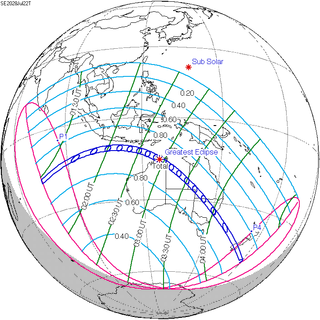
Solar eclipse of July 22, 2028
Total eclipse From Wikipedia, the free encyclopedia
A total solar eclipse will occur at the Moon's descending node of orbit on Saturday, 22 July 2028,[1] with a magnitude of 1.056. A solar eclipse occurs when the Moon passes between Earth and the Sun, thereby totally or partly obscuring the image of the Sun for a viewer on Earth. A total solar eclipse occurs when the Moon's apparent diameter is larger than the Sun's, blocking all direct sunlight, turning day into darkness. Totality occurs in a narrow path across Earth's surface, with the partial solar eclipse visible over a surrounding region thousands of kilometres wide. Occurring about 1.8 days before perigee (on 23 July 2028, at 23:20 UTC), the Moon's apparent diameter will be larger.[2]

The central line of the path of the eclipse will cross the Australian continent from the Kimberley region in the north-west and continue in a south-easterly direction through Western Australia, the Northern Territory, south-west Queensland and New South Wales, close to the towns of Wyndham, Kununurra, Tennant Creek, Birdsville, Bourke and Dubbo, and continuing on through the centre of Sydney, where the eclipse will have a duration of over three minutes. It will also cross Queenstown and Dunedin, New Zealand. Totality will also be viewable from two of Australia's external territories: Christmas Island and the Cocos (Keeling) Islands. A partial eclipse will be visible for parts of Southeast Asia, Australia, and Oceania.[citation needed]
This is the first time Sydney will experience a total solar eclipse since 26 March 1857 and will be the last until 3 June 2858.[3]
Details of the totality by location
| Country or Territory | City or Town | Start of partial eclipse (Local Time) |
Start of total eclipse (Local Time) |
End of total eclipse (Local Time) |
Duration of total eclipse |
End of partial eclipse (Local Time) |
Magnitude |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| West Island | 07:03:37 | 08:12:03 | 08:15:29 | 3 min 27 s | 09:35:13 | 1,048 | |
| Flying Fish Cove | 07:39:41 | 08:54:49 | 08:58:42 | 3 min 53 s | 10:25:35 | 1,052 | |
| Wyndham, Western Australia | 09:25:54 | 10:57:53 | 11:00:48 | 3 min 22 s | 12:31:30 | 1,056 | |
| Kununurra, Western Australia | 09:27:48 | 10:59:41 | 11:02:35 | 2 min 54 s | 12:33:09 | 1,056 | |
| Tennant Creek, Northern Territory | 11:16:50 | 12:48:01 | 12:51:25 | 3 min 23 s | 14:17:33 | 1,056 | |
| Bedourie, Queensland | 12:06:46 | 13:34:24 | 13:38:55 | 4 min 31 s | 14:59:30 | 1,054 | |
| Bourke, New South Wales | 12:27:18 | 13:50:11 | 13:54:16 | 4 min 05 s | 15:09:54 | 1,052 | |
| Nyngan, New South Wales | 12:31:11 | 13:53:15 | 13:56:30 | 3 min 15 s | 15:10:53 | 1,052 | |
| Dubbo, New South Wales | 12:34:35 | 13:55:23 | 13:59:13 | 3 min 51 s | 15:12:20 | 1,051 | |
| Orange, New South Wales | 12:36:16 | 13:57:09 | 13:59:29 | 2 min 18 s | 15:12:48 | 1,051 | |
