Top Qs
Timeline
Chat
Perspective
Friso-Saxon dialects
West-Germanic dialect group From Wikipedia, the free encyclopedia
Remove ads
Friso-Saxon (Dutch: friso-saksische tongvallen,[1] friso-saksisch) is a group of West Germanic dialects found around the North Sea coast of the Netherlands and Germany, in an area historically known as Frisia.[2][3] They are dialects of Low German/Low Saxon that have experienced strong influence from a Frisian language.
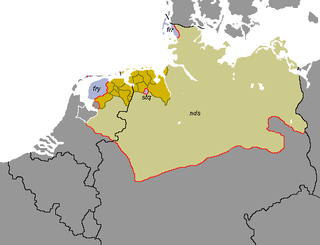
Friso-Saxon dialects: Low German/Low Saxon dialects with a substrate of a Frisian language

The term was established by the Dutch researcher Johan Winkler in his work about Dutch, Low German and Frisian dialects in the region.[4] In the following decades the term was adopted by some of Winkler's successors.[3]
The Friso-Saxon dialects are spoken in areas which were historically Frisian-speaking, until Frisian was gradually replaced with Low Saxon beginning in the Late Middle Ages. However, Frisian has remained as a substratum since then in the regions concerned. The only exception to this rule is Stellingwarfs, a Low Saxon dialect which has undergone influence especially from West Frisian. Most of the other Friso-Saxon dialects underwent most influence from East Frisian, for example East Frisian Low Saxon and Gronings. The, by philological history, not philological categorization Friso-Saxon, Dithmarschen dialect underwent most influence from North Frisian.
Remove ads
See also
References
Wikiwand - on
Seamless Wikipedia browsing. On steroids.
Remove ads
