Kapampangan people
Austronesian ethnic group From Wikipedia, the free encyclopedia
The Kapampangan people (Kapampangan: Taung Kapampangan), Pampangueños or Pampangos, are the sixth largest ethnolinguistic group in the Philippines, numbering about 2,784,526 in 2010.[2] They live mainly in the provinces of Pampanga, Bataan and Tarlac, as well as Bulacan, Nueva Ecija and Zambales.
This article needs additional citations for verification. (September 2020) |
| Total population | |
|---|---|
| 3,209,738 (2020 census)[1] (3% of the Philippine population) | |
| Regions with significant populations | |
| Philippines (Central Luzon, Metro Manila) United States Canada Worldwide | |
| Languages | |
| Kapampangan, Tagalog, English | |
| Religion | |
| Predominantly Roman Catholicism, minority Protestantism (including Iglesia ni Cristo), Islam, Buddhism and Animism (Ariya) | |
| Related ethnic groups | |
| Pangasinan, Sambal, Tagalog, Ilocano, Bicolano, other Filipino ethnic groups, Austronesian peoples |
Distribution
Summarize
Perspective
This section needs additional citations for verification. (September 2020) |
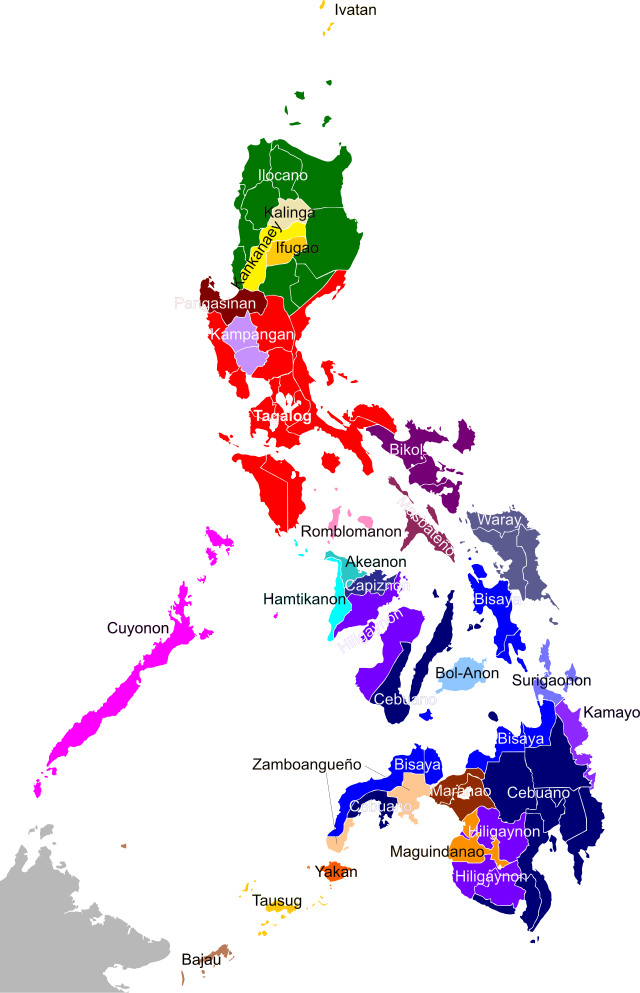
The province of Pampanga is the traditional homeland of the Kapampangans. Once occupying a vast stretch of land that extended from Tondo[3] to the rest of Central Luzon, huge chunks of territories were carved out of Pampanga so as to create the provinces of Bulacan, Bataan, Nueva Ecija, Aurora and Tarlac.[4][5][6][7] As a result, Kapampangans now populate a region that extends beyond the political boundaries of the small province of Pampanga. In the province of Tarlac, the indigenous population of Tarlac City and the municipalities of Bamban, Capas and Concepcion are Kapampangans, while the municipalities of Victoria, La Paz, have a significant Kapampangan population.
In Bataan, Kapampangans populate the municipalities of Dinalupihan and Hermosa, and the barangays of Mabatang in Abucay and Calaguiman in Samal. Kapampangans can be found scattered all across the southern barrios of Cabiao in the province of Nueva Ecija and in the western section of the province of Bulacan. Kapampangan enclaves still exist in Tondo and other parts of the National Capital Region. Kapampangans have also migrated to Mindoro, Palawan and Mindanao and have formed strong Kapampangan organizations called aguman in Cagayan de Oro, Davao City and General Santos.
