Mainland India
Region comprising most of India From Wikipedia, the free encyclopedia
Mainland India is a geo-political term sometimes used to refer to India excluding the region of Northeast India and Kashmir,[a][3][4][5] with the north-east connected by the Siliguri Corridor.[6][7][8][9][10]
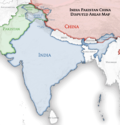
India's international borders in Kashmir (left) and Northeast India (right), outside of mainland India, are disputed by Pakistan and China (centre).
In a geographical context, Mainland India includes the entirety of India (including Northeast India) in continental Asia, excluding islands such as the union territories of Andaman and Nicobar Islands and Lakshadweep.
Geopolitical term
History
During the colonial era, British officials conceptualised of an "India proper" which was perceived as totally distinct from present-day Northeast India due primarily to racial differences.[11]
Contemporary
Mainland India has been noted for having neglected Northeast India to a significant extent due to the Northeast's distinctness,[12] with the Northeast having become somewhat alienated as a result,[8][13] and ending up trending towards East Asian cultural influences as a result.[14]
See also
- Geography of India
- List of islands of India, considered distinct from mainland India
- Indian Himalayan Region, including non-mainland India
- China proper
References
Wikiwand - on
Seamless Wikipedia browsing. On steroids.