East Asian languages
Proposed language family From Wikipedia, the free encyclopedia
The East Asian languages are a language family (alternatively macrofamily or superphylum) proposed by Stanley Starosta in 2001. The proposal has since been adopted by George van Driem and others.
| East Asian | |
|---|---|
| (proposed, under study) | |
| Geographic distribution | East Asia, South Asia, Southeast Asia, Oceania, Madagascar |
| Linguistic classification | Proposed language family |
| Subdivisions |
|
| Language codes | |
| ISO 639-3 | – |
| Glottolog | None |
Classifications
Summarize
Perspective
Early proposals
Early proposals of similar linguistic macrophylla, in narrower scope:[1]
- Austroasiatic, Austronesian, Kra-Dai, Tibeto-Burman: August Conrady (1916, 1922)[2][3] and Kurt Wulff (1934, 1942)[4][5]
- Austroasiatic, Austronesian, Kra-Dai, Hmong-Mien: Paul K. Benedict (1942),[6] Robert Blust (1996),[7] Ilia Peiros (1998)[8]
- Austroasiatic, Austronesian, Kra-Dai, Tibeto-Burman, Hmong-Mien: Stanley Starosta (2001)
Precursors to the East Asian proposal:
- Austro-Tai (Kra-Dai and Austronesian): Gustave Schlegel (1901, 1902),[9][10] Weera Ostapirat (2005)[11][12]
- Austric (Austroasiatic and Austronesian): Wilhelm Schmidt (1906),[13] Lawrence Reid (1994, 2005)[14][15]
Starosta (2005)

Stanley Starosta's (2005)[16] East Asian proposal includes a "Yangzian" branch, consisting of Austroasiatic and Hmong–Mien, to form an East Asian superphylum. However, Starosta believes his proposed Yangzian to be a direct sister of Sino-Tibetan rather than Austronesian, which is more distantly related to Sino-Tibetan as a sister of Sino-Tibetan-Yangzian. He concludes Proto-East Asian was a disyllabic (CVCVC) language spoken from 6,500 to 6,000 BCE by Peiligang culture and Cishan culture millet farmers on the North China Plain (specifically the Han River, Wei River, and central Yellow River areas).[17]
- East Asian
- Austronesian
- (various Formosan branches)
- Extra-Formosan
- Sino-Tibetan-Yangzian
- Sino-Tibetan
- Yangzian
- Austronesian
Starosta (2005) proposes the following Proto-East Asian morphological affixes, which are found in Proto-Tibeto-Burman and Proto-Austronesian, as well as in some morphologically conservative Austroasiatic branches such as Nicobaric.[18]
- *m(V)- 'agent of V-ing'
- *-Vn 'patient of V-ing'
- *sV- 'instrument of V-ing'
- *n(V)- 'perfective'
van Driem (2012)
The following tree of East Asian superphylum (macrofamily) was proposed by George van Driem in 2012 at the 18th Himalayan Languages Symposium, held at the Benares Hindu University.[1][19]
- East Asian
- Austro-Tai
- Austroasiatic
- Himalayan-Yangtzean
- Trans-Himalayan
- Sino-Bodic
- Burmo-Qiangic
- Brahmaputran
- Gongduk, etc.
- Kiranti, etc.
- Yangtzean
- Trans-Himalayan

According to van Driem, the linguistic evidence for the East Asian languages matches the genetic evidence from Y-DNA Haplogroup O.[20] (Further information: Father Tongue hypothesis)
Larish (2006, 2017)
According to Michael D. Larish, the languages of Southeast and East Asia descended from one proto-language (which he calls "Proto-Asian"). Japonic is grouped together with Koreanic as one branch of the Proto-Asian family. The other branch consists of the Austronesian, Austroasiatic, Kra-Dai, Hmong-Mien and Sino-Tibetan languages.[21][22]
- East Asian
- Japano-Koreanic
- Austro-Asian
Vocabulary comparison
Summarize
Perspective
Below is a comparison of basic vocabulary items for proto-languages of all 5 East Asian language families.