Agumans based in the United States and Canada are active in the revival of the Kapampangan language and culture. California-based organizations promoted Kapampangan language and culture and raised funds for charitable and cultural projects in California and in Pampanga.[citation needed]
Languages
Kapampangans speak Kapampangan language, which belongs to Central Luzon languages of Malayo-Polynesian languages. They even speak other languages within the environment of other ethnic groups in areas they settled and grew up in, like Sambal, Pangasinan, Ilocano, and Tagalog (all in Central Luzon).
Kapampangan settlers in Mindanao can also speak Cebuano, Hiligaynon as well as Tagalog and various indigenous Mindanaoan languages in addition to their native language but their descendants (especially newer generations born in Mindanao) only speak Cebuano, Hiligaynon, Tagalog and various indigenous Mindanaoan languages with varying fluency in Kapampangan or none at all.
History
Summarize
Perspective
This section needs additional citations for verification. (September 2020) |


The oldest artifact ever found in the Province of Pampanga is a 5000-year-old stone adze found in Candaba. It is said to be a tool used in building boats. Earthenware and tradeware dating back to 1500 BC have also been found in Candaba and Porac.[8] Farming and fishing were the main industries of the Kapampangan people.
Kapampangans, along with Sambal people and the Sinauna (lit. "those from the beginning"), originated in southern Luzon, where they made contact with the migrating Tagalog settlers, of which contact between the Kapampangans and Tagalogs was most intensive.[9] After this, the original settlers moved northward: Kapampangans moved to modern Tondo, Navotas, Bulacan, Nueva Ecija, Aurora, Pampanga, south Tarlac, and east Bataan[5][10][11] and Sambals to the modern province of Zambales,[12] in turn, displacing the Aetas. Tagalogs from southern Luzon, most specifically Cavite, migrated to parts of Bataan. Aetas were displaced to the mountain areas by the end of the 16th century. Kapampangans settled Aurora alongside Aetas and Bugkalots.
The growth of the Malacca as the largest Southeast Asian entrepôt in the Maritime Silk Road led to a gradual spread of its cultural influence eastward throughout insular Southeast Asia. Malay became the regional lingua franca of trade and many polities enculturated Islamic Malay customs and governance to varying degrees, including Kapampangans, Tagalogs and other coastal Philippine peoples. According to Bruneian folklore, at around 1500 Sultan Bolkiah launched a successful northward expedition to break Tondo’s monopoly as a regional entrepot of the Chinese trade and established Maynila (Selurong?) across the Pasig delta, ruled by his heirs as a satellite.[13] Subsequently, Bruneian influence spread elsewhere around Manila Bay, present-day Batangas, and coastal Mindoro through closer trade and political relations, with a growing overseas Kapampangan-Tagalog population based in Brunei and beyond in Malacca in various professions as traders, sailors, shipbuilders, mercenaries, governors, and slaves.[14][15]
Kapampangans have played a dynamic yet conflicting role in Philippine history. It was the Kapampangans of Macabebe who were formerly Muslim were the first to defend the Luzon Empire from Spanish domination in 1571.[16] Yet it was the Kapampangans that the Spaniards relied on to defend their new colony from the Dutch. It was at this time that "one Castillan plus three Kapampangans" were considered as "four Castillans" as long they gallantly served in the colonial armed forces. Such behaviour earned them the stereotype of being quislings in exchange for personal wealth and self-aggrandisement all throughout the archipelago.[16] After their successful battle against the Dutch in 1640, only Kapampangans were allowed to study side by side with the Spaniards in exclusive Spanish academies and universities in Manila, by order of Governor-General Sebastián Hurtado de Corcuera.[4] When the province of Bataan was established on January 11, 1757 out of territories belonging to Pampanga and the corregimiento of Mariveles, Tagalogs migrated to east Bataan, where Kapampangans assimilated to the Tagalogs. Kapampangans were displaced to the towns near Pampanga by that time, along with the Aetas.
