Huvishka
Kushan emperor from c. 150 to c. 190 From Wikipedia, the free encyclopedia
Huvishka (Kushan: Οοηϸκι, Ooēški, Brahmi: 𑀳𑀼𑀯𑀺𑀱𑁆𑀓; Hu-vi-ṣka, Huviṣka;[3] Kharosthi: 𐨱𐨂𐨬𐨅𐨮𐨿𐨐 Hu-ve-ṣka, Huveṣka[4]) was the emperor of the Kushan Empire from the death of Kanishka (assumed on the best evidence available to be in 150 CE) until the succession of Vasudeva I about thirty years later.
| Huvishka | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Kushan emperor | |||||
 Coin of Huvishka. Legend in Kushan language and Greek script (with the Kushan letter Ϸ "sh"): ϷΑΟΝΑΝΟϷΑΟ ΟΟΗϷΚΙ ΚΟϷΑΝΟ ("Shaonanoshao Ooishki Koshano"): "King of kings, Huvishka the Kushan". | |||||
| Reign | 150–190 CE | ||||
| Coronation | 150 CE | ||||
| Predecessor | Kanishka | ||||
| Successor | Vasudeva I | ||||
| Born | 130 AD Kabul | ||||
| Died | 190 AD (59 years) Kashmir | ||||
| Burial | 190 AD | ||||
| Spouse | Unknown | ||||
| Issue | Vasudeva I Kanishka II | ||||
| |||||
| House | Unknown | ||||
| Dynasty | Kushan Dynasty | ||||
| Father | Kanishka | ||||
| Mother | Unknown | ||||
| Religion | Shaivism[1][2] | ||||
His rule was a period of consolidation for the Empire. Huvishka's territory encompassed Balkh in Bactria to Mathura in India, locations where it is known that he minted his coinage. Gold coins and amulets in his effigy were found as far as Pataliputra and Bodh Gaya, including one such amulet as an offering under the Enlightenment Throne of the Buddha in Bodh Gaya, suggesting with other finds of Kushan coins in the area that Kushan rule may have extended this far east.[5] His reign seems to have been essentially peaceful, consolidating Kushan power in northern India, and moving the centre of the Kushan Empire to the southern capital city of Mathura.[6]
Religion
Summarize
Perspective

Huvishka was the son of Kanishka. His reign is also known as the golden age of Kushan rule.
Mahayana Buddhism
The reign of Huvishka corresponds with the first known epigraphic evidence of the Buddha Amitabha, on the bottom part of a 2nd-century statue which has been found in Govindo-Nagar, and now at the Mathura Museum. The statue is dated to "the 28th year of the reign of Huvishka", and dedicated to "Amitabha Buddha" by a family of merchants.[8][9]
There is also some evidence that Huvishka was a follower of Mahāyāna Buddhism. A Sanskrit manuscript fragment in the Schøyen Collection describes Huvishka as one who has "set forth in the Mahāyāna." This depiction of Huviska as a Mahayana follower does not necessarily confirm his involvement in promoting Mahayana. However, it does suggest that "Huviska's era was a crucial period in the evolution of Mahayana."[10]
Some reliefs from Gandhara are also thought to portray Huvishka making donations to the Buddha.[7]
Huvishka is widely attested to have supported Buddhism, but the Buddha does not appear on his coinage, possibly out of respect to the Buddha.[11]
- Earliest known "Mahayana" inscription: inscribed pedestal with the first known occurrence of the name of "Amitabha Buddha" in the "year 26" (153 CE, first year of Huvishka)[12]
- First known Mahayana inscription: words







 "Bu-ddha-sya A-mi-tā-bha-sya" ("of Amitabha Buddha") in Brahmi script in the inscription.[9]
"Bu-ddha-sya A-mi-tā-bha-sya" ("of Amitabha Buddha") in Brahmi script in the inscription.[9] - Fragment of a Bodhisattva sculpture inscribed "in the year 33" (𑀲𑀁𑁝𑁔) of "the Great King, son of God, Huvishka" (Mahārājasya Devaputrasya Huviṣka,
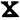
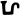

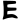








 ), Art of Mathura.[13]
), Art of Mathura.[13] - Pedestal of a Buddha statue, with inscription in the name of Huvishka "in the year 45" (𑀲𑀁𑁞𑁔). Starts with Mahārājasya Huviṣkasya Devaputrasya...,
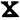










 ... Uttar Pradesh. Chhatrapati Shivaji Maharaj Vastu Sangrahalaya Museum.
... Uttar Pradesh. Chhatrapati Shivaji Maharaj Vastu Sangrahalaya Museum.
Graeco-Roman deities

