Top Qs
Timeline
Chat
Perspective
Ergine
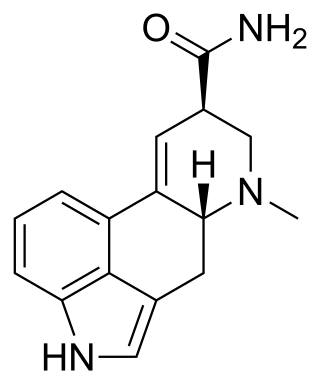
Chemical compound From Wikipedia, the free encyclopedia
Remove ads
Ergine, also known as lysergic acid amide (LSA or LAA) as well as LA-111, is a psychoactive compound of the ergoline and lysergamide families related to lysergic acid diethylamide (LSD).[10][13][9][14] Ergine is an ergoline alkaloid found in fungi such as Claviceps paspali (ergot) and Periglandula species such as Periglandula clandestina,[13][15] which are permanently connected with many morning glory vines.[13] Ergine induces relatively mild psychedelic effects as well as pronounced sedative effects.[10][16][17][18][19][20][21]
The most common sources of ergine for use as a drug are the seeds of morning glory species including Ipomoea tricolor (tlitliltzin), Ipomoea corymbosa (ololiuhqui), and Argyreia nervosa (Hawaiian baby woodrose).[13][22][16][23] Morning glory seeds have a history of entheogenic use in Mesoamerica dating back at least hundreds of years.[13][18][24] They have also since been used by many Westerners.[25] In addition to ergine, morning glory seeds contain other ergolines such as lysergic acid hydroxyethylamide (LSH), lysergic acid propanolamide (ergonovine), and isoergine.[17][18][13] Some of these compounds are pharmacologically active and are thought to contribute to the effects of the seeds as well.[17][18][13][26][27] There has been debate about the role of ergine in causing the psychedelic effects of morning glory seeds.[16][28][29][20]
Ergine was first described by Sidney Smith and Geoffrey Timmis after they isolated it from ergot in 1932.[12] It was first synthesized subsequent to its isolation in the 1930s.[17][30] Albert Hofmann, the discoverer of LSD's psychedelic effects in 1943, evaluated the effects of ergine in humans in 1947 and described the results many years later.[16][17][27][31] He and his colleagues also isolated ergine from morning glory seeds in 1960.[32][33][17][13] Morning glory seeds started to become frequently used as a recreational drug that same year[25] and have been widely used since.[13][32][34][35] Recreational use of morning glory seeds may be increasing due to their inexpensiveness, widespread availability, and lack of legal restrictions.[10][32] Ergine has been encountered as a novel designer drug in Europe.[36] Ergine, though not morning glory seeds, has become a controlled substance in various places in the world.[37][38]
Remove ads
Use
Summarize
Perspective
Ergine is most commonly used as a drug in the form of morning glory seeds, including those of Ipomoea tricolor (tlitliltzin), Ipomoea corymbosa (ololiuhqui), and Argyreia nervosa (Hawaiian baby woodrose).[13] They may be consumed whole and intact, crushed or ground up, or drunk as an extract following soaking of the seeds in water.[39][9][10] A hallucinogenic dose (~0.5–1 mg) is 150 to 200 seeds (3–6 g) of Ipomoea tricolor (0.02% ergine by dry weight) or 5 to 10 seeds (0.5–1 g) of Argyreia nervosa (0.14% ergine by dry weight).[39][9][10][25][20] The onset is 0.3 to 3 hours and the duration is 4 to 10 hours.[39][9][10]
Ergine may be used as a drug in pure or purified form as well, either isolated or synthesized.[16][19][40] Albert Hofmann and colleagues found that a 0.5 to 2 mg dose by intramuscular or subcutaneous injection produced relatively weak but significant hallucinogenic effects as well as marked sedation.[16][17][31][25][19][40][41] Another study described the effects of pure ergine by injection but the doses were not clearly provided (although appeared to be around 0.1–1 mg).[25][32][42][43] Based on the preceding studies, Alexander Shulgin describes pure ergine as having a dosage of 0.5 to 1 mg and being 10-fold less potent than LSD, but as being "not hallucinogenic".[28] Hofmann also stated that ergine was 10- to 40-fold less potent than LSD and that it had qualitatively different effects.[31][41] Robert Oberlender has stated that ergine is about 30-fold less potent than LSD in humans.[44] Heim and colleagues assessed ergine at higher doses of 3 to 6 mg orally and observed toxic-like effects, whereas isoergine at 2 to 5 mg orally produced notable hallucinogenic effects, including some euphoria, synaesthesia, and altered time perception.[20][45][27]