When the British occupation of Manila happened in 1762, many Tagalog refugees from Manila escaped to Bulacan and to neighboring Nueva Ecija, where the original Kapampangan settlers welcomed them; Bulacan & Nueva Ecija were natively Kapampangan when Spaniards arrived; majority of Kapampangans sold their lands to the newly-arrived Tagalog settlers and others intermarried with and assimilated to the Tagalog, which made Bulacan & Nueva Ecija dominantly Tagalog.[17] The same situation happened in modern Aurora, where it was repopulated by settlers from Tagalog and Ilocos regions, with other settlers from Cordillera and Isabela, and married with some Aeta and Bugkalots, this led to the assimilation of Kapampangans to the Tagalog settlers.[18][19][5][20][21][22] In 1896, Kapampangans were one of the principal ethnic groups to push and fuel the Philippine revolution against Spain. Yet it was also the Kapampangans of Macabebe that fiercely defended the last Spanish garrison against the revolutionaries.[citation needed]
With the outbreak of World War II, Japanese planes invaded the main province of Pampanga and attacked the United States Air Base at Clark Field in Angeles, Pampanga on December 8, 1941. Later Japanese soldiers entered the province of Pampanga in 1942 and the Japanese Occupation formally began. Many Kapampangans joined a group of stronghold soldiers that survived the invasion and officially trained under the 31st Infantry Division, Philippine Commonwealth Army. USAFFE was stationed in Pampanga on July 26, 1941, before the surrender by the Japanese to April 9, 1942. After the Battle of Bataan in 1942, some Kapampangan soldiers of the USAFFE 31st Infantry Division fought four years of battles against Japanese troops. After the fall of Bataan on April 9, 1942, many Kapampangan soldiers of the USAFFE 31st Division surrendered to the Japanese and then participated in the Bataan Death March from Mariveles, Bataan, to Capas, Tarlac.[citation needed]
Many Kapampangans joined the guerrilla resistance fighters of the Hukbalahap Communist resistance. Many Kapampangan guerrillas and Hukbalahap communist groups fought for more than three years of insurgency during the Japanese Occupation and also fought side by side with allied forces in the main province of Pampanga, helping local troops of the Philippine Commonwealth Army and incoming Philippine Constabulary 3rd Constabulary Regiments stationed at the general headquarters in Pampanga in operations in Central Luzon from 1942 to 1945 against the Imperial Japanese troops.[citation needed]
Culture
Summarize
Perspective


Festivals
Many Kapampangan festivals display an indigenous flavor unique only to the Kapampangan people. Consider the Curaldal or "street dancing" that accompanies the Feast of Santa Lucia in Sasmuan or the Aguman Sanduk were men cross-dress as women to welcome the New Year in Minalin or the Batalla Festival to re-enact the battle between the native Muslim Moor and the new colonist Native Capampangan Christians, the historical battle between the two religious native Kapampangans. They start the battle in Ugtung-aldo or afternoon and they end it in Sisilim or sunset with the tune of what Macabebeanons and Masantuleñios called BATTALA Masantol, Macabebe and Lubao.
The Pistang Danum of the barrios of Pansinao, Mandasig, Lanang and Pasig in Candaba, where food is served on floating banana rafts on the waters of the Pampanga River was originally a non-Christian holiday that is now made to coincide with the baptism of Christ. The Kapampangan New Year or Bayung Banwa that welcomes the coming of the monsoons and the start of the planting season is made to coincide with the feast of John the Baptist. The colourful Apung Iru fluvial procession of Apalit, once a thanksgiving celebration in honour of the river, has become the feast of Saint Peter.
The most dramatic festivals can be witnessed during the Mal ay Aldo, which is the Kapampangan expression of the Holy Week. These include the erection of a temporary shrine known as the puni where the pasion or the story of Christ's suffering is chanted in archaic Kapampangan. The melody of the Kapampangan pasion was said to have been taken from their traditional epic, whose original words were lost and replaced by the story of Christ. The highlight of the Mal ay Aldo celebration is the procession of the magdarame or sasalibatbat penitents covered in blood from self-flagellation. Some of them even have themselves crucified every Good Friday at the dried up swamp of barrio Cutud in San Fernando.
Cuisine
Kapampangan cuisine, or Lutung Kapampangan, has gained a favourable reputation among other Philippine ethnic groups, which hailed Pampanga as the "Culinary Capital of the Philippines". Some popular Kapampangan dishes that have become mainstays across the country include sisig, kare-kare, tocino or pindang and their native version of the longaniza.
Other Kapampangan dishes, which are an acquired taste for the other ethnic groups include buru (fish fermented in rice), betute tugak (stuffed frogs), arobung kamaru (mole crickets sauteed in vinegar and garlic), estofadong barag (spicy stewed monitor lizard), sisig, kalderetang asu (spicy dog stew), sigang liempu, dagis a tinama (marinated rats), laman panara and bobotu.
