Prostaglandin H2
Chemical compound From Wikipedia, the free encyclopedia
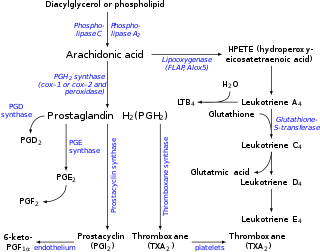
Prostaglandin H2 (PGH2), or prostaglandin H2 (PGH2), is a type of prostaglandin and a precursor for many other biologically significant molecules. It is synthesized from arachidonic acid in a reaction catalyzed by a cyclooxygenase enzyme.[2] The conversion from arachidonic acid to prostaglandin H2 is a two-step process. First, COX-1 catalyzes the addition of two free oxygens to form the 1,2-dioxane bridge and a peroxide functional group to form prostaglandin G2 (PGG2).[3] Second, COX-2 reduces the peroxide functional group to a secondary alcohol, forming prostaglandin H2. Other peroxidases like hydroquinone have been observed to reduce PGG2 to PGH2.[4] PGH2 is unstable at room temperature, with a half life of 90–100 seconds,[1] so it is often converted into a different prostaglandin.
 | |
| Names | |
|---|---|
| Other names
PGH2, Endoperoxide H2, Prostaglandin R2 | |
| Identifiers | |
3D model (JSmol) |
|
| ChEBI | |
| ChemSpider | |
| MeSH | Prostaglandin+H2 |
PubChem CID |
|
| UNII | |
CompTox Dashboard (EPA) |
|
| |
| |
| Properties | |
| C20H32O5 | |
| Molar mass | 352.465 g/mol |
| Density | 1.129 ± 0.06 g/mL |
| Boiling point | 490 ± 40.0 °C |
| 0.034 g/L | |
Except where otherwise noted, data are given for materials in their standard state (at 25 °C [77 °F], 100 kPa).
| |
It is acted upon by:
- prostacyclin synthase to create prostacyclin
- thromboxane-A synthase to create thromboxane A2 and 12-(S)-hydroxy-5Z,8E,10E-heptadecatrienoic acid (HHT) (see 12-Hydroxyheptadecatrienoic acid)
- prostaglandin D2 synthase to create prostaglandin D2
- prostaglandin E synthase to create prostaglandin E2
It rearranges non-enzymatically to:
- A mixture of 12-(S)-hydroxy-5Z,8E,10E-heptadecatrienoic acid (HHT) and 12-(S)-hydroxy-5Z,8Z,10E-heptadecatrienoic acid (see 12-hydroxyheptadecatrienoic acid)
Functions of prostaglandin H2:
- regulating the constriction and dilation of blood vessels
- stimulating platelet aggregation
- binds to thromboxane receptor on platelets' cell membranes to trigger platelet migration and adhesion to other platelets.[5]
Effects of aspirin on prostaglandin H2:
- Aspirin has been hypothesized to block the conversion of arachidonic acid to prostaglandin

References
Wikiwand - on
Seamless Wikipedia browsing. On steroids.