| Wollongong, New South Wales | 12:40:27 | 13:59:42 | 14:02:33 | 2 min 51 s | 15:14:21 | 1,051 | |
| Sydney, New South Wales | 12:40:42 | 13:59:33 | 14:03:22 | 3 min 48 s | 15:14:40 | 1,051 | |
| Central Coast, New South Wales | 12:40:56 | 14:00:37 | 14:03:11 | 2 min 54 s | 15:14:54 | 1,051 | |
| Queenstown | 15:07:26 | 16:15:07 | 16:18:01 | 2 min 55 s | 17:20:06 | 1,045 | |
| Dunedin | 15:09:01 | 16:15:48 | 16:18:39 | 2 min 51 s | 17:15:24 (sunset) | 1,045 | |
| Antipodes Islands | 15:14:08 | 16:17:21 | 16:19:55 | 2 min 34 s | 16:28:47 (sunset) | 1,042 |
Eclipse details
Summarize
Perspective
Shown below are two tables displaying details about this particular solar eclipse. The first table outlines times at which the moon's penumbra or umbra attains the specific parameter, and the second table describes various other parameters pertaining to this eclipse.[4]
| Event | Time (UTC) |
|---|---|
| First Penumbral External Contact | 2028 July 22 at 00:28:44.4 UTC |
| First Umbral External Contact | 2028 July 22 at 01:31:51.9 UTC |
| First Central Line | 2028 July 22 at 01:33:16.8 UTC |
| First Umbral Internal Contact | 2028 July 22 at 01:34:42.2 UTC |
| Greatest Duration | 2028 July 22 at 02:53:30.9 UTC |
| Greatest Eclipse | 2028 July 22 at 02:56:39.6 UTC |
| Ecliptic Conjunction | 2028 July 22 at 03:02:52.3 UTC |
| Equatorial Conjunction | 2028 July 22 at 03:17:00.0 UTC |
| Last Umbral Internal Contact | 2028 July 22 at 04:18:21.6 UTC |
| Last Central Line | 2028 July 22 at 04:19:49.0 UTC |
| Last Umbral External Contact | 2028 July 22 at 04:21:15.8 UTC |
| Last Penumbral External Contact | 2028 July 22 at 05:24:22.4 UTC |
| Parameter | Value |
|---|---|
| Eclipse Magnitude | 1.05602 |
| Eclipse Obscuration | 1.11518 |
| Gamma | −0.60557 |
| Sun Right Ascension | 08h08m03.8s |
| Sun Declination | +20°10'53.0" |
| Sun Semi-Diameter | 15'44.5" |
| Sun Equatorial Horizontal Parallax | 08.7" |
| Moon Right Ascension | 08h07m16.7s |
| Moon Declination | +19°36'14.4" |
| Moon Semi-Diameter | 16'24.3" |
| Moon Equatorial Horizontal Parallax | 1°00'12.3" |
| ΔT | 73.2 s |
Eclipse season
This eclipse is part of an eclipse season, a period, roughly every six months, when eclipses occur. Only two (or occasionally three) eclipse seasons occur each year, and each season lasts about 35 days and repeats just short of six months (173 days) later; thus two full eclipse seasons always occur each year. Either two or three eclipses happen each eclipse season. In the sequence below, each eclipse is separated by a fortnight.
| July 6 Ascending node (full moon) | July 22 Descending node (new moon) |
|---|---|
 |  |
| Partial lunar eclipse Lunar Saros 120 | Total solar eclipse Solar Saros 146 |
Related eclipses
Eclipses in 2028
- A partial lunar eclipse on January 12.
- An annular solar eclipse on January 26.
- A partial lunar eclipse on July 6.
- A total solar eclipse on 22 July.
- A total lunar eclipse on December 31.