Per Shulgin in his 1997 book TiHKAL (Tryptamines I Have Known and Loved) however, both ergine and isoergine are "probably correctly dismissed" as not contributing to the effects of morning glory seeds.[16] The poorly-stable lysergic acid hydroxyethylamides (LSHs) might alternatively be involved in the psychedelic effects of morning glory seeds per Shulgin.[46]
Sleepy grass (Achnatherum robustum) and Claviceps paspali (ergot) have similar ergoline constituents as morning glory seeds and have also been used to produce psychoactive effects, albeit rarely.[47][48]
Remove ads
Effects
Summarize
Perspective
Subjective effects
Ergine has only been given a minuscule amount of attention. Albert Hofmann and his colleagues self-administered ergine.[17] In addition, it was assessed in two clinical studies by other researchers.[42][27] Synthetic ergine was used in all of these cases.[42][17][27] Hofmann stated that ergine induces a "psychotomimetic" effect with "a marked narcotic component": "Tired, dreamy, incapable of clear thoughts. Very sensitive to noises which give an unpleasant sensation."[17] There are parallels between Hofmann's comments and the ones in the two trials:[17]
Heim 1968 also noted "paraesthesia", "synesthesia" and an "overestimation of the time that had passed" (isoergine), but also concluded, "our experiments with ᴅ-lysergic acid amide also confirm the results that Sᴏʟᴍꜱ had made with this substance, namely a predominantly sedative intoxication." Hofmann emphasized this sedative effect:[excessive quote]
"Furthermore there is not only a quantitative difference between the principles of Ipomoea [tricolor] and Turbina corymbosa and LSD; there is likewise a qualitative one, LSD being a very specific hallucinogen, whereas the psychic effects of lysergic acid amide and the total alkaloids of these two plants are characterized by a pronounced narcotic component (Hofmann, 1968)."[49]
"A substance very closely related to LSD, the monoethylamide of lysergic acid (LAE-32), in which an ethyl group is replaced by a hydrogen atom on the diethylamide residue of LSD, proved to be some ten times less psychoactive than LSD. The hallucinogenic effect is also qualitatively different: it is characterized by a narcotic component. This narcotic effect is yet more pronounced in lysergic acid amide (LA-111), in which both ethyl groups of LSD are displaced by hydrogen atoms. These effects, which I established in comparative self-experiments with LA-111 and LAE-32, were corroborated by subsequent clinical investigations."[31]
"The experience had some strong narcotic effect, but at the same time there was a very strange sense of voidness. In this [void], everything loses its meaning. It is a very mystical experience."[14]
Physiological effects
While its physiological effects vary from person to person, the following symptoms have been attributed to the consumption of ergine or ergine containing seeds: sedation, visual hallucinations, auditory hallucinations, euphoria, loss of motor control, nausea, vasoconstriction, delusions, anxiety, paranoia, and irregular heartbeats.[23][50][51][52]
One study found that two of four human subjects experienced cardiovascular dysregulation and the study had to be halted, concluding that the ingestion of seeds containing ergine was less safe than commonly believed. Importantly this may have been a product of other substances within the seeds. The same study also observed that reactions were highly differing in type and intensity between different subjects.[52]
Remove ads
Side effects
Summarize
Perspective
A 2016 study showed that penniclavine was the predominant alkaloid in Ipomoea tricolor seeds.[53] Ergoclavines are known to cause convulsive ergotism,[54] the milder form of ergotism. Gangrenous ergotism is caused by ergopeptines: the complex peptide moiety forces persistence at the receptor sites.[55] Ergopeptines are rare in Convolvulaceae, being found in 10 species,[55][56] not including the three that are commonly ingested, although Paulke 2014 says analytical evidence suggests that A. nervosa contains ergopeptines.[57] Many people desire purified seed extracts, but the efficacy of this is questionable, as even pure ergine and ergonovine have shown toxic effects.
