Motala
Place in Östergötland, Sweden From Wikipedia, the free encyclopedia
Motala (Swedish pronunciation: [ˈmûːˌtɑːla] ⓘ)[2] is a locality and the seat of Motala Municipality, Östergötland County, Sweden with a municipal population of 43,717 inhabitants in 2024.[3] It is the third largest city of Östergötland, following Linköping and Norrköping. Motala is situated on the eastern shore of Lake Vättern and is regarded as the main centre of both the Göta Canal and the surrounding lake region.
Motala | |
|---|---|
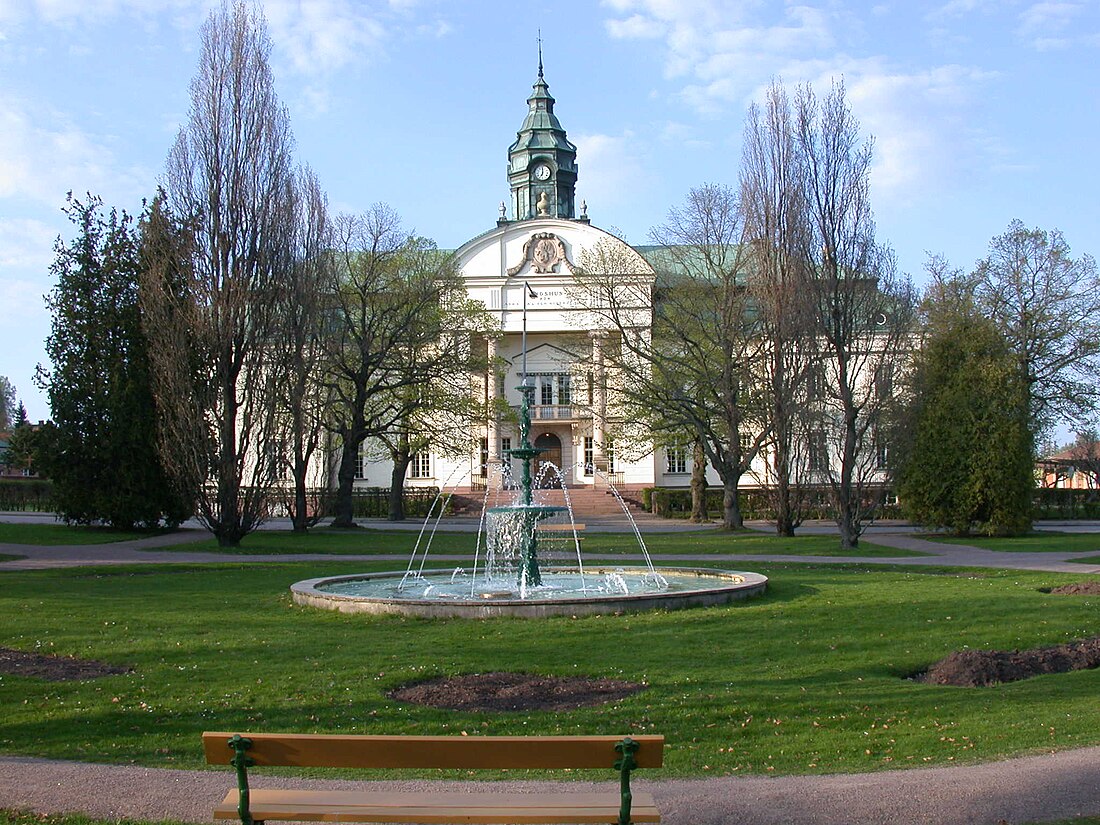
 The old court house | |
| Coordinates: 58°32′N 15°02′E | |
| Country | Sweden |
| Province | Östergötland |
| County | Östergötland County |
| Municipality | Motala Municipality |
| Area | |
• Total | 20.56 km2 (7.94 sq mi) |
| Population (31 December 2023)[1] | |
• Total | 31 367 |
| Time zone | UTC+1 (CET) |
| • Summer (DST) | UTC+2 (CEST) |
History
Summarize
Perspective

Motala Church dates from the 13th century. For several centuries, Motala remained a small village, mainly regarded as a stopping post on the road to the nearby town of Vadstena, one of the cultural centres of medieval Sweden. However, King Gustav Vasa had a manor house built at Motala and later Queen Kristina had a summer residence built at the spa resort of Medevi, 20 km (12.4 mi) north of the town.
When the Göta Canal was built in the early 19th century, Motala became an important town for the trade on the canal. The builder of the canal, Baltzar von Platen, has his grave beside it. The town received the minor privilege status of köping in 1823, while full city rights were granted as of April 1, 1881. With the Swedish municipal reform of 1971, Motala became the seat of Motala Municipality.