Metonic
- Preceded by: Solar eclipse of October 2, 2024
- Followed by: Solar eclipse of May 9, 2032
Tzolkinex
- Preceded by: Solar eclipse of June 10, 2021
- Followed by: Solar eclipse of September 2, 2035
Half-Saros
- Preceded by: Lunar eclipse of July 16, 2019
- Followed by: Lunar eclipse of July 27, 2037
Tritos
- Preceded by: Solar eclipse of August 21, 2017
- Followed by: Solar eclipse of June 21, 2039
Solar Saros 146
- Preceded by: Solar eclipse of July 11, 2010
- Followed by: Solar eclipse of August 2, 2046
Inex
- Preceded by: Solar eclipse of August 11, 1999
- Followed by: Solar eclipse of July 1, 2057
Triad
- Preceded by: Solar eclipse of September 21, 1941
- Followed by: Solar eclipse of May 24, 2115
Solar eclipses of 2026–2029
This eclipse is a member of a semester series. An eclipse in a semester series of solar eclipses repeats approximately every 177 days and 4 hours (a semester) at alternating nodes of the Moon's orbit.[5]
The partial solar eclipses on June 12, 2029 and December 5, 2029 occur in the next lunar year eclipse set.
| Solar eclipse series sets from 2026 to 2029 | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Ascending node | Descending node | |||||
| Saros | Map | Gamma | Saros | Map | Gamma | |
| 121 | February 17, 2026 Annular |
−0.97427 | 126 | August 12, 2026 Total |
0.89774 | |
| 131 | February 6, 2027 Annular |
−0.29515 | 136 | August 2, 2027 Total |
0.14209 | |
| 141 | January 26, 2028 Annular |
0.39014 | 146 | July 22, 2028 Total |
−0.60557 | |
| 151 | January 14, 2029 Partial |
1.05532 | 156 | July 11, 2029 Partial |
−1.41908 | |
Saros 146
This eclipse is a part of Saros series 146, repeating every 18 years, 11 days, and containing 76 events. The series started with a partial solar eclipse on September 19, 1541. It contains total eclipses from May 29, 1938 through October 7, 2154; hybrid eclipses from October 17, 2172 through November 20, 2226; and annular eclipses from November 30, 2244 through August 10, 2659. The series ends at member 76 as a partial eclipse on December 29, 2893. Its eclipses are tabulated in three columns; every third eclipse in the same column is one exeligmos apart, so they all cast shadows over approximately the same parts of the Earth.
The longest duration of totality was produced by member 26 at 5 minutes, 21 seconds on June 30, 1992, and the longest duration of annularity will be produced by member 63 at 3 minutes, 30 seconds on August 10, 2659. All eclipses in this series occur at the Moon’s descending node of orbit.[6]
| Series members 16–37 occur between 1801 and 2200: | ||
|---|---|---|
| 16 | 17 | 18 |
 March 13, 1812 |
 March 24, 1830 |
 April 3, 1848 |
| 19 | 20 | 21 |
 April 15, 1866 |
 April 25, 1884 |
 May 7, 1902 |
| 22 | 23 | 24 |
 May 18, 1920 |
 May 29, 1938 |
 June 8, 1956 |
| 25 | 26 | 27 |
 June 20, 1974 |
 June 30, 1992 |
 July 11, 2010 |
| 28 | 29 | 30 |
 July 22, 2028 |
 August 2, 2046 |
 August 12, 2064 |
| 31 | 32 | 33 |
 August 24, 2082 |
 September 4, 2100 |
 September 15, 2118 |
| 34 | 35 | 36 |
 September 26, 2136 |
 October 7, 2154 |
 October 17, 2172 |
| 37 | ||
 October 29, 2190 | ||
Metonic series
The metonic series repeats eclipses every 19 years (6939.69 days), lasting about 5 cycles. Eclipses occur in nearly the same calendar date. In addition, the octon subseries repeats 1/5 of that or every 3.8 years (1387.94 days). All eclipses in this table occur at the Moon's descending node.