The side effects of ergine have been described as follows: "The expression and behavior of the test subjects changed just 45 minutes after taking the substance: the test subjects appeared to be suffering, their facial expressions were deteriorating as if they had suffered a serious illness, and their movements were noticeably slower. [...] In the self-reports of both test subjects, complaints about vegetative symptoms predominated: unpleasant, flu-like feeling of illness, nausea, sudden onset of nausea, with vomiting that could be stopped with 2 cm3 of Cyclicinum hydrochloricum. In addition, sensations of heat, sweating, dizziness, a feeling of heaviness and general tiredness were observed."[27]
And the side effects of ergonovine have been described as follows: "Walking in this dreamy state was difficult due to leg cramps and slight incoordination. There was always a great desire to lie supine. [...] One of us (J.B.) felt the cramping in the legs as painful and debilitating. [...] We all had a slight hangover the following morning. [...] The mild entheogenic effects of ergonovine are similar to those of LSD. However, in dramatic contrast to LSD, the somatic effects of ergonovine greatly overshadow its psychic effects, so much so that we had no wish to ingest more than 10.0 mg, [...]".[58]
Like other psychedelics, ergine is not considered to be addictive. Additionally, there are no known deaths directly associated with pharmacological effects of ergine consumption. All associated deaths are due to indirect causes, such as self-harm, impaired judgement, and adverse drug interactions. One known case involved a suicide that was reported in 1964 after ingestion of morning glory seeds.[59] Another instance is a death due to falling off of a building after ingestion of Hawaiian baby woodrose seeds and alcohol.[60] A study gave mice 3000 mg/kg with no lethal effects.[citation needed]
Chemical coatings on seeds
Garden seeds, in general, may be coated with fungicides et. al. (e.g. neonicotinoids, Thiram, and ApronMaxx). It is rumored that this is the cause of the severe adverse effects that have been observed, but the seeds, themselves, contain toxins, specifically glycoresins[61][62] and ergoclavines.[54] Some[who?] even believe that an emetic chemical is purposely added to the seeds to prevent people from ingesting them, but that has never been proven.[citation needed] One 1964 article states that reported adverse effects must come from the seeds, as the stated insecticide is too "inocuous" to humans to be responsible.[51][59][63]
A related rumor is that the seeds contain cyanogenic glycosides. The UseNet post on which this is based contains two references, but neither of them support that claim,[64] and Eckart Eich says that they probably don't occur in many Convolvulaceae.[55] There is a similar claim in a publication from 1973, warning about "a strychnine-like alkaloid",[65] but that is probably just a misapplication of the claim that peyote contains strychnine, which, itself, is a rumor.[66]
Remove ads
Overdose
Cases of overdose of ergine and morning glory seeds and associated toxicity have been reported.[20]
Interactions
The interactions of ergine and of morning glory seeds have been discussed.[20]
Pharmacology
Summarize
Perspective
Pharmacodynamics
Ergine interacts with serotonin, dopamine, and adrenergic receptors similarly to but with lower affinity than lysergic acid diethylamide (LSD).[67][68] It is known to act as an agonist of the serotonin 5-HT2A and 5-HT2B receptors similarly to LSD, albeit much less potently and with reduced activational efficacy.[68] The drug has about 4.3% of the antiserotonergic activity of LSD in the isolated rat uterus in vitro.[44][70] The psychedelic effects of ergine can be attributed to activation of serotonin 5-HT2A receptors.[71][72][73]
Remove ads
Chemistry
Ergine, also known as lysergic acid amide (LSA) or as lysergamide, is a ergoline and lysergamide. It is the simplest lysergamide and is the parent structure of this family of compounds. Hence, all lysergamides are derivatives of ergine. Lysergic acid diethylamide (LSD) is the analogue of ergine with two ethyl groups substituted on its amide moiety.
The extraction of ergine from morning glory seeds has been described.[74][75]
Remove ads
Natural occurrence
Summarize
Perspective
Ergine is not a biosynthetic endpoint itself, but rather a hydrolysis product of lysergic acid hydroxyethylamide (LSH), lysergic acid propanolamide (ergonovine), and ergopeptines or their ergopeptam precursors.[76][77][78][79][80]
LSH is very vulnerable to this hydrolysis,[25][49] and many analyses of ergoline-containing products show little to no LSH and substantial amounts of ergine.
An ergine analog, 8-hydroxyergine, has also been found in natural products in two studies.[81][82] Methylergonovine and methysergide (1-methylmethylergonovine) have also been found in a natural product in one study;[57] these are documented as semisynthetic compounds, so the findings need to be repeated for certainty. The aforementioned chemicals are the only natural lysergamides.
