L
,
∧
,
∨
,
⊤
,
⊥
)
{\displaystyle (L,\land ,\lor ,\top ,\bot )}
¬
:
L
→
L
{\displaystyle \lnot \colon L\to L}
동치 이다.
(순서 반대 보존) 임의의
x
,
y
∈
L
{\displaystyle x,y\in L}
x
≤
y
{\displaystyle x\leq y}
¬
x
≥
¬
y
{\displaystyle \lnot x\geq \lnot y}
(드 모르간 법칙 1) 임의의
x
,
y
∈
L
{\displaystyle x,y\in L}
¬
(
x
∧
y
)
=
¬
x
∨
¬
y
{\displaystyle \lnot (x\land y)=\lnot x\lor \lnot y}
(드 모르간 법칙 2) 임의의
x
,
y
∈
L
{\displaystyle x,y\in L}
¬
(
x
∨
y
)
=
¬
x
∧
¬
y
{\displaystyle \lnot (x\lor y)=\lnot x\land \lnot y}
증명:
순서 반대 보존 ⇒ 드 모르간 법칙 1: 임의의
x
,
y
∈
L
{\displaystyle x,y\in L}
x
∧
y
≤
x
{\displaystyle x\land y\leq x}
x
∧
y
≤
y
{\displaystyle x\land y\leq y}
이므로
¬
(
x
∧
y
)
≥
¬
x
{\displaystyle \lnot (x\land y)\geq \lnot x}
¬
(
x
∧
y
)
≥
¬
y
{\displaystyle \lnot (x\land y)\geq \lnot y}
이다. 따라서, 상한 의 정의에 따라
¬
(
x
∧
y
)
≥
¬
x
∨
¬
y
{\displaystyle \lnot (x\land y)\geq \lnot x\lor \lnot y}
이다.
순서 반대 보존 ⇒ 드 모르간 법칙 2: 위의 경우를 쌍대화하면 된다.
드 모르간 법칙 1 ⇒ 순서 반대 보존:
x
,
y
∈
L
{\displaystyle x,y\in L}
x
≤
y
{\displaystyle x\leq y}
x
=
x
∧
y
{\displaystyle x=x\land y}
이므로
¬
x
=
¬
(
x
∧
y
)
=
¬
x
∨
¬
y
{\displaystyle \lnot x=\lnot (x\land y)=\lnot x\lor \lnot y}
이다. 따라서
¬
x
≥
¬
y
{\displaystyle \lnot x\geq \lnot y}
이다.
드 모르간 법칙 2 ⇒ 순서 반대 보존:
유계 격자
(
L
,
∧
,
∨
,
⊤
,
⊥
)
{\displaystyle (L,\land ,\lor ,\top ,\bot )}
직교 여원 (直交餘元, 영어 : orthocomplementation )
¬
:
L
→
L
{\displaystyle \lnot \colon L\to L}
함수 이다.[ 1] :52, §II.14 [ 2] :§2
(대합 ) 임의의
x
∈
L
{\displaystyle x\in L}
¬
¬
x
=
x
{\displaystyle \lnot \lnot x=x}
(순서 반대 보존) 임의의
x
,
y
∈
L
{\displaystyle x,y\in L}
x
≤
y
{\displaystyle x\leq y}
¬
x
≥
¬
y
{\displaystyle \lnot x\geq \lnot y}
(배중률 ) 임의의
x
∈
L
{\displaystyle x\in L}
¬
x
∨
x
=
⊤
{\displaystyle \lnot x\lor x=\top }
(비모순율 ) 임의의
x
∈
L
{\displaystyle x\in L}
¬
x
∧
x
=
⊥
{\displaystyle \lnot x\land x=\bot }
직교 여원 격자 (영어 : orthocomplemented lattice )는 직교 여원이 부여된 격자이다. 이들의 모임은 대수 구조 다양체 를 이룬다. 두 직교여원 격자 사이의 직교 여원 격자 사상 (영어 : orthocomplemented lattice morphism )
f
:
L
→
L
′
{\displaystyle f\colon L\to L'}
함수 이다.
