Aram-Damascus
Ancient Aramean state to 732 BCE From Wikipedia, the free encyclopedia
Aram-Damascus (/ˈærəm ... / ARR-əm ...) was an Aramean polity that existed from the late-12th century BCE until 732 BCE, and was centred around the city of Damascus in the Southern Levant.[1] Alongside various tribal lands, it was bounded in its later years by the polities of Assyria to the north, Ammon to the south, and Israel to the west.
Aram-Damascus | |||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| c. 12th century BCE–732 BCE | |||||||||
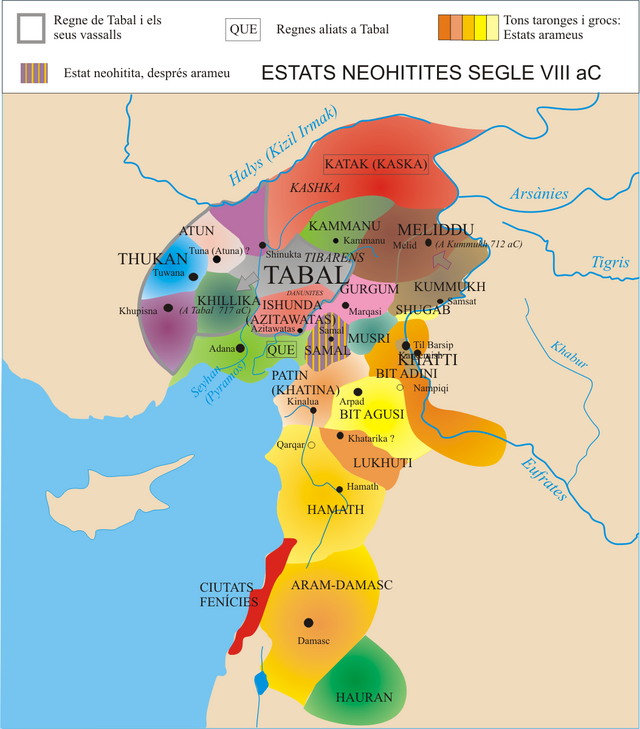
 The region around 830 BCE, with Aram-Damascus in green | |||||||||
| Capital | Damascus | ||||||||
| Common languages | Old Aramaic | ||||||||
| Religion | Ancient Semitic religion | ||||||||
| King | |||||||||
• 885 BCE–865 BCE | Ben-Hadad I | ||||||||
• 865 BCE–842 BCE | Ben-Hadad II | ||||||||
• 842 BCE–796 BCE | Hazael | ||||||||
• 796 BCE–792 BCE | Ben-Hadad III | ||||||||
• 754 BCE–732 BCE | Rezin (last) | ||||||||
| History | |||||||||
• Established | c. 12th century BCE | ||||||||
| 732 BCE | |||||||||
| |||||||||
| Today part of | Syria Jordan Israel Lebanon | ||||||||
The compound name "Aram-Damascus" is only found in the Hebrew Bible, where it sometimes also is referred to as simply "Aram" or "Damascus". It is also referred to as "Aram" in some Aramaic inscriptions. In Assyrian sources, "Aram" was never used to designate it. It was often referred to as "Damascus" or "imērīšu" (meaning "his donkey"), and sometimes "Bīt-Ḫaza’ili" (meaning "house of Hazael"), in Assyrian sources.[2]
History
The Tanakh gives accounts of Aram-Damascus' history, mainly in its interaction with Israel and Judah. There are biblical texts referencing battles that took place between the United Kingdom of Israel under David and the Arameans in Southern Syria in the 10th century BCE.[3]
In the 9th century BCE, Hazael fought against the Assyrians, had some influence over the northern Syrian state of Unqi, and conquered Israel.[4][5]
To the southwest, Aram-Damascus reached most of the Golan to the Sea of Galilee.[6]
In the 8th century BCE, Rezin had been a tributary of Tiglath-Pileser III, a king of Assyria.[7] In c. 732 BCE, he formed an alliance with Pekah, a king of Israel, to attack Ahaz, a king of Judah; Ahaz appealed to Tiglath-Pileser III for help, which was provided by the Assyrian king after Judah paid tribute.[8] Subsequently, Tiglath-Pileser III attacked Damascus and annexed Aram.[7] The kingdom's population was deported and Rezin was executed. Tiglath-Pileser III recorded this act in one of his inscriptions.[9]
Kings
- Hezion, ca. 960 BCE
- Tabrimmon, ca. 930 BCE, son of Hezion
- Ben-Hadad I, 885–865 BCE
- Ben-Hadad II, 865–842 BCE
- Hazael, 842–805/796 BCE, usurper
- Ben-Hadad III, 796–792 BCE, son of Hazael
- Rezin, 754 BCE–732 BCE
See also
- Aram (region), a historical region in the Levant mentioned in the Bible
- Aram Rehob, an early Aramean kingdom
References
Sources
Wikiwand - on
Seamless Wikipedia browsing. On steroids.