LSH and ergine are predominant in Claviceps paspali,[83][84][85] but are only found in trace amounts in the more well-known Claviceps purpurea.[86][87] Both are ergot-spreading fungi. The major products of C. purpurea are ergopeptines, but C. paspali does not generate ergopeptines.[80] Ergonovine is the only lysergamide in C. purpurea in a substantial amount.[87]
LSH and ergine are also found in the related fungi, Periglandula, which are permanently connected with Ipomoea tricolor, Ipomoea corymbosa, Argyreia nervosa ("morning glory", coaxihuitl, Hawaiian baby woodrose), and an estimated over 440 other Convolvulaceae[88] (ergolines have been identified in 42 of these plants and not all of them contain ergine).[55] Ergonovine is present in Ipomoea tricolor in one-tenth to one-third of the amount of ergine.[53] This variable may account for the varying reports about the psychedelic effect of these seeds.[26]
Other fungi that have been found to contain LSH and/or ergine:
- Unidentified Acremonium species that infects sleepy grass (C. purpurea also infects sleepy grass[89]).[82]
- Unidentified Acremonium species that infects drunken horse grass[90]
- Acremonium coenophialum (infects Festuca arundinacea)[91]
- Epichloë gansuensis var. inebriens (infects drunken horse grass)[92]
- Metarhizium brunneum[93]
- Metarhizium acridum[93]
- Metarhizium anisopliae[93]
- Metarhizium flavoviride[93]
- Metarhizium robertsii[93]
- Aspergillus leporis[94]
- Aspergillus homomorphus[94]
- Aspergillus hancockii[94]
All of these fungi are related to Claviceps fungi. Aspergillus is considered to be a more distant relative of Claviceps.
Other fungi that possibly contain ergine (i.e. they have been found to contain ergonovine and/or ergopeptines):
- Claviceps hirtella[95]
- Neotyphodium lolii[96]
- Unidentified Epichlöe and Neotyphodium (asexual forms of Epichlöe) species[97]
- Aspergillus fumigata[98]
- Aspergillus flavus[98]
- Botritis fabae[98]
- Curvularia lunata[98]
- Geotrichum candidum[98]
- Balansia cyperi[98]
- Balansia claviceps[98]
- Balansia epichloë[98]
- Epichloë amarillans[99]
- Epichloë cabralii (H)[100]
- Epichloë canadensis (H)[101][102]
- Epichloë coenophiala (H)[101][103][104][105]
- Epichloë festucae[99]
- Epichloë festucae var. lolii[96][106]
- Epichloë festucae var. lolii x E. typhina (H)[101][107]
- Epichloë inebriens[99]
- Epichloë glyceriae[99]
- Epichloë mollis[101]
- Epichloë typhina[98]
- Epichloë typhina ssp. poae[99][100]
- Epichloë typhina ssp. clarkii[108]
- Epichloë sp. AroTG-2(H)[109]
- Epichloë sp. FaTG-2(H)[101][103][105][110][107]
- Epichloë sp. FaTG-4(H)[101][105]
- Hypomyces aurantius[98]
- Sepedonium sp.[98]
- Cunnigbamella blakesleana[98]
- Mucor biemalis[98]
- Rhizopus nigricans[98]
Biosynthesis

The biosynthetic pathway to ergine starts like most other ergoline alkaloid- with the formation of the ergoline scaffold. This synthesis starts with the prenylation of L-tryptophan in an SN1 fashion with dimethylallyl diphosphate (DMAPP) as the prenyl donor and catalyzed by prenyltransferase 4-dimethylallyltryptophan synthase (DMATS), to form 4-L-dimethylallyltryptophan (4-L-DMAT). The DMAPP is derived from mevalonic acid. A three strep mechanism is proposed to form 4-L-DMAT: the formation of an allylic carbocation, a nucleophilic attack of the indole nucleus to the cation, followed by deprotonation to restore aromaticity and to generate 4-L-DMAT.[111] 4-Dimethylallyltyptophan N-methyltransferase (EasF) catalyzes the N-methylation of 4-L-DMAT at the amino of the tryptophan backbone, using S-Adenosyl methionine (SAM) as the methyl source, to form 4-dimethylallyl-L-abrine (4-DMA-L-abrine).[111] The conversion of 4-DMA-L-abrine to chanoclavine-I is thought to occur through a decarboxylation and two oxidation steps, catalyzed by the FAD dependent oxidoreductase, EasE, and the catalase, EasC. The chanoclavine intermediate is then oxidized to chanoclavine-l-aldehyde, catalyzed by the short-chain dehydrogenase/reductase (SDR), EasD.[111][112]