격자 사상이다. 즉, 임의의
x
,
y
∈
L
{\displaystyle x,y\in L}
f
(
x
∧
y
)
=
f
(
x
)
∧
f
(
y
)
{\displaystyle f(x\land y)=f(x)\land f(y)}
f
(
x
∨
y
)
=
f
(
x
)
∨
f
(
y
)
{\displaystyle f(x\lor y)=f(x)\lor f(y)}
임의의
x
∈
L
{\displaystyle x\in L}
f
(
¬
x
)
=
¬
f
(
x
)
{\displaystyle f(\lnot x)=\lnot f(x)}
이 경우, 임의의
x
∈
L
{\displaystyle x\in L}
f
(
⊤
)
=
f
(
x
∨
¬
x
)
=
f
(
x
)
∨
¬
f
(
x
)
=
⊤
{\displaystyle f(\top )=f(x\lor \lnot x)=f(x)\lor \lnot f(x)=\top }
f
(
⊥
)
=
f
(
x
∧
¬
x
)
=
f
(
x
)
∧
¬
f
(
x
)
=
⊥
{\displaystyle f(\bot )=f(x\land \lnot x)=f(x)\land \lnot f(x)=\bot }
이므로 이는 자동적으로 유계 격자 사상이 된다.
육각형 격자의 하세 도형 직교 여원 격자
L
{\displaystyle L}
동치 이며, 이를 만족시키는 직교 여원 격자를 직교모듈러 격자 (영어 : orthomodular lattice )라고 한다.
임의의
x
,
y
∈
L
{\displaystyle x,y\in L}
x
≤
y
{\displaystyle x\leq y}
y
C
x
{\displaystyle y\operatorname {\mathsf {C}} x}
x
∨
(
¬
x
∧
y
)
=
y
{\displaystyle x\lor (\lnot x\land y)=y}
[ 2] :§2 [ 1] :53, Theorem II.21
임의의
x
,
y
∈
L
{\displaystyle x,y\in L}
x
∨
(
¬
x
∧
(
x
∨
y
)
)
=
x
∨
y
{\displaystyle x\lor (\lnot x\land (x\lor y))=x\lor y}
[ 2] :§2
가환 관계는 대칭 관계 이다. 즉, 임의의
x
,
y
∈
L
{\displaystyle x,y\in L}
x
C
y
{\displaystyle x\operatorname {\mathsf {C}} y}
y
C
x
{\displaystyle y\operatorname {\mathsf {C}} x}
[ 2] :Proposition 2.2(2) [ 1] :53, Theorem II.21
임의의
x
,
y
∈
L
{\displaystyle x,y\in L}
x
C
y
{\displaystyle x\operatorname {\mathsf {C}} y}
¬
x
C
y
{\displaystyle \lnot x\operatorname {\mathsf {C}} y}
[ 2] :Proposition 2.2(3)
임의의
x
,
y
∈
L
{\displaystyle x,y\in L}
x
≤
y
{\displaystyle x\leq y}
¬
x
∧
y
=
⊥
{\displaystyle \lnot x\land y=\bot }
x
=
y
{\displaystyle x=y}
[ 2] :Proposition 2.1(2) [ 1] :54, Exercise II.14.7(i)
임의의
x
,
y
,
z
∈
L
{\displaystyle x,y,z\in L}
x
≤
y
≤
z
{\displaystyle x\leq y\leq z}
x
∨
(
¬
y
∧
z
)
=
(
x
∨
¬
y
)
∧
z
{\displaystyle x\lor (\lnot y\land z)=(x\lor \lnot y)\land z}
[ 1] :54, Exercise II.14.7(ii)
육각형 격자를 부분 격자로 갖지 않는다.[ 2] :Proposition 2.1(3) 여기서 육각형 격자 (영어 : hexagon lattice )는 다음과 같은 유계 격자 이다.
L
=
{
⊥
,
a
,
b
,
c
,
d
,
⊤
}
{\displaystyle L=\{\bot ,a,b,c,d,\top \}}
⊥
≤
a
≤
b
≤
⊤
{\displaystyle \bot \leq a\leq b\leq \top }
⊥
≤
c
≤
d
≤
⊤
{\displaystyle \bot \leq c\leq d\leq \top }