Top Qs
Timeline
Chat
Perspective
Provinces of Vietnam
List of Vietnam's subdivisions From Wikipedia, the free encyclopedia
Remove ads
Vietnam is divided into 34 first-level subdivisions, comprising 28 provinces (tỉnh) and six municipalities under the command of the central government (Vietnamese: thành phố trực thuộc trung ương).
This article's factual accuracy may be compromised due to out-of-date information. The reason given is: The province-level administrative subdivisions of Vietnam have been reorganized following major governmental reforms in 2025. (June 2025) |
Municipalities are the highest-ranked cities in Vietnam.[1] Municipalities are centrally-controlled cities and have special status equal to that of the provinces.
The provinces and municipalities are divided into communes (xã), wards (phường) and special administrative regions (đặc khu) as the second-tier units.
Remove ads
Governance
Summarize
Perspective
Provincial Committee of the Communist Party
Provincial Committee of the Communist Party (Đảng bộ Đảng Cộng sản cấp tỉnh or Tỉnh ủy Đảng Cộng sản, simply Tỉnh ủy - Provincial Committee for short) is a provincial subordinate of the Communist Party of Vietnam. Since Vietnam is a one party state, the provincial committee of the Communist Party is the most prominent organ of provincial governance.
Each provincial committee of the Communist Party is headed by a Secretary (Bí thư). The Secretary is de facto leader of the province.
People's Council
The legislative branch of a province is the People's Council (Hội đồng Nhân dân or HÐND for short). The People's Council votes on the policy, regulations and orders for development of the province.
Members of the People's Council are called delegates or councillors (đại biểu) and are elected by people living within that province. It is equivalent to the legislative National Assembly of Vietnam. The People's Council is headed by a Chairman (Chủ tịch) and a Vice Chairman (Phó Chủ tịch).
The number of councillors varies from province to province, depending on the population of that province. The People's Council appoints a People's Committee, which acts as the executive arm of the provincial governance. This arrangement is a somewhat simplified version of the situation in Vietnam's national government. Provincial governments are subordinates to the central government.
People's Committee
The executive branch of a province is the People's Committee (Ủy ban Nhân dân or UBND for short). The People's Committee is responsible for implementing policy and executing laws and orders. The People's Committee is equivalent to the executive Government of Vietnam. People's Committee also manages the provincial departments (Sở) which are equivalent to the Ministries.
Members of the People's Committee are called commissioners (Ủy viên). The People's Committee is headed by a Chairman (Chủ tịch) and Vice Chairmen (Phó Chủ tịch), and consists of between 4 and 7 commissioners. The number of commissioners depends on the population of the province. The chairman and Vice Chairmen of the People's Committee are also councillors of the People's Council.
People's Court
The judiciary branch of a province is the People's Court (Tòa án Nhân dân or TAND for short). The People's Court is responsible for judiciary processes and trials. The People's Court is equivalent to the judiciary Supreme People's Court of Vietnam.
The People's Court is headed by a Chief Judge (Chánh án) and consists of a number of judges (thẩm phán).
Police Department
The provincial police department is under direct command of the Ministry of Public Security.
State Treasury
Provincial Military Command
Remove ads
List and statistics
Summarize
Perspective
By the end of 2024, the population of Vietnam was 101,343,800.[2] The most populous top-level administrative unit is Hồ Chí Minh City, one of the six centrally governed cities, having 14,002,598 people living within its official boundary. The second most populous administrative unit is Hà Nội with 8,807,523 people. The least populous is Lai Châu, a mountainous province in the remote northwest with 512,601 people.
In land area, the largest province is Lâm Đồng with 24,233.09 km2, the smallest is Hưng Yên (2,514.81 km2), located in the populous Red River Delta region.
The following is a table of Vietnam's provinces broken down by population and area.[3] Municipalities are written in bold.
