Lanzarote Airport
International airport in San Bartolomé, Canary Islands, Spain From Wikipedia, the free encyclopedia
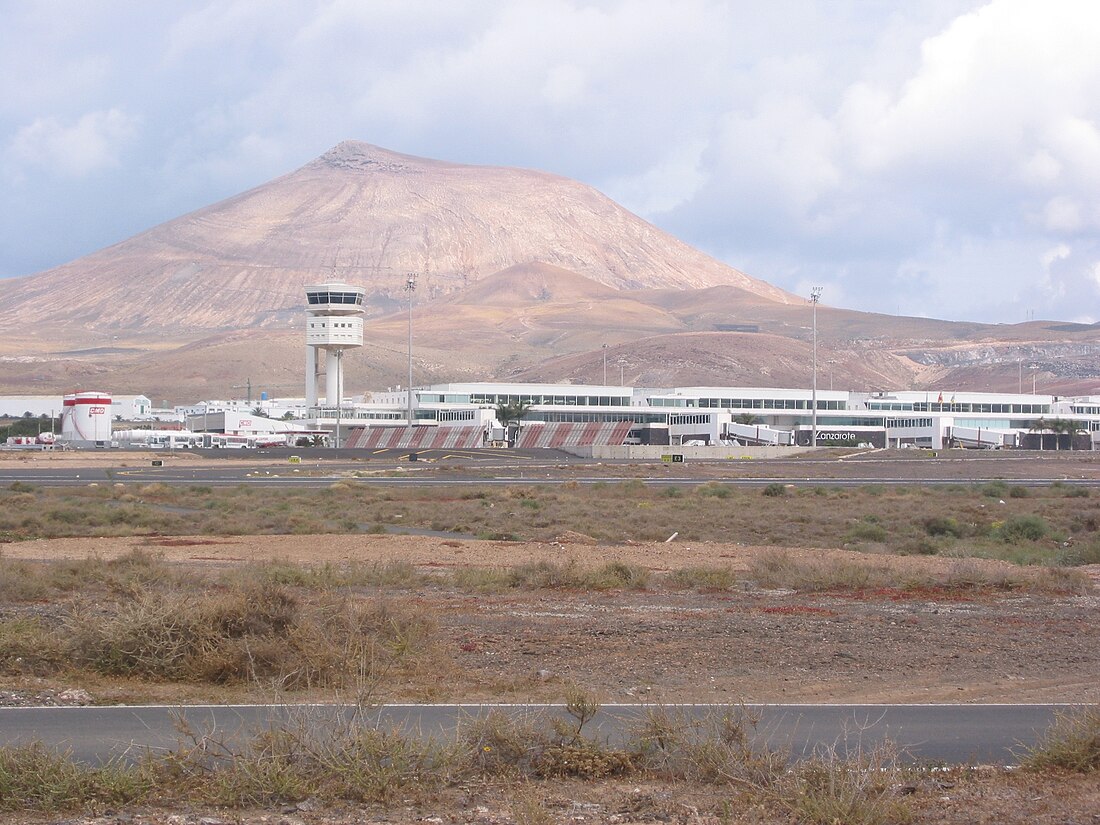
César Manrique-Lanzarote Airport[3] (IATA: ACE, ICAO: GCRR) (Spanish: Aeropuerto de César Manrique-Lanzarote), commonly known as Lanzarote Airport and also known as Arrecife Airport, is the airport serving the island of Lanzarote in the Canary Islands. The airport is located in San Bartolomé, Las Palmas, 5 kilometres (3.1 mi) southwest of the island's capital, Arrecife.[1] It handles flights to many European airports, with hundreds of thousands of tourists each year, as well as domestic flights to other Spanish airports. It handled 7,350,451 passengers in 2022.