Motala Verkstad is an engineering company specialising in bridge and railway construction equipment. In the 1870 science fiction novel Twenty Thousand Leagues Under the Seas by Jules Verne, the prow of the submarine Nautilus was built at Motala Verkstad. Later major Swedish industrial manufacturers such as Electrolux and Luxor had their main factories built in the city.
In 1963, Tetra Pak installed the first Tetra Brik packaging machine in Motala.
Climate
Motala has a temperate climate. Lake Vättern provides Motala with slightly cooler summers and milder winters compared to areas of inner Östergötland (±0.5–0.9 °C (1–2 °F) compared to the nearby city of Linköping[4]). The warmest month is July with an average daily mean temperature at 16.4 °C (61.5 °F), and an average daytime temperature at 21.6 °C (70.9 °F). The coldest month is February with an average daily mean at −3.3 °C (26.1 °F), and an average daytime temperature at +0.1 °C (32.2 °F).[5] Record temperatures between 1961 and 1990, as registered by Motala Kraftverk weather station, reaches from −26.3 °C (−15.3 °F) in February 1985 to 32.6 °C (90.7 °F) in August 1975. The most recent data is from Swedish Armed Forces' weather station located approximately 30 km north-east of the city centre. Its inland position renders greater diurnal temperature difference. In addition the geographic location makes seasonal lag is less visible compared to station located near Vättern. [6] Motala generally experiences much rainfall, with the wettest month being August with an average of 71 millimetres (2.8 in) of rain. The driest month is March, with an average of 29 millimetres (1.1 in) of rain.[5]
Climate table
| Climate data for Kvarn (1991–2020 averages & extremes since 1901) | |||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Month | Jan | Feb | Mar | Apr | May | Jun | Jul | Aug | Sep | Oct | Nov | Dec | Year |
| Record high °C (°F) | 11.1 (52.0) |
13.1 (55.6) |
16.4 (61.5) |
24.9 (76.8) |
28.6 (83.5) |
30.7 (87.3) |
32.4 (90.3) |
33.6 (92.5) |
26.2 (79.2) |
21.9 (71.4) |
17.5 (63.5) |
12.8 (55.0) |
33.6 (92.5) |
| Mean daily maximum °C (°F) | −0.1 (31.8) |
0.0 (32.0) |
3.9 (39.0) |
10.2 (50.4) |
16.3 (61.3) |
19.2 (66.6) |
21.6 (70.9) |
20.2 (68.4) |
15.1 (59.2) |
9.8 (49.6) |
3.8 (38.8) |
0.8 (33.4) |
10.1 (50.2) |
| Daily mean °C (°F) | −2.7 (27.1) |
−2.8 (27.0) |
0.0 (32.0) |
4.8 (40.6) |
9.9 (49.8) |
13.7 (56.7) |
16.2 (61.2) |
15.0 (59.0) |
10.7 (51.3) |
5.6 (42.1) |
1.5 (34.7) |
−1.4 (29.5) |
5.9 (42.6) |
| Mean daily minimum °C (°F) | −5.3 (22.5) |
−5.6 (21.9) |
−3.9 (25.0) |
−0.6 (30.9) |
3.5 (38.3) |
8.2 (46.8) |
10.8 (51.4) |
9.8 (49.6) |
6.3 (43.3) |
1.4 (34.5) |
−0.8 (30.6) |
−3.6 (25.5) |
1.7 (35.1) |
| Average precipitation mm (inches) | 35.4 (1.39) |
23.8 (0.94) |
28.5 (1.12) |
31.0 (1.22) |
37.5 (1.48) |
44.5 (1.75) |
65.7 (2.59) |
61.1 (2.41) |
58.8 (2.31) |
44.3 (1.74) |
46.0 (1.81) |
39.3 (1.55) |
515.9 (20.31) |
| Source 1: SMHI[7] | |||||||||||||
| Source 2: SMHI Monthly Data 2015–2019[8] | |||||||||||||
| Climate data for Motala 1991–2020 | |||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Month | Jan | Feb | Mar | Apr | May | Jun | Jul | Aug | Sep | Oct | Nov | Dec | Year |
| Mean daily maximum °C (°F) | 2.1 (35.8) |
2.3 (36.1) |
6.3 (43.3) |
12.4 (54.3) |
17.3 (63.1) |
21.1 (70.0) |
22.8 (73.0) |
22.0 (71.6) |
17.5 (63.5) |
11.3 (52.3) |
6.2 (43.2) |
3.5 (38.3) |
11.9 (53.4) |
| Daily mean °C (°F) | 0.0 (32.0) |
−0.1 (31.8) |
2.6 (36.7) |
7.3 (45.1) |
12.2 (54.0) |
16.0 (60.8) |
18.4 (65.1) |
17.6 (63.7) |
13.3 (55.9) |
8.3 (46.9) |
4.2 (39.6) |
1.4 (34.5) |
8.4 (47.1) |
| Mean daily minimum °C (°F) | −2.1 (28.2) |
−2.5 (27.5) |
−1.1 (30.0) |
2.2 (36.0) |
7.1 (44.8) |
10.9 (51.6) |
14.0 (57.2) |
13.4 (56.1) |
9.2 (48.6) |
5.3 (41.5) |
2.2 (36.0) |
−0.5 (31.1) |
4.8 (40.6) |
| Source 1: SMHI Open Data[9] | |||||||||||||