Remove ads
Regions
Summarize
Perspective
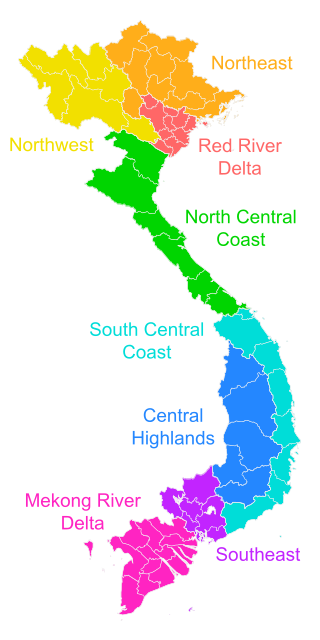
The Vietnamese government often groups the various provinces into eight regions, which are often grouped into three macro-regions: Northern, Central and Southern. These regions are not always used, and alternative classifications are possible. The regions include:
^† Municipality (thành phố trực thuộc trung ương)
Remove ads
Historical provinces of Vietnam
- Ái Châu – existed during the third Chinese domination.
- An Xuyên – existed from 1956 until the Vietnamese reunification of 1976.
- Bà Rịa–Vũng Tàu – existed from 1991 until merged with Ho Chi Minh City in 2025.
- Bạc Liêu – existed from 1997 until merged with Cà Mau province in 2025.
- Bắc Giang – existed from 1997 until merged with Bắc Ninh province in 2025.
- Bắc Kạn – existed from 1997 until merged with Thái Nguyên province in 2025.
- Bắc Thái – administrative grouping of Bắc Kạn and Thái Nguyên provinces between 1965 and 1996.
- Bến Tre – existed from 1976 until merged with Vĩnh Long province in 2025.
- Biên Hòa – existed from 1832 until the Vietnamese reunification of 1976.
- Bình Dương – existed from 1997 until merged with Hồ Chí Minh City province in 2025.
- Bình Định – existed from 1989 until merged with Gia Lai province in 2025.
- Bình Phước – existed from 1997 until merged with Đồng Nai province in 2025.
- Bình Thuận – existed from 1991 until merged with Lâm Đồng province in 2025.
- Bình Trị Thiên – administrative grouping of Quảng Bình, Quảng Trị and Thừa Thiên – Huế provinces between 1976 and 1992.
- Bình Tuy – existed from 1956 until the Vietnamese reunification of 1976.
- Chợ Lớn – existed from 1900 until 1957.
- Chương Thiện – existed from 1961 until the Vietnamese reunification of 1976.
- Cửu Long – administrative grouping of Vĩnh Long and Vĩnh Bình provinces between 1976 and 1992.
- Đắk Nông – existed from 2004 until merged with Lâm Đồng province in 2025.
- Định Tường – existed from 1832 until the Vietnamese reunification of 1976.
- Gia Định – existed from 1832, became Hồ Chí Minh City following the Vietnamese reunification of 1976.
- Gia Lai – Kon Tum – administrative grouping of Gia Lai and Kon Tum provinces between 1975 and 1991.
- Gò Công – existed from 1900 until the Vietnamese reunification of 1976.
- Hà Bắc – administrative grouping of Bắc Giang and Bắc Ninh provinces between 1962 and 1996.
- Hà Đông – existed from 1904 until 1965.
- Hà Giang – existed from 1991 until merged with Tuyên Quang province in 2025.
- Hà Nam – existed from 1991 until merged with Ninh Bình province in 2025.
- Hà Nam Ninh – administrative grouping of Hà Nam, Nam Định and Ninh Bình provinces between 1975 and 1991.
- Hà Sơn Bình – administrative grouping of Hà Tây (old) and Hòa Bình provinces between 1975 and 1991.
- Hà Tây – existed from 1965 to 1975 and 1991 until 2008, when it was merged into Hà Nội.
- Hà Tuyên – administrative grouping of Hà Giang and Tuyên Quang provinces between 1975 and 1991.
- Hải Hưng – administrative grouping of Hải Dương and Hưng Yên provinces between 1968 and 1996.