| 21 eclipse events between July 22, 1971 and July 22, 2047 | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| July 22 | May 9–11 | February 26–27 | December 14–15 | October 2–3 |
| 116 | 118 | 120 | 122 | 124 |
 July 22, 1971 |
 May 11, 1975 |
 February 26, 1979 |
 December 15, 1982 |
 October 3, 1986 |
| 126 | 128 | 130 | 132 | 134 |
 July 22, 1990 |
 May 10, 1994 |
 February 26, 1998 |
 December 14, 2001 |
 October 3, 2005 |
| 136 | 138 | 140 | 142 | 144 |
 July 22, 2009 |
 May 10, 2013 |
 February 26, 2017 |
 December 14, 2020 |
 October 2, 2024 |
| 146 | 148 | 150 | 152 | 154 |
 July 22, 2028 |
 May 9, 2032 |
 February 27, 2036 |
 December 15, 2039 |
 October 3, 2043 |
| 156 | ||||
 July 22, 2047 | ||||
Tritos series
This eclipse is a part of a tritos cycle, repeating at alternating nodes every 135 synodic months (≈ 3986.63 days, or 11 years minus 1 month). Their appearance and longitude are irregular due to a lack of synchronization with the anomalistic month (period of perigee), but groupings of 3 tritos cycles (≈ 33 years minus 3 months) come close (≈ 434.044 anomalistic months), so eclipses are similar in these groupings.
| Series members between 1801 and 2200 | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|
 April 4, 1810 (Saros 126) |
 March 4, 1821 (Saros 127) |
 February 1, 1832 (Saros 128) |
 December 31, 1842 (Saros 129) |
 November 30, 1853 (Saros 130) |
 October 30, 1864 (Saros 131) |
 September 29, 1875 (Saros 132) |
 August 29, 1886 (Saros 133) |
 July 29, 1897 (Saros 134) |
 June 28, 1908 (Saros 135) |
 May 29, 1919 (Saros 136) |
 April 28, 1930 (Saros 137) |
 March 27, 1941 (Saros 138) |
 February 25, 1952 (Saros 139) |
 January 25, 1963 (Saros 140) |
 December 24, 1973 (Saros 141) |
 November 22, 1984 (Saros 142) |
 October 24, 1995 (Saros 143) |
 September 22, 2006 (Saros 144) |
 August 21, 2017 (Saros 145) |
 July 22, 2028 (Saros 146) |
 June 21, 2039 (Saros 147) |
 May 20, 2050 (Saros 148) |
 April 20, 2061 (Saros 149) |
 March 19, 2072 (Saros 150) |
 February 16, 2083 (Saros 151) |
 January 16, 2094 (Saros 152) |
 December 17, 2104 (Saros 153) |
 November 16, 2115 (Saros 154) |
 October 16, 2126 (Saros 155) |
 September 15, 2137 (Saros 156) |
 August 14, 2148 (Saros 157) |
 July 15, 2159 (Saros 158) |
 June 14, 2170 (Saros 159) |
 May 13, 2181 (Saros 160) |
 April 12, 2192 (Saros 161) | ||||
Inex series
This eclipse is a part of the long period inex cycle, repeating at alternating nodes, every 358 synodic months (≈ 10,571.95 days, or 29 years minus 20 days). Their appearance and longitude are irregular due to a lack of synchronization with the anomalistic month (period of perigee). However, groupings of 3 inex cycles (≈ 87 years minus 2 months) comes close (≈ 1,151.02 anomalistic months), so eclipses are similar in these groupings.
| Series members between 1801 and 2200 | ||
|---|---|---|
 December 9, 1825 (Saros 139) |
 November 20, 1854 (Saros 140) |
 October 30, 1883 (Saros 141) |
 October 10, 1912 (Saros 142) |
 September 21, 1941 (Saros 143) |
 August 31, 1970 (Saros 144) |
 August 11, 1999 (Saros 145) |
 July 22, 2028 (Saros 146) |
 July 1, 2057 (Saros 147) |
 June 11, 2086 (Saros 148) |
 May 24, 2115 (Saros 149) |
 May 3, 2144 (Saros 150) |
 April 12, 2173 (Saros 151) |
||
References
External links
Wikiwand - on
Seamless Wikipedia browsing. On steroids.