Isomerization
Transformation of the chemical structure of a molecule or ion From Wikipedia, the free encyclopedia
In chemistry, isomerization or isomerisation is the process in which a molecule, polyatomic ion or molecular fragment is transformed into an isomer with a different chemical structure.[1] Enolization is an example of isomerization, as is tautomerization.[2]
When the activation energy for the isomerization reaction is sufficiently small, both isomers can often be observed and the equilibrium ratio will shift in a temperature-dependent equilibrium with each other. Many values of the standard free energy difference, , have been calculated, with good agreement between observed and calculated data.[3]
Examples and applications
Summarize
Perspective
Alkanes
Skeletal isomerization occurs in the cracking process, used in the petrochemical industry to convert straight chain alkanes to isoparaffins as exemplified in the conversion of normal octane to 2,5-dimethylhexane (an "isoparaffin"):[4]
Fuels containing branched hydrocarbons are favored for internal combustion engines for their higher octane rating.[5] Diesel engines however operate better with straight-chain hydrocarbons.
Alkenes
Cis vs trans
Trans-alkenes are about 1 kcal/mol more stable than cis-alkenes. An example of this effect is cis- vs trans-2-butene. The difference is attributed to unfavorable non-bonded interactions in the cis isomer. This effects helps to explain the formation of trans-fats in food processing. In some cases, the isomerization can be reversed using UV-light. The trans isomer of resveratrol converts to the cis isomer in a photochemical reaction.[6]
Terminal vs internal
Terminal alkenes prefer to isomerize to internal alkenes:
- H2C=CHCH2CH3 → CH3CH=CHCH3
The conversion essentially does not occur in the absence of metal catalysts. This process is employed in the Shell higher olefin process to convert alpha-olefins to internal olefins, which are subjected to olefin metathesis.
Other organic examples
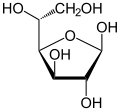
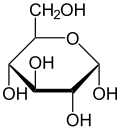
Isomerism is a major topic in sugar chemistry. Glucose, the most common sugar, exists in four forms.
Aldose-ketose isomerism, also known as Lobry de Bruyn–van Ekenstein transformation, provides an example in saccharide chemistry.[citation needed]
Inorganic and organometallic chemistry
The compound with the formula (C5H5)2Fe2(CO)4 exists as three isomers in solution. In one isomer the CO ligands are terminal. When a pair of CO are bridging, cis and trans isomers are possible depending on the location of the C5H5 groups.[7]
Another example in organometallic chemistry is the linkage isomerization of decaphenylferrocene, [(η5-C5Ph5)2Fe].[8][9]

See also
References
Wikiwand - on
Seamless Wikipedia browsing. On steroids.