César Manrique-Lanzarote Airport Aeropuerto de César Manrique-Lanzarote | |||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
 | |||||||||||||
 | |||||||||||||
| Summary | |||||||||||||
| Airport type | Public | ||||||||||||
| Owner/Operator | Aena | ||||||||||||
| Serves | Lanzarote | ||||||||||||
| Location | San Bartolomé, Las Palmas | ||||||||||||
| Elevation AMSL | 14 m / 47 ft | ||||||||||||
| Coordinates | 28°56′44″N 13°36′19″W | ||||||||||||
| Website | aena.es | ||||||||||||
| Map | |||||||||||||
 | |||||||||||||
| Runways | |||||||||||||
| |||||||||||||
| Statistics (2022) | |||||||||||||
| |||||||||||||
History
Summarize
Perspective
Early years

In the 1930s, a need for an aerodrome on the island became evident when connections were required with the other islands and the mainland, as well as a refuelling point for aircraft. Subsequently, an airfield was built at Llanos de Guacimeta. The first aircraft to land at the airport was a Junkers Ju 52 EC-DAM on 24 July 1941. The Spanish Air Force then saw a need for a permanent aerodrome for defence purposes, and this was constructed in Arrecife. In 1946, the airport provisionally accepted civil traffic. Improvements were carried out to the existing facilities, with a runway extension and additional ramp space provided.[4]
A new passenger terminal was constructed along with a control centre, and on 3 March 1970 international and domestic flights began using the airport. A centrepiece of the Guacimeta terminal was the mural created by César Manrique entitled Lanzarote.[4]
Development since the 1990s
The growing use of the airport called for the need of improved facilities. DME, ILS and VOR facilities were installed for Runway 03/21 along with additional holding points. New runway lighting and a fire station were also commissioned. In 1999, a new passenger terminal opened (Terminal 1), with a capacity of 6 million passengers per annum. Since then, the original passenger terminal has been revamped and is now used for inter-island flights (Terminal 2).[4]
In 2002, in response to interest from both tourists and local people about the island's aviation heritage, Aena decided to use the Guacimeta passenger terminal as an aviation museum. The museum provides a comprehensive and detailed insight into the history of aviation on the island. There are a number of audio-visual presentations.[4]
As a tribute to the legacy left behind by local artist César Manrique, the airport's official name was changed in 2019, coinciding with the centenary of the artist's birth.[5]
Airlines and destinations
Summarize
Perspective
The following airlines operate regular scheduled and charter flights at Lanzarote Airport:


Ground transportation
There are four bus lines connecting Lanzarote Airport with the rest of the island. The airport is connected via bus lines 22 and 23 to the city of Arrecife, and via lines 161 and 261 to Playa Blanca and Puerto del Carmen.[94]
Statistics
Passenger numbers
Graphs are unavailable due to technical issues. Updates on reimplementing the Graph extension, which will be known as the Chart extension, can be found on Phabricator and on MediaWiki.org. |
Annual passenger traffic at ACE airport.
See Wikidata query.
| Year | Passengers | Aircraft movements | Cargo (tonnes) |
|---|---|---|---|
| 2004[95] | 5,517,136 | 48,446 | 7,996 |
| 2005[96] | 5,467,499 | 47,158 | 6,629 |
| 2006[97] | 5,626,087 | 50,172 | 6,114 |
| 2007[98] | 5,625,580 | 52,968 | 5,785 |
| 2008[99] | 5,438,178 | 53,375 | 5,430 |
| 2009[100] | 4,701,669 | 42,915 | 4,147 |
| 2010[101] | 4,938,343 | 46,669 | 3,787 |
| 2011[102] | 5,543,744 | 49,675 | 2,873 |
| 2012[103] | 5,168,775 | 44,787 | 2,108 |
| 2013 | 5,334,599 | 44,259 | 2,081 |
| 2014 | 5,883,039 | 49,575 | 2,050 |
| 2015 | 6,128,971 | 50,448 | 1,805 |
| 2016 | 6,684,564 | 54,632 | 1,776 |
| 2017 | 7,388,964 | 59,477 | 1,824 |
| 2018[104] | 7,327,019 | 60,955 | 1,606 |
| 2019[105] | 7,292,720 | 60,524 | 1,346 |
| 2020[106] | 2,538,345 | 30,056 | 583 |
| 2021[107] | 3,438,219 | 38,740 | 498 |
| 2022[108] | 7,350,451 | 63,764 | 589 |
| Source: Aena Statistics[2] | |||
Busiest routes
| Rank | Destination | Passengers | Change 2021 / 22 |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | 539,878 | ||
| 2 | 471,037 | ||
| 3 | 456,670 | ||
| 4 | 274,965 | ||
| 5 | 247,796 | ||
| 6 | 246,227 | ||
| 7 | 227,659 | ||
| 8 | 181,460 | ||
| 9 | 168,813 | ||
| 10 | 166,110 | ||
| 11 | 127,031 | ||
| 12 | 121,275 | ||
| 13 | 116,328 | ||
| 14 | 113,481 | ||
| 15 | 101,342 | ||
| 16 | 90,194 | ||
| 17 | 89,138 | ||
| 18 | 85,114 | ||
| 19 | 74,094 | ||
| 20 | 70,400 | ||
| Source: Estadísticas de tráfico aereo[109] | |||
| Rank | Destination | Passengers | Change 2021 / 22 |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | 807,811 | ||
| 2 | 635,946 | ||
| 3 | 406,022 | ||
| 4 | 270,619 | ||
| 5 | 134,381 | ||
| 6 | 133,690 | ||
| 7 | 106,457 | ||
| 8 | 67,160 | ||
| 9 | 65,049 | ||
| 10 | 52,847 | ||
| 11 | 41,624 | ||
| 12 | 33,355 | ||
| 13 | 17,028 | ||
| 14 | 9,145 | ||
| 15 | 2,118 | ||
| Source: Estadísticas de tráfico aereo[109] | |||
See also
References
External links
Wikiwand - on
Seamless Wikipedia browsing. On steroids.