Top Qs
Timeline
Chat
Perspective
Southern Vietnam
One of the three geographical regions in Vietnam From Wikipedia, the free encyclopedia
Remove ads
Southern Vietnam (Vietnamese: Nam Bộ) is one of the three geographical regions of Vietnam, the other two being Northern and Central Vietnam. It includes 2 administrative subregions, which in turn are divided into 19 First Tier units, of which 17 are provinces and 2 are municipalities.
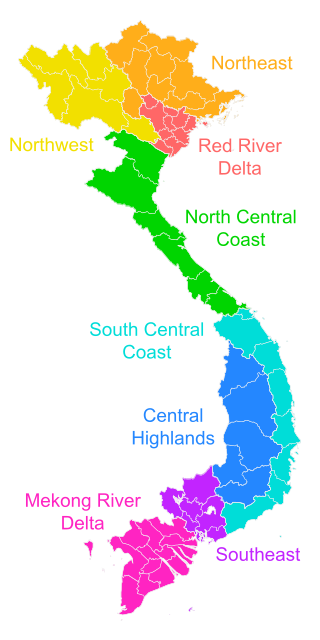
Known as Nam Bộ today in Vietnamese, it was historically called Gia Định (1779–1832), Nam Kỳ (1832–1945, during Nguyễn's Lục tỉnh and French Cochinchina), Nam Bộ (1945 to the present, encompassing the Empire of Vietnam and the Democratic Republic of Vietnam), and Nam Phần, sometimes Nam Việt (1948–1975, during the State of Vietnam and the Republic of Vietnam).[1] Cochinchina is a historical exonym for this region during the colonial period, which referred to the entire domain of Đàng Trong in the feudal period. A more accurate term for the southern region is Lower Cochinchina, or Basse-Cochinchine in French.
In the early period, Southern Vietnam was under the Kingdom of Funan (from the 1st century CE until the 7th century CE) and later the Khmer Empire (from the 9th century CE to the 15th century). Southern Vietnam was conquered by the Nguyễn lords in the 17th and 18th centuries.[2]
The main ethnicities in Southern Vietnam are Kinh, Khmer and Hoa.[3]
Remove ads
Administration
^† Municipality (thành phố trực thuộc trung ương)
Remove ads
See also
- Northern, Central and Southern Vietnam
- Regions of Vietnam
- Six Provinces of Southern Vietnam or Lục Tỉnh
- Cochinchina – a historical exonym for South Vietnam
- Champa, ancient coastal states in modern Central and South Vietnam
References
External links
Wikiwand - on
Seamless Wikipedia browsing. On steroids.
Remove ads