- Hải Dương – existed from 1997 until merged with Haiphong city in 2025.
- Hậu Giang – existed from 2004 until merged with Cần Thơ city in 2025.
- Hậu Nghĩa – existed from 1963 until the Vietnamese reunification of 1976.
- Hòa Bình – existed from 1991 until merged with Phú Thọ province in 2025.
- Hoàng Liên Sơn – administrative grouping of Lào Cai and Yên Bái provinces between 1975 and 1991.
- Hưng Hóa – existed from 1831 until 1903.
- Kiên Giang – existed from 1976 until merged with An Giang province in 2025.
- Kiến An – existed from 1888 until merged with Hải Phòng City in 1962.
- Kon Tum – existed from 1991 until merged with Quảng Ngãi province in 2025.
- Long An – existed from 1976 until merged with Tây Ninh province in 2025.
- Long Khánh – existed from 1956, became Đồng Nai province following the Vietnamese reunification of 1976.
- Minh Hải – administrative grouping of Cà Mau and Bạc Liêu provinces between 1976 and 1996.
- Nam Định – existed from 1991 until merged with Ninh Bình province in 2025.
- Nghệ Tĩnh – administrative grouping of Nghệ An and Hà Tĩnh provinces between 1976 and 1991.
- Nghĩa Bình – administrative grouping of Quảng Ngãi and Bình Định provinces between 1975 and 1989.
- Ninh Thuận – existed from 1992 until merged with Khánh Hòa province in 2025.
- Phú Bổn – in 1962 split from Pleiku province until 1976.
- Phú Khánh – administrative grouping of Phú Yên and Khánh Hòa provinces between 1975 and 1989.
- Phú Yên – existed from 1989 until merged with Đắk Lắk province in 2025.
- Phúc Yên – existed from 1904 until merged with Vĩnh Yên in 1950.
- Phước Long – existed from 1956 until the Vietnamese reunification of 1976.
- Phước Thành – existed from 1959 until 1965.
- Phước Tuy – existed from 1956 until the Vietnamese reunification of 1976.
- Quảng Bình – existed from 1989 until merged with Quảng Trị province in 2025.
- Quảng Đức – existed from 1959 until 1976.
- Quảng Nam – existed from 1997 until merged with Đà Nẵng city in 2025.
- Quảng Nam–Đà Nẵng/Quảng Đà – administrative grouping of Quảng Nam provinces and Đà Nẵng city, between 1975 and 1996.
- Quảng Tín – existed from 1962 until the Vietnamese reunification of 1976.
- Sa Đéc – existed from 1900 until the Vietnamese reunification of 1976.
- Sóc Trăng – existed from 1991 until merged with Cần Thơ city in 2025.
- Sông Bé – administrative grouping of Bình Dương and Bình Phước provinces between 1976 and 1997.
- Tân An – existed from 1900 until 1956.
- Thái Bình – existed from 1890 until merged with Hưng Yên province in 2025.
- Thừa Thiên Huế, the southernmost province of Vietnam's North Central Coast region, existed until 2025 of which the whole province is now direct-controlled as a municipality.
- Thuận Hải – administrative grouping of Ninh Thuận and Bình Thuận provinces between 1975 and 1991.
- Tiền Giang – existed from 1976 until merged with Đồng Tháp province in 2025.
- Trà Vinh – existed from 1992 until merged with Vĩnh Long province in 2025.
- Tuyên Đức – existed from 1958 until 1976.
- Vĩnh Bình – existed from 1956 until the Vietnamese reunification of 1976.
- Vĩnh Phú – administrative grouping of Vĩnh Phúc and Phú Thọ provinces between 1968 and 1996.
- Vĩnh Phúc – existed from 1997 until merged with Phú Thọ province in 2025.
- Yên Bái – existed from 1991 until merged with Lào Cai province in 2025.
Remove ads
See also
References
External links
Wikiwand - on
Seamless Wikipedia browsing. On steroids.
Remove ads