Religion
Kapampangans are mostly Christians, a majority of which are Roman Catholics, Aglipay, Methodists, and the Church of Jesus Christ of Latter-day Saints (LDS Church). A few belong to non-Christian religions. However, traces of native-Austronesian Anitism, Hinduism, and Buddhism can still be found among their folk practices and traditions, as these were the majority beliefs of the Kapampangan before the imposition of Christianity in the 16th century. A few Kapampangans practice Islam, mostly by former Christians either by study abroad or contact with Moro migrants from the southern Philippines.[23] By the early 16th century, some Kapampangans (especially merchants) were Muslim due to their links with Bruneian Malays.[24] The old Kapampangan-speaking Kingdom of Tondo was ruled as a Muslim kingdom,[25] Islam was prominent enough in coastal areas of Kapampangan region that Spaniards mistakenly called them "Moros" due to abundance of indications of practicing Muslim faith and their close association with Brunei.[26]
Prominent Kapampangans
Summarize
Perspective
This section has multiple issues. Please help improve it or discuss these issues on the talk page. (Learn how and when to remove these messages)
|
The Kapampangans have produced many Rajahs, Datus, four Philippine presidents, three chief justices, a senate president, the first Filipino cardinal, one Huk Supremo, many Huk Commanders and NPA cadres and many notable figures in public service, education, religion, diplomacy, journalism, the arts and sciences, entertainment and business.
For a list of prominent or noteworthy Kapampangans, see Category:Kapampangan people.
History, politics and religion
- Benigno Aquino – Filipino senator whose assassination triggered the events that led to the People Power Revolution. Born and raised in Concepcion, Tarlac
- Corazon Cojuangco Aquino – a Filipina politician who served as President of the Philippines. She was the first woman to hold that office, and the first female president in Asia. She is regarded by international diplomatic community as the Mother of Asian Democracy.
- Benigno S. Aquino III – the 15th President of the Republic of the Philippines.
- Dr. Rey B. Aquino – a former mayor of San Fernando City and the CEO of Philippine Health Insurance.
- Don Juan Macapagal – Datu of Arayat, the great-grandson of Lakandula.[27] He was given the title Maestre de Campo General of the natives Arayat, Candaba and Apalit for his aid in suppressing the Kapampangan Revolt of 1660 and was the only native in the Philippines to become an encomendero.
- Diosdado Pangan Macapagal – the 9th President of the Republic of the Philippines and a native of Lubao, Pampanga.
- Gloria Macapagal Arroyo – the 14th President of the Republic of the Philippines. A daughter of the 9th President of the Republic Diosdado Macapagal, she was the country's first female Vice President during the tenure of Joseph Estrada.
- Elmer Cato – Filipino journalist and diplomat who is currently the Consul General of the Republic of the Philippines in New York. A career diplomat with the rank of Chief of Mission Class 2, Cato had previously served as Chargé d'Affaires and Head of Mission of the Embassy of the Philippines in Baghdad (2015–2018) and in Tripoli (2019–2021), who joined the Department of Foreign Affairs (Philippines)(DFA) in 1998.[28][29][30] He is from Angeles City.
- Jomar Sadie – Philippine Diplomat to Iraq, Mensa International member, and Anti-Trafficking advocate.[31][32][33] He is a native of Angeles City.
- Armando Biliwang – the former municipal mayor of San Fernando and was well known for his stand against Communism during his term as municipal councilor and mayor.
- Tarik Sulayman, a precolonial Muslim ruler from Macabebe who battled Spanish forces at the Battle of Bangkusay Channel
- Francisco Tongio Liongson, a politician and doctor, was a native of Pampanga's ancient capital, Villa de Bacolor, who became Pampanga's governor and its first senator.
- Pedro Tongio Liongson, lawyer and judge, was a native of Pampanga's ancient capital, Villa de Bacolor, who served as member of the Malolos Congress (1898–1899) and as Judge Advocate General of the army of the First Philippine Republic (1899–1900).
- Bishop La Verne D. Mercado – From Lubao, Pampanga, elected bishop of the United Methodist Church in the Philippines and also served as general secretary of the National Council of Churches in the Philippines.
- Bishop Emerito P. Nacpil – A Kapampangan from Tarlac. Dr. Nacpil was elected bishop of the United Methodist Church in the Philippines and also served as Professor of Theology at the Union Theological Seminary in Dasmarinas, Cavite.
- José Abad Santos – a native of the City of San Fernando who became the 5th Chief Justice of the Supreme Court of the Philippines. He was killed by Japanese forces during the occupation of the Philippines in World War II.