- Sources
- Proto-Tibeto-Burman: Matisoff (2015)[23]
- Proto-Hmong-Mien: Ratliff (2010)[24]
- Proto-Austroasiatic: Sidwell (2024);[25] Sidwell & Rau (2015)[26]
- Proto-Austronesian: Blust & Trussel (2020)[27]
- Proto-Tai: Pittayaporn (2009)[28]
- Proto-Hlai: Norquest (2007)[29]
- Proto-Kra: Ostapirat (2000)[30]
| Sino-Tibetan | Hmong-Mien | Austroasiatic | Austronesian | Kra-Dai | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| gloss | Proto-Tibeto-Burman | Proto-Hmong-Mien | Proto-Austroasiatic | Proto-Austronesian | Proto-Tai | Proto-Hlai | Proto-Kra |
| hair | *(t)sam | *pljei | *sukˀ, *sɔkˀ | *bukeS | *prɤmA | *hnom | *m-səmA |
| eye | *s-myak | *mu̯ɛjH | *matˀ | *maCa | *p.taːA | *tʃʰaː | *m-ʈaA |
| ear | *r/g-na | *mbræu | *Ctoːr | *Caliŋa | *krwɯːA | *ljəy | *k-raA |
| nose | *s-na ~ *s-naːr | *mbruiH | *muːh, *muːɕ | *ujuŋ | *ɗaŋA | *kʰət | *hŋətD |
| tooth | *s/p-wa | *hmjinʔ | *muɲ, *məɲ | *lipen, *n/ŋipen | *wanA | *fjən | *l-pənA |
| tongue | *m/s-lay ~ *s-ley | *mblet | *lntaːkˀ | *Sema, *lidam | *liːnC | *hliːnʔ | *l-maA |
| hand | *lak ~ *C-yak | *-bɔuʔ | *tiːˀ | *kamay | *mwɯːA | *C-mɯː | *mjaA |
| bone | *s/m/g-rus | *tshuŋʔ | *cʔaːŋ | *CuqelaN | *C̥.dukD | *Cuɾɯːk | *dəkD |
| blood | *s-hywəy-t | *ntshjamʔ | *(m)ɕaːm | *daRaq | *lɯətD | *alaːc | *platD |
| liver | *m-sin | *-hri̯ən | *kləːm;[26] *gre(ː)ɕ | *qaCay | *tapD | *ɗəy | *təpD |
| meat, flesh | *sya-n | P-Mienic *ʔaB | *sacˀ | *Sesi | *n.mɤːC | *rəmʔ | *ʔaɯC |
| dog | *d-kʷəy-n | P-Hmongic *hmaŋC | *cɔʔ | *asu | *ʰmaːA | *hmaː | *x-maA |
| bird | *s-ŋak | *m-nɔk | *ciːm | *manuk | *C̬.nokD | *səc | *ɳokD |
| fish | *s-ŋya | *mbrəuʔ | *kaʔ | *Sikan | *plaːA | *hlaː | *p-laA |
| louse | *s-r(y)ik | *ntshjeiʔ | *ciʔ | *kuCux | *trawA | *tʃʰwəw | *C-ʈuA |
| leaf | *lay | P-Hmongic *mblɔŋA, P-Mienic *nɔmA |
*slaʔ | *waSaw | *ɓaɰA | *ɓɯː | *ɖiŋA |
| sun, day | *s-nəy | P-Mienic *hnu̯ɔiA | *tŋiːˀ | *waRi, *qajaw | *ŋwanA | *hŋwən | *(l-/h)wənA |
| moon | *s/g-la | *hlaH | *khe(ː)ʔ | *bulaN, *qiNaS | *ɓlɯənA | *C-ɲaːn | *(C-)tjanA |
| water | *m-t(w)əy-n ~ *m-ti-s | *ʔu̯əm | *ɗaːkˀ; Pal. *ʔoːm | *daNum | *C̬.namC | *C-nəmʔ | *ʔuŋC |
| rain | *r/s/g-wa | P-Hmongic *m-noŋC | *gmaːˀ | *quzaN | *C̥.wɯnA | *fun | *jəlA |
| fire | *mey | *douʔ | *ʔuːɕ | *Sapuy | *wɤjA | *fiː | *puiA |
| name | *r-mi(ŋ/n) | *mpɔuH | *ɟmuh, *ɟmɨh | *ŋajan | *ɟɤːB | *pʰaːŋ | *n(ʒ)iA |
| eat | *m-dz(y)a-k/n/t/s | P-Mienic *ɲənC | *ca(ː)ʔ | *kaen | *kɯɲA | *kʰən | *kanA |
| die | *səy | *dəjH | *kceːt[26] | *ma-aCay | *p.taːjA | *hlaːwɦ | *pɣonA |
| I | *ŋa-y ~ *ka | P-Hmongic *kɛŋB | *ʔaɲ | -ku | *kuːA | *ɦuː | *kuA |
| you (sg.) | *na-ŋ | *mu̯ei | *miːˀ, *meːˀ | -mu | *mɯŋA | *C-mɯː | *məA/B |
Distributions
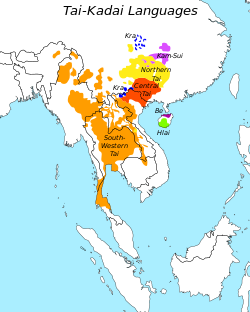
- Distribution of Sino-Tibetan languages
- Distribution of Kra–Dai languages
- Distribution of Austroasiatic languages
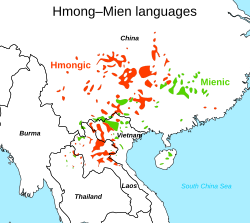
- Distribution of Hmong–Mien languages
- Dispersal of Austronesian languages
- Distribution of Japonic languages
- Distribution of Koreanic languages
See also
Notes and references
External links
Wikiwand - on
Seamless Wikipedia browsing. On steroids.