Loading AI tools
Chemical compound From Wikipedia, the free encyclopedia
Oxyfedrine, sold under the brand names Ildamen and Myofedrin among others, is a sympathomimetic agent and coronary vasodilator which is used in the treatment of coronary heart disease, angina pectoris, and acute myocardial infarction.[1][3][4][5][6][7] It is taken by mouth or intravenously.[1]
 | |
| Clinical data | |
|---|---|
| Trade names | Ildamen, Modacor, Myofedrin |
| Other names | Oxyfedrin; Oxyphedrine; Oxyphedrin; Oxifedrine; Oxifedrin; Oxiphedrine; Oxiphedrin |
| AHFS/Drugs.com | International Drug Names |
| Routes of administration | Oral, intravenous[1] |
| Drug class | Sympathomimetic; Coronary vasodilator; β-Adrenergic receptor partial agonist; Norepinephrine releasing agent |
| ATC code | |
| Pharmacokinetic data | |
| Bioavailability | Oral: 85%[1] |
| Protein binding | Almost 100%[1] |
| Metabolites | • Norephedrine[2] |
| Elimination half-life | 4.2 hours[1] |
| Excretion | Urine (active metabolites 90%)[1] |
| Identifiers | |
| |
| CAS Number | |
| PubChem CID | |
| ChemSpider | |
| UNII | |
| KEGG | |
| ChEMBL | |
| CompTox Dashboard (EPA) | |
| Chemical and physical data | |
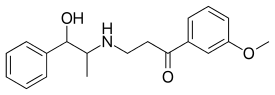
| Formula | C19H23NO3 |
| Molar mass | 313.397 g·mol−1 |
| 3D model (JSmol) | |
| |
| |
| (verify) | |
The drug acts as a β-adrenergic receptor partial agonist.[1][7] It may also act as a norepinephrine releasing agent via its major active metabolite norephedrine.[2] Oxyfedrine is a phenethylamine and amphetamine derivative.[6][7]
Oxyfedrine has been marketed in Europe, Hong Kong, India, Central America, and elsewhere.[4][8][9] It appears to remain marketed only in India.[9]
Oxyfedrine is a β-adrenergic receptor partial agonist.[1][7] It appears to be non-selective for the β1- and β2-adrenergic receptors.[7] It is selective for the β-adrenergic receptors over the α-adrenergic receptors.[7] However, it has also been reported to interact with the α-adrenergic receptors at high concentrations, acting as a partial agonist or antagonist of these receptors.[7] Norephedrine, a norepinephrine releasing agent, is a major active metabolite of oxyfedrine, and hence oxyfedrine may additionally act as an indirectly acting sympathomimetic.[2]
It has been found to depress the tonicity of coronary vessels, improve myocardial metabolism (so that heart can sustain hypoxia better) and also exert a positive chronotropic and inotropic effects,[1] thereby not precipitating angina pectoris. The latter property (positive chronotropic and inotropic effects) is particularly important, because other vasodilators used in angina may be counter productive causing coronary steal phenomenon.[additional citation(s) needed]
The drug is chemically and pharmacologically unrelated to any other antianginal drugs.[1]
Oxyfedrine's oral bioavailability is 85%.[1] The plasma protein binding is almost 100%.[1] Its elimination half-life is 4.2 hours.[1] Norephedrine is a major active metabolite of oxyfedrine.[2] The excretion of the active metabolites of oxyfedrine is 90% in urine.[1] About 75 to 100% of oxyfedrine is excreted as norephedrine.[2]
Oxyfedrine is a substituted phenethylamine and amphetamine derivative.[7] It is l-norephedrine with a bulky and lipophilic 3-methoxypropiophenone substituent at the nitrogen atom.[7]
Mannich condensation of phenylpropanolamine (1) with formaldehyde and m-acetanisole (3-acetylanisole) (2) yields oxyfedrine (3).[10]

Synergistic effects of oxyfedrine with antibiotics against bacteria have been suggested.[11]
Seamless Wikipedia browsing. On steroids.
Every time you click a link to Wikipedia, Wiktionary or Wikiquote in your browser's search results, it will show the modern Wikiwand interface.
Wikiwand extension is a five stars, simple, with minimum permission required to keep your browsing private, safe and transparent.