- Pedro Abad Santos – a doctor, lawyer, Marxist, and politician who later became a leader of the first of two Communist rebellions from the 1930s to the 1950s. He is the older brother of José Abad Santos.
- Félix Ysagun-Manalo – founder of the Christian religious organization Iglesia ni Cristo.
- Eliseo Soriano – evangelist and presiding minister of the Philippine-based Members Church of God International. He is known as Brother Eli in his radio and television programs Ang Dating Daan (The Old Path).
- Satur Ocampo – cofounder of the National Democratic Front, he is a politician, journalist, and writer. Also a representative for the Bayan Muna party in the Lower House of Philippine Congress.
- Luis Taruc – a political figure and Communist revolutionary. He was the leader of the Hukbalahap rebel group between 1942 and 1954.
- Rufino Jiao Santos – the former Archbishop of Manila from 1953 to 1973 and was the first Filipino to be named Cardinal.
- Tito Morales Mendiola – a former mayor of Floridablanca and the senior vice president of Philippine Health (PHILHEALTH) Insurance for operations and area vice president for Mindanao.
- Eddie Panlilio – the first Catholic priest in the Philippines to be elected as a provincial governor. He campaigns for good governance and opposes patronage politics and corruption.
- Yeng Guiao – a former vice-governor of Pampanga and a professional basketball head coach for the NLEX Road Warriors in the Philippine Basketball Association. Guiao won four PBA titles since starting his head coaching job for Swift in the early 1990s. He is a former Philippine Basketball League commissioner from 1997 to 2000.
- Gil J. Puyat – was the Senate President of the Philippines from 1967 to 1972.
- Rogelio dela Rosa – was one of the most popular Filipino matinee idols of the 20th century and was elected to the Senate in 1957. He was also the first film actor able to parlay his fame into a political career, paving the way for other Filipino entertainers-turned-politicians. He had an equally famous brother, Jaime dela Rosa, also a matinee idol in the 1950s.
- Francis "Kiko" Pangilinan – senator and husband of celebrity Sharon Cuneta
- Randy David – a political analyst, newspaper columnist, and professor at the University of the Philippines in Diliman.
- Honesto Ongtioco – 2nd Bishop of Balanga (June 18, 1998 – August 28, 2003), 1st Bishop of Cubao (August 28, 2003–present), and sede vacante Apostolic Administrator of Malolos (May 11, 2018 – August 21, 2019).
- Apollo Quiboloy – televangelist; born in Davao City to Kapampangan parents from Lubao.
Arts and culture
- Padre Anselmo Jorge Fajardo – Father of Kapampangan Literature. Author of the first and longest metrical romance in any Philippine language, Gonzalo de Córdoba. He was a native delegate to the Spanish Cortez.

- Juan Crisostomo Soto – Kapampangan writer, revolutionary leader and veteran of the Philippine–American War. Father of Kapampangan poetic debate, Crissotan, and author of "Alang Dios" (There is no God), Perlas quing Burac, Anac ning Katipunan, Lydia and many others Zarzuelas and Playwrights.
- Francisco Alonso Liongson – Outstanding Philippine playwright in Spanish and founding president of Círculo Escenico, Pampanga's Spanish theatrical group that became nationally renowned.
- Aurelio Tolentino – one of the mystics of the Katipunan, a compadre of Andrés Bonifacio, a nationalist writer in both Kapampangan and Tagalog. He coined the word dulâ for drama and ironically became known in Philippine history as the Father of Tagalog Drama for his anti-US colonial masterpiece Kahapon, Ngayon at Bukas. A theatre at the Cultural Center of the Philippines is named Tanghalang Aurelio Tolentino in his honor.
- Jose Gallardo – Kapampangan Poet Laureate and one of the most prolific Kapampangan writers of the late 20th century.
- Amado Yuzon – Kapampangan Poet Laureate, a Philippine academic, journalist, and writer.
- Alejandro T. Quiboloy – Kapampangan educator, public servant, writer and Protestant minister. Born in Lubao, Pampanga on May 3, 1909.
- Vicente Manansala – a National Artist of the Philippines in Visual Arts, was a direct influence on his fellow Filipino neo-realists.
