Top Qs
Timeline
Chat
Perspective
Rectified 5-cell
Uniform polychoron From Wikipedia, the free encyclopedia
Remove ads
Remove ads
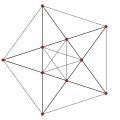
In four-dimensional geometry, the rectified 5-cell is a uniform 4-polytope composed of 5 regular tetrahedral and 5 regular octahedral cells. Each edge has one tetrahedron and two octahedra. Each vertex has two tetrahedra and three octahedra. In total it has 30 triangle faces, 30 edges, and 10 vertices. Each vertex is surrounded by 3 octahedra and 2 tetrahedra; the vertex figure is a triangular prism.
| Rectified 5-cell | ||
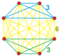
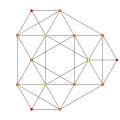
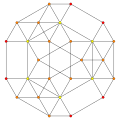
 Schlegel diagram with the 5 tetrahedral cells shown. | ||
| Type | Uniform 4-polytope | |
| Schläfli symbol | t1{3,3,3} or r{3,3,3} {32,1} = | |
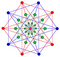
| Coxeter-Dynkin diagram | ||
| Cells | 10 | 5 {3,3} 5 3.3.3.3 |
| Faces | 30 {3} | |
| Edges | 30 | |
| Vertices | 10 | |
| Vertex figure |  Triangular prism | |
| Symmetry group | A4, [3,3,3], order 120 | |
| Petrie polygon | Pentagon | |
| Properties | convex, isogonal, isotoxal | |
| Uniform index | 1 2 3 | |

Topologically, under its highest symmetry, [3,3,3], there is only one geometrical form, containing 5 regular tetrahedra and 5 rectified tetrahedra (which is geometrically the same as a regular octahedron). It is also topologically identical to a tetrahedron-octahedron segmentochoron.[clarification needed]
The vertex figure of the rectified 5-cell is a uniform triangular prism, formed by three octahedra around the sides, and two tetrahedra on the opposite ends.[1]
Despite having the same number of vertices as cells (10) and the same number of edges as faces (30), the rectified 5-cell is not self-dual because the vertex figure (a uniform triangular prism) is not a dual of the polychoron's cells.
Remove ads
Wythoff construction
Seen in a configuration matrix, all incidence counts between elements are shown. The diagonal f-vector numbers are derived through the Wythoff construction, dividing the full group order of a subgroup order by removing one mirror at a time.[2]
Remove ads
Structure
Together with the simplex and 24-cell, this shape and its dual (a polytope with ten vertices and ten triangular bipyramid facets) was one of the first 2-simple 2-simplicial 4-polytopes known. This means that all of its two-dimensional faces, and all of the two-dimensional faces of its dual, are triangles. In 1997, Tom Braden found another dual pair of examples, by gluing two rectified 5-cells together; since then, infinitely many 2-simple 2-simplicial polytopes have been constructed.[3][4]
Remove ads
Semiregular polytope
It is one of three semiregular 4-polytopes made of two or more cells which are Platonic solids, discovered by Thorold Gosset in his 1900 paper. He called it a tetroctahedric for being made of tetrahedron and octahedron cells.[5]
E. L. Elte identified it in 1912 as a semiregular polytope, labeling it as tC5.
Alternate names
- Tetroctahedric (Thorold Gosset)
- Dispentachoron
- Rectified 5-cell (Norman W. Johnson)
- Rectified 4-simplex
- Fully truncated 4-simplex
- Rectified pentachoron (Acronym: rap) (Jonathan Bowers)
- Ambopentachoron (Neil Sloane & John Horton Conway)
- (5,2)-hypersimplex (the convex hull of five-dimensional (0,1)-vectors with exactly two ones)
Images
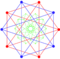
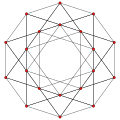
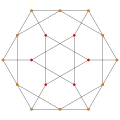
 stereographic projection (centered on octahedron) |
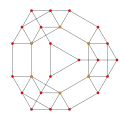
 Net (polytope) |
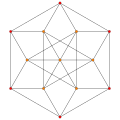
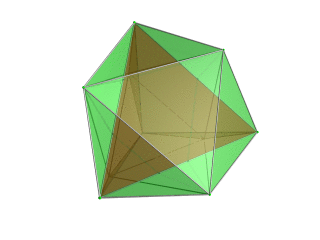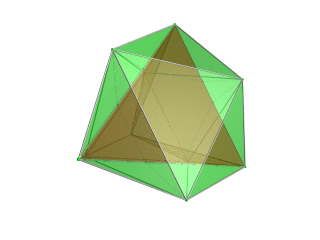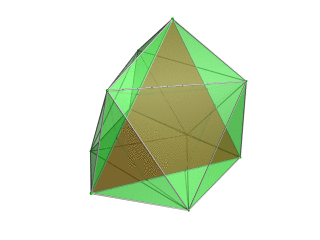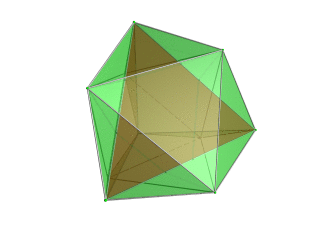 |
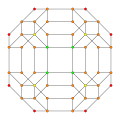
Tetrahedron-centered perspective projection into 3D space, with nearest tetrahedron to the 4D viewpoint rendered in red, and the 4 surrounding octahedra in green. Cells lying on the far side of the polytope have been culled for clarity (although they can be discerned from the edge outlines). The rotation is only of the 3D projection image, in order to show its structure, not a rotation in 4D space. |
Remove ads
Coordinates
Summarize
Perspective
The Cartesian coordinates of the vertices of an origin-centered rectified 5-cell having edge length 2 are:
More simply, the vertices of the rectified 5-cell can be positioned on a hyperplane in 5-space as permutations of (0,0,0,1,1) or (0,0,1,1,1). These construction can be seen as positive orthant facets of the rectified pentacross or birectified penteract respectively.
Remove ads
Related 4-polytopes
Summarize
Perspective
The rectified 5-cell is the vertex figure of the 5-demicube, and the edge figure of the uniform 221 polytope.
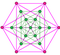
Compound of the rectified 5-cell and its dual
The convex hull the rectified 5-cell and its dual (of the same long radius) is a nonuniform polychoron composed of 30 cells: 10 tetrahedra, 20 octahedra (as triangular antiprisms), and 20 vertices. Its vertex figure is a triangular bifrustum.
Pentachoron polytopes
The rectified 5-cell is one of 9 Uniform 4-polytopes constructed from the [3,3,3] Coxeter group.
Semiregular polytopes
The rectified 5-cell is second in a dimensional series of semiregular polytopes. Each progressive uniform polytope is constructed as the vertex figure of the previous polytope. Thorold Gosset identified this series in 1900 as containing all regular polytope facets, containing all simplexes and orthoplexes (tetrahedrons and octahedrons in the case of the rectified 5-cell). The Coxeter symbol for the rectified 5-cell is 021.
Isotopic polytopes
Remove ads
Notes
References
External links
Wikiwand - on
Seamless Wikipedia browsing. On steroids.
Remove ads





 ,
,  ...
...




























 ...
...





 ...
...