From here, the biosynthesis diverges and the products formed are plant and fungus-specific. The biosynthesis of ergine in Claviceps purpurea will be exemplified, in which agroclavine is produced following the formation of chanoclavine-l-aldehyde, catalyzed by EasA through a keto-enol tautomerization to facilitate rotation about the C-C bond, followed by tautomerization back to the aldehyde and condensation with the proximal secondary amine to form an iminium species, which is subsequently reduced to the tertiary amine and yielding agroclavine.[111][112] Cytochrome P450 monooxygenases (CYP450) are then thought to catalyze the formation of elymoclavine from argoclavine via a 2 electron oxidation. This is further converted to paspalic acid via a 4 electron oxidation, catalyzed by cloA, a CYP450 monooxygenase. Paspalic acid then undergoes isomerization of the C-C double bond in conjugation with the acid to form D-lysergic acid.[111] While the specifics of the formation of ergine from D-lysergic acid are not known, it is proposed to occur through a nonribosomal peptide synthase (NRPS) with two enzymes primarily involve: D-lysergyl peptide synthase (LPS) 1 and 2.[111][112]

Remove ads
History
Summarize
Perspective
Ergine was first obtained by Sidney Smith and Geoffrey Willward Timmis in 1932.[12]
Albert Hofmann was first to identify ergine as a natural constituent of Turbina corymbosa seeds.[23]
Albert Hofmann describes ergine as "the main constituent of ololiuhqui".[113] Ololiuhqui was used by South American healers in shamanic healing ceremonies.[50] Similarly, ingestion of morning glory seeds by Mazatec tribes to "commune with their gods" was reported by Richard Schultes in 1941 and is still practiced today.[114][50]
According to the ethnobotanist R. Gordon Wasson, Thomas MacDougall and Francisco Ortega ("Chico"), a Zapotec guide and trader, should be credited for the discovery of the ceremonial use of Ipomoea tricolor seeds in Zapotec towns and villages in the uplands of southern Oaxaca. The seeds of both Ipomoea tricolor and Rivea corymbosa, another species which has a similar chemical profile, are used in some Zapotec towns.[115]
The Central Intelligence Agency conducted research on the psychedelic properties of Rivea corymbosa seeds for MKULTRA.[116]
My chemical investigations of Ololiuhqui seeds led to the unexpected discovery that the entheogenic principles of Ololiuhqui are alkaloids, especially lysergic acid amide, which exhibits a very close relationship to lysergic acid diethylamide (=ʟsᴅ). It follows therefrom that ʟsᴅ, which hitherto had been considered to be a synthetic product of the laboratory, actually belongs to the group of sacred Mexican drugs.
— Albert Hofmann, Burg i.L., Switzerland, November 1992[117]
Hofmann's discovery of ergine and related compounds in morning glory seeds, which are closely structurally related to LSD, was said to have initially been met with "a state of disbelief bordering on accusations of scientific fraud", but was soon confirmed by other researchers.[45]
Society and culture
Legal status
The legality of consuming, cultivating, and possessing ergine varies depending on the country.
Australia
In most Australian states, the consumption of ergine containing materials is prohibited under state legislation.
Canada
In Canada, ergine is not illegal to possess as it is not listed under Canada's Controlled Drugs and Substances Act, though it is likely illegal to sell for human consumption.[37]
New Zealand
In New Zealand, ergine is a controlled drug, however the plants and seeds of the morning glory species are legal to possess, cultivate, buy, and distribute.
United Kingdom
Ergine is considered a Class A substance in the United Kingdom, categorized as a precursor to LSD.
United States
There are no laws against possession of ergine-containing seeds in the United States. However, possession of the pure compound without a prescription or a DEA license would be prosecuted, as ergine, under the name "lysergic acid amide", is listed under Schedule III of the Controlled Substances Act.[38]
Remove ads
See also
- Substituted lysergamide
- Isoergine (isolyergic acid amide; iso-LSA; isolysergamide)
- Aztec use of entheogens § Ololiuqui and Tlitliltzin
- Morning glory § Chemistry and ethnobotany
- List of entheogens
- List of psychoactive plants
References
External links
Wikiwand - on
Seamless Wikipedia browsing. On steroids.
Remove ads