- Isidoro C. Soto [Anac ning Baculud] Born on April 4, 1918, in Suban Bacolor, Pampanga. One of the greatest artist-decorator-designers of Pampanga. One of his living artworks is the ceiling painting of Betis church, painted with Dr. Juco as his mentor. He was also the designer of the logo of Philippine Rabbit Bus Liner. He used to decorate for Circulo Fernandino, Batu-Balani, Old legs, Circilo Masantoleno, to name a few. He is a descendant of Juan Crisostomo Soto, the famous Pampango poet. Isidoro died at the age of 70 on June 9, 1988.
- Ambeth Ocampo – is a Filipino historian, academic, journalist and author best known for his column in the Philippine Daily Inquirer, "Looking Back."
- Gene Gonzales – nationally renowned chef, restaurateur, educator management consultant and author. He is the author of Cocina Sulipeña: Culinary from Old Pampanga.
- Zoilo Hilario – a member of the Institute of National Language who dedicated his life to imposing the ABAKADA on Kapampangan writing through the Akademyang Kapampangan, the organization he created.
- Mon David – is a jazz singer from Sto. Tomas, Pampanga. He won the grand prize in the prestigious 2006 London International Jazz Competition (LIJC).
- Eduardo Mutuc – is a 2005 NCCA GAMABA National Living Treasure Awardee for upholding the traditional Kapampangan art of pinukpuk or silver inlaying and embossing on retablos, carosas and altar pieces.
- Brillante Mendoza – is a Filipino film director who won the award for Best Director for his film Kinatay at the recently concluded 62nd Cannes Film Festival in France.
- Jess Española – is a Filipino former animator, layout artist, and assistant director who won the Primetime Emmy Award for his contribution as an assistant director of "Eternal Moonshine of the Simpson Mind" from the 19th season of The Simpsons – the first time not only a Filipino, but an Asian and Kapampangan had won such tremendous honor.[a][35]
Popular culture, sports and entertainment
- Dolphy – born as Rodolfo Quizon and known as the King of Philippine Comedy was born in Pampanga in 1928 to Kapampangan parents and was raised in Tondo, Manila.
- Vilma Santos – queen of Philippine movies born in Bamban, Tarlac, and Governor of Batangas.
- Melanie Marquez – (b. 16 July 1964), is a Filipina personality development coach, actress, film producer, author, and celebrity endorser. She was a former beauty queen and model who won the 1979 Miss International beauty pageant in Tokyo, Japan, representing the Philippines, born and raised in Mabalacat.
- Ricardo "Dong" Puno Jr – is a Filipino television public affairs host, media executive, newspaper columnist, and lawyer.
- Efren "Bata" Reyes – is referred to as "The Magician" and a popular Filipino billiards player who hails from Angeles City. He is considered to be one of history's greatest practitioners of billiards.
- Francisco Bustamante – next to Bata, shoots the most powerful breaks in World Billiards. With Bata they are one of the greatest billiard tandems in the world.
- apl.de.ap (Allan Pineda Lindo) – is a member of the Grammy Award-winning group, The Black Eyed Peas, and was born in Sapang Bato, Angeles City. He is famous throughout the Filipino community after the release of his life story of his homeland Philippines in a song called "The Apl Song."
- Allen Dizon – International actor. Born in Sta. Ana, Pampanga
- Lito Lapid – a famous star turned politician. He became governor of Pampanga and later became a member of the Philippine senate.
- Joey Marquez – Philippine basketball star turned actor-comedian turned politician. Brother of popular beauty queen Melanie Marquez
- Ato Agustin – former professional basketball player in PBA, and became an MVP in 1992.
- Arwind Santos – San Miguel Beerman superstar from Lubao, Pampanga. 2 time Finals MVP of the PBA, 8 time PBA all star ft
- Japeth Aguilar – Gilas Pilipinas Center/Forward born and raised in Sasmuan, Pampanga
- Coco Martin – is an actor, martial artist, film director and producer known for starring in the acclaimed television series Ang Probinsyano.
- Calvin Abueva – Alaska Aces Small Forward born and raised in Angeles City, Pampanga. Nicknamed "The Beast"\
- Jayson Castro – Talk n Text and Gilas Pilipinas superstar guard born and raised in Guagua, Pampanga
- Gary David – Meralco Bolts sharpshooter born and raised in Dinalupihan, Bataan
- JC Intal – Barako Bull and Gilas Pilipinas born in Minalin, Pampanga. He is married to television host and model Bianca Gonzalez
- Yeng Guiao – is a Filipino professional basketball head coach for the NLEX Road Warriors in the Philippine Basketball Association. Guiao won four PBA titles since starting his head coaching job for Swift in the early 1990s. He is a former Philippine Basketball League commissioner from 1997 to 2000. He is also a former Vice Governor and Congressman of 1st district of the province of Pampanga.