| Source 2: SMHI Average Data 2002–2018[10] | |||||||||||||
| Climate data for Motala | |||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Month | Jan | Feb | Mar | Apr | May | Jun | Jul | Aug | Sep | Oct | Nov | Dec | Year |
| Average temperature Vättern °C | 3.2 |
2.0 |
1.3 |
3.8 |
8.1 |
14.5 |
18.2 |
18.3 |
14.8 |
10.5 |
7.5 |
4.9 |
8.9 |
| Mean daily daylight hours | 7.0 | 10.0 | 12.0 | 15.0 | 17.0 | 18.0 | 17.0 | 15.0 | 13.0 | 11.0 | 8.0 | 6.0 | 12.4 |
| Average Ultraviolet index | 0 | 1 | 2 | 4 | 5 | 6 | 6 | 5 | 4 | 2 | 1 | 0 | 3 |
| Source: Weather Atlas[11] | |||||||||||||
Longwave radio
Summarize
Perspective

Another important episode of Motala history began in 1927, when the Swedish national Motala longwave transmitter station was built. The town marks the middle of a straight line between Sweden's two biggest cities, Stockholm and Gothenburg. Radio programs were transferred from studios in Stockholm to Motala by telephone wire. The call was "Stockholm-Motala". The transmitter operated on 191 kHz until 1962, when the transmissions were moved to Orlunda. Since 1991 there have been no longwave transmissions at all by the Swedish Broadcasting Company, but the Motala transmitter, which is a museum today, sometimes makes low power transmissions which may only be received in the Motala area.
At Ervasteby, near Motala, there is a 332-metre (1,089 ft) tall guyed mast, used for FM- and TV-broadcasting.
Some years before the broadcasting station was established the Luxor company was founded in Motala. Luxor soon became one of the largest radio and later television manufacturers in Sweden. In the 1980s Luxor started producing their own line of computers, like the ABC 80. In 1985 Luxor was acquired by Nokia, and eventually production moved elsewhere.
Main sights
- The Motala Motor Museum (site) contains cars and many hundreds of other period pieces, including motorbikes, racing cars, radios, record players, tools, and many, many, other objects from the first 70 or so years of the 20th century.
- The Swedish Broadcasting Museum with the twin radio towers.
- The Göta Canal with locks.
- The old Motala Works with museums and exhibitions in historical buildings.
- Motala Church, dating back to the 13th Century.
- Motala Museum at Charlottenborg Castle.
- Varamon beach.
- Baltzar Von Platen's gravesite, located along the Göta Canal
For sights surrounding Motala, see Motala Municipality.
Sports
The following sports clubs are located in Motala:
- BK Zeros (football)
- IFK Motala (bandy)
- Motala AIF (football)
- Piraterna (speedway), who race at the Motala Arena
- Motala Segelsällskap
Archaeogenetics
A November 2015 genetic study published in Nature included an analysis of six hunter-gatherers buried at Motala between ca. 6000 BC and 5700 BC. Of the four males surveyed, three carried the paternal haplogroup I2a1 or various subclades of it, while the other carried I2c. With regards to mtDNA, four individuals carried subclades of U5a, while two carried U2e1.[12][13]
Notable people
- Alexander Bard, musician and political activist
- Torbjörn Caspersson (1910–1997), cytogeneticist
- Anders Holmertz, swimmer
- Per Holmertz, swimmer
- Ulla Håkanson, equestrian
- Sophia Isberg (1819–1875), artist
- Jan Jönsson, equestrian
- Helena Kallenbäck, actress
- Hanna Lindblad, musical artist and singer
- Andreas Norlén, politician and Speaker of the Riksdag since 2018
- Ilmar Reepalu, politician
- Åsa Regnér, politician
- Agnes Sandström (1887–1985), Titanic survivor
- Lars Stjernkvist, politician
- Fredrik Virtanen, journalist
- Baltzar von Platen (1766–1829), statesman and founder of Göta Kanal
- Owe Wiktorin, Swedish Air Force officer, previous Supreme Commander of the Swedish Armed Forces
References
Sources
External links
Wikiwand - on
Seamless Wikipedia browsing. On steroids.