Top Qs
Timeline
Chat
Perspective
BRD4
Protein-coding gene in the species Homo sapiens From Wikipedia, the free encyclopedia
Remove ads
Bromodomain-containing protein 4 is a protein that in humans is encoded by the BRD4 gene.[5][6]
BRD4 is a member of the BET (bromodomain and extra terminal domain) family, which also includes BRD2, BRD3, and BRDT.[7] BRD4, similar to other BET family members, contains two bromodomains that recognize acetylated lysine residues.[8] BRD4 also has an extended C-terminal domain with little sequence homology to other BET family members.[7]
Remove ads
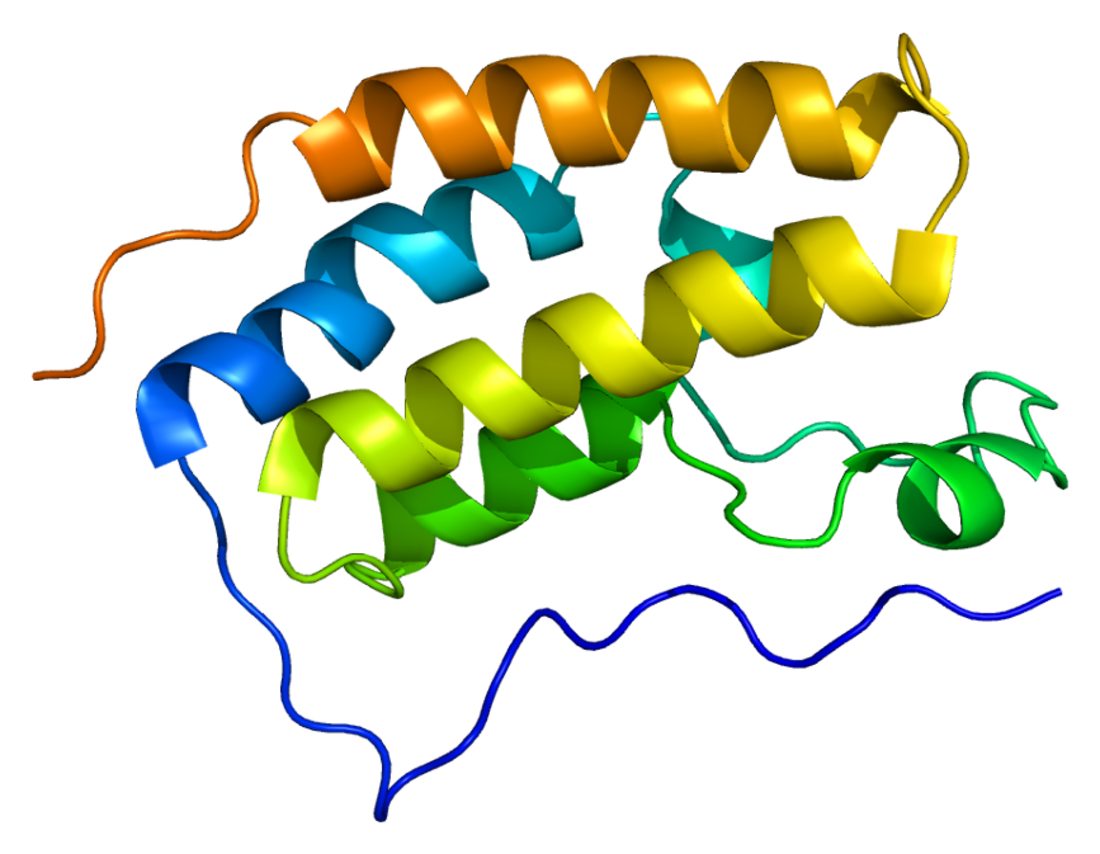
Structure
The two bromodomains in BRD4, termed BD1 and BD2, consist of 4 alpha-helices linked by 2 loops.[9] The ET domain structure is made up of 3 alpha-helices and a loop.[10] The C-terminal domain of BRD4 has been implicated in promoting gene transcription through interaction with the transcription elongation factor P-TEFb and RNA polymerase II.[11][12][13]
Function
The protein encoded by this gene is homologous to the murine protein MCAP, which associates with chromosomes during mitosis, and to the human BRD2 (RING3) protein, a serine/threonine kinase. Each of these proteins contains two bromodomains, a conserved sequence motif which may be involved in chromatin targeting. This gene has been implicated as the chromosome 19 target of translocation t(15;19)(q13;p13.1), which defines the NUT midline carcinoma. Two alternatively spliced transcript variants have been described.[6]
Remove ads
Role in cancer
Most cases of NUT midline carcinoma involve translocation of the BRD4 gene with NUT genes.[14] BRD4 is often required for expression of Myc and other "tumor driving" oncogenes in hematologic cancers including multiple myeloma, acute myelogenous leukemia and acute lymphoblastic leukaemia.[15]
BRD4 is a major target of BET inhibitors,[15][16] a class of pharmaceutical drugs currently being evaluated in clinical trials.
Interactions
Notably, BRD4 interacts with P-TEFb via its P-TEFb interaction domain (PID), thereby stimulating its kinase activity and stimulating its phosphorylation of the carboxy-terminal domain (CTD) of RNA polymerase II.[17]
BRD4 has been shown to interact with GATA1,[18] JMJD6,[19] RFC2,[20] RFC3,[20] RFC1,[20] RFC4[20] and RFC5.[20]
BRD4 has also been implicated in binding with the diacetylated Twist protein, and the disruption of this interaction has been shown to suppress tumorigenesis in basal-like breast cancer.[21]
BRD4 has also been shown to interact with a variety of inhibitors, such as MS417; inhibition of BRD4 with MS417 has been shown to down-regulate NF-κB activity seen in HIV-associated kidney disease.[22] BRD4 also interacts with apabetalone (RVX-208), which is being evaluated for treatment of atherosclerosis and cardiovascular disease.[23]
Remove ads
References
Further reading
External links
Wikiwand - on
Seamless Wikipedia browsing. On steroids.
Remove ads