- Rey Langit – is a TV Personality, columnist of Tempo, Balita, People's Tonight, DWIZ-AM Station Manager, and host of Kasangga Mo ang Langit and Biyaheng Langit, both of which are aired over Radio Philippines Network and DWIZ.
- Rogelio dela Rosa – was one of the most popular Filipino matinee idols of the 20th century and was elected to the Senate in 1957. He was also the first film actor who was able to parlay his fame into a political career, paving the way for other Filipino entertainers-turned-politicians. He had an equally famous brother, Jaime dela Rosa, also a matinee idol in the 1950s.
- Rudy Fernandez – the son of the late film director Gregorio Fernandez.[1][3] Both his parents were from Lubao, Pampanga, which he considered his hometown.[4]
- Lorna Tolentino – is an actress, host, executive producer and wife of fellow Kapampangan actor Rudy Fernandez. She was born in Concepcion, Tarlac and was raised in Manila.
- Jean García – is a television and film actress who hails from Angeles City. Her most famous role was in the telenovela Pangako sa 'Yo where she played antagonist Madam Claudia.
- Carlos Badion – Philippine Basketball Team members, first Asian MVP in the now so called FIBA Asia. His moniker is "The Bad Boy". Known for his bicycle drive and jackknife layup.
- Ed Ocampo – an Olympian with the Big J. One of the great basketball players & coaches in the Philippines. Shin Dong Pa the Korean legend says Ocampo and Jaworski are his great opponents in basketball in the Asian Region.
- Mark Lapid – is an actor, film producer, and former governor of Pampanga (2004–2007). He is the husband of an actress Tanya Garcia.
- Helen Gamboa – Helen Gamboa-Sotto (born May 7, 1948) in Pampanga, Philippines, is a veteran Filipina actress, singer, and former beauty queen.[1]
- Gaudencio "Dencio" Cabanela – Kapampangan boxing hero from San fernando, Pampanga. Beating a French and an Australian holder of three Oriental Titles, first Pinoy boxing hero. Died 1921, next boxing hero was Pancho Villa took the international fame.
- Rufa Mae Quinto – popular comedian from Bubble Gang.
- Angel Aquino – fashion model and FAMAS and Gawad Urian Award-nominated Filipino film and television actress, born in Dumaguete City to Kapampangan parents from Tarlac
- Liza Lorena – born Elizabeth Ann Jolene Luciano Winsett s a Filipino former beauty queen and multi-awarded actress in the Philippines. She was a First Runner-Up in the Bb. Pilipinas pageant in 1966.
- Fernando Poe Jr. – born Ronald Allan Kelley Poe and colloquially known as FPJ and Da King, was a Filipino actor and later politician, having run an unsuccessful bid for President of the Philippines in the 2004 presidential elections against the incumbent Gloria Macapagal Arroyo. His mother, Elizabeth Gatbonton Kelly is a Kapampangan from Candaba.[36]
- Sharon Cuneta – dubbed as the "Megastar of Philippine Showbiz," is a popular Filipina actress, TV host, singer, endorser, grand slam awardee, box-office queen, hall of famer and a recipient of several lifetime achievement awards at a relatively young age. Her mother Elaine Gamboa-Cuneta (sister of Helen Gamboa ) is from Santa Ana, Pampanga.[37]
- KC Concepcion – daughter of Philippine singer-actress Sharon Cuneta, and adopted daughter of senator Francis Pangilinan. Her biological father was 80's heartthrob Gabby Concepcion.
- Lea Salonga – is a Tony Award-winning singer and actress who is best known for her portrayal of Kim in the musical Miss Saigon. She spent the first six years of her childhood in Angeles City before moving to Manila.
- Judy Ann Santos – is a film and television actress. Her mom hails from San Fernando City, Pampanga.
- Paquito Diaz – is a veteran actor and director, whose mother is a Kapampangan.
- Leah Dizon – is a model, singer, and a TV personality and media icon in Japan and upcoming in the Philippines with the upcoming ABS-CBN artist and personality, born in Las Vegas, Nevada.
- Vanessa Minnillo – is an American television personality born in Clark Air Base, Angeles City and raised in the US. She was Miss Teen USA 1998 and is currently a host on MTV's Total Request Live.