Huvishka also incorporates in his coins for the first and only time in Kushan coinage the Hellenistic-Egyptian Serapis (under the name ϹΑΡΑΠΟ, "Sarapo").[14][15] Since Serapis was the supreme deity of the pantheon of Alexandria in Egypt, this coin suggests that Huvishka had a strong orientation towards Roman Egypt, which may have been an important market for the products coming from the Kushan Empire.[14]
Another coin possibly depicts the Goddess Roma ("Roma aeterna"), under the name "Rishti" (Greek: ΡΙϷΤ),[16] or "Riom" (Greek: ΡΙΟΜ).[17][18][19]
- Another coin of Huvishka holding a scepter, with, on the reverse, deity Serapis (ϹΑΡΑΠΟ, "Sarapo")
- Coin of Huvishka. Obverse: ϷΑΟΝΑΝΟϷΑΟ ΟΟΗϷΚΙ ΚΟϷΑΝΟ (Shaonanoshao Ooishki Koshano, "King of kings, Huvishka the Kushan"). Reverse: Herakles with legend ΗΡΑΚΙΛΟ (Erakilo).
- Possible depiction of "Roma Aeterna". The legend has been variously read Riom (Greek: ΡΙΟΜ), or more recently Rishti (Greek: ΡΙϷΤ).
Iranian deities
Huvishka is also known to have included Iranian deities in his pantheon. Between 164 and 174, he established a temple to Pharro ("Royal splendour")-Ardoxsho in the stronghold of Ayrtam, near Termez, according to the Ayrtam inscription.[14] He also issued numerous coins in the name of these deities. Many more Iranian deities are also known from his coinage, such as Miiro (Mitra), Mao (the Lunar deity Mah), Nana (Anahita), Atsho (Atar, "The Royal fire").[20] Another Zoroastrian deity, the supreme god Ooromozdo (Ahura Mazda), and Mazdo oana ("Mazda the victorious") also appears.[20] Other Zoroastrian deities include Rishti ("Uprightness", Arshtat), Ashaeixsho ("Best righteousness", Asha Vahishta), the Lunar deity Mah (Mao), Shaoreoro ("Best royal power", Khshathra Vairya).[20][21]
- Coin of Kushan ruler Huvishka diademed, with deity Pharro ("ΦΑΡΡΟ"). Circa CE 152-192
- Coin of Kushan ruler Huvishka diademed, with deity Ardoxsho. Circa CE 152-192
- Huvihska with Ahuramazda (ωΡΟΜ, Orom[zdo]).[20]
- Huvishka with "Asha Vahishta" (ΑϷΑΕΙΧϷΟ, Ashaiexsho).[20]
Indian deities

Huvishka is known to have restored a temple in Mathura, where provisions were made for hospitality towards the Brahmans.[14] Some of the coins of Huvishka also featured Maaseno on his coins, the Kushan incarnation of the Hindu god Karttikeya, or Skanda, whose epithet was "Mahasena".[22] This god being particularly important to the Yaudheyas, it may have been incorporated into Kushan coinage when the Kushans expanded into Yaudheya territory in order to establish control of the Mathura area. It may also have been adopted as a way to appease the warlike Yaudheyas. In effect, the Kushans became the suzerains of the Yaudheyas in the area.[23][24]
In a departure from his predecessor Kanishka, Huvishka also added Oesho ("ΟΗϷΟ", Shiva) on some of his coinage. In replacement of the Iranian god of war Ořlagno, he also added several Indian war gods, such as Skando (Old Indian Skanda), Komaro (Old Indian Kumara), Maaseno (Old Indian Mahāsena), Bizago (Old Indian Viśākha), and even Ommo (Old Indian Umā), the consort of Siva. This could suggest an evolution toward Indian deities among the Kushans, possibly motivated by the enlisting of Indian warriors.[22]
Coinage and statuary
Summarize
Perspective
The coinage of Huvishka is characterized by a great variety of designs and the large quantity of gold coins that were minted: more gold coins from Huvishka are known than from all other Kushan rulers combined.[6] The locations of his mints were mainly in Balkh and Peshawar, with smaller mints in Kashmir and Mathura.[6]
One of the great remaining puzzles of Huvishka's reign is the devaluation of his coinage. Early in his reign the copper coinage plunged in weight from a standard of 16g to about 10–11g. The quality and weight then continued to decline throughout the reign until at the start of the reign of Vasudeva the standard coin (a tetradrachm) weighed only 9g. The devaluation led to a massive production of imitations, and an economic demand for the older, pre-devaluation coins in the Gangetic valley. However, the motivation and some of the details of this devaluation are still unknown.
|
|
References
Sources
External links
Wikiwand - on
Seamless Wikipedia browsing. On steroids.
