- Isabel Preysler – is a Filipino journalist, socialite, and television host, the Kapampangan ancestry of the Arrastia family is from Bataan.[38] Besides the Iglesias children her socialite daughters Tamara Falco and Ana Boyer born from different relationships would also be of Kapampangan descent.
- Enrique Iglesias – is a Spanish singer-songwriter and occasional actor, son of Filipina Isabel Preysler.
- Chábeli Iglesias – is a Spanish socialite, the daughter of Filipina socialite Isabel Preysler and the elder sister of Julio Iglesias Jr. and Enrique Iglesias.
- Julio Iglesias Jr. – is a Spanish singer, son of Filipina Isabel Preysler.
- Hilda Koronel – is an actress who starred in around 45 films, many of which are critically acclaimed. Born Susan Reid, her father was an American serviceman.
- Lalaine Vergara – is an American actress, singer and spokesperson.
- Rufa Mae Quinto – is a popular actress and TV host, known for her comedy role in the film, Booba.
- Abbygale Williamson Arenas – is a former international model and beauty queen. She is now a freelance make-up artist.
- Francisco "Django" Bustamante – is a world-class billiards player from Tarlac.
- Mikee Cojuangco Jaworski – is a former Olympian (equestrian) and celebrity from Tarlac.
- Rosa Rosal – is a Philippine Red Cross advocate who hails from Sta. Rita, Pampanga.
- Elwood Perez – is a movie director from Mabalacat, Pampanga.[39]
- Chris Tiu – is a TV host of Pinoy Records and an MVP of Ateneo Blue Eagles Basketball Team.
- Sarah Geronimo – is a popular singer, actress, movie star. She traces her roots in Concepcion, Tarlac while her father hails from Floridablanca, Pampanga.
- Ryzza Mae Dizon – (born June 12, 2005)is a Filipina child actress, comedian and television personality. She rose to prominence in 2012 when she won that year's edition of Eat Bulaga!'s Little Miss Philippines.Currently, she is the youngest host in the present roster of presenters in the variety show Eat Bulaga!, and hosts her own morning talk show The Ryzza Mae Show.
- Rosa del Rosario – a famous actress. Her real name was Rose del Rosario Stagner. Her mother was from Pampanga. She is the first female action hero who portrayed Darna in 1951 under Royal Films.
- Thia Megia – a participant of American Idol Season 10. She is from Angeles City.
- John Prats – mom hails from Angeles City.
- Maricel Laxa – her father Tony Ferrer was a popular actor from the 60's and 70's.
- Jimmy Manansala – basketball player. Won Rookie of the Year and four PBA championships.
- Julian Manansala – film studio founder and director. Called the "Father of Philippine Nationalist Films."
- Luis Manzano – mom Vilma Santos was born and raised in Bamban, Tarlac.
- Bamboo Manalac – parents hail from Floridablanca, Pampanga.
- Aljur Abrenica – GMA turned ABS-CBN star from Angeles City.
- Kris Aquino – Kristina Bernadette Cojuangco Aquino (born February 14, 1971), professionally known as Kris Aquino, is a Filipina television personality and actress who gained prominence and numerous endorsements from her talk shows, game shows, horror movies, massacre movies. She is the youngest daughter of former Philippine senator Benigno S. Aquino Jr., and Corazon Cojuangco-Aquino, who served as the 11th President of the Philippines, and sister of Benigno S. Aquino, III, the 15th President of the Philippines.
- Dimples Romana – (born November 13, 1984, Dianne Marie Romana)[citation needed] is a Filipina actress and commercial model.
- Ellie Tiglao Chef based in Boston, Massachusetts. Her mother is from Angeles City and her father from Macabebe.
- Dr. Tracy Timberlake YouTube Vlogger and Internet Personality. Born in Clark Air Base, her mother is Kapampangan from Bamban, Tarlac.
- Michael Alim – Born in San Fernando. Resided in Angeles City during his childhood and presently resides at Dau, Mabalacat City. First Kapampangan chef who works at the oldest restaurant in the world by the Guinness Book of World Records.[citation needed]
See also
Notes
- Some sources identified Española as being “the first Pinoy” to win an Emmy, but none of these Filipino-born have a Primetime Emmy, both win and nominated, before 2008; some have won Emmys other than Primetime in the past, including Ronnie Del Carmen won a Daytime Emmy while Rochit Tañedo and Rita Nazareno also won the News and Documentary Emmy and Regional Emmy Award, respectively.[34]
References
Further reading
External links
Wikiwand - on
Seamless Wikipedia browsing. On steroids.