Akula-class submarine
Class of nuclear attack submarines From Wikipedia, the free encyclopedia
The Akula class, Soviet designation Project 971 Shchuka-B (Russian: Щука-Б, lit. 'Pike-B', NATO reporting name Akula) is a series of fourth generation nuclear-powered attack submarines (SSNs) first deployed by the Soviet Navy in 1986. There are four sub-classes or flights of Shchuka-B, consisting of the original seven Project 971 boats (codenamed Akula I), commissioned between 1984 and 1990; six Project 971Is (Improved Akulas), commissioned between 1991 and 2009; one Project 971U (Akula II), commissioned in 1995; and one Project 971M (Akula III), commissioned in 2001. The Russians call all of the submarines Shchuka-B, regardless of modifications.[7]
 Akula-class SSN profile | |
 | |
| Class overview | |
|---|---|
| Name | Akula class |
| Builders | |
| Operators | |
| Preceded by | Victor class, Sierra class |
| Succeeded by | Yasen class |
| Cost | est. $1.55 billion (1995 dollars) |
| Built | 1983–1999 |
| In commission | 1984–present |
| Planned | 20 |
| Completed | 15 |
| Cancelled | 4 (1 Iribis suspended 42% complete since 1996) |
| Active | 4 (4 active +6 on modernization in Russia) |
| Retired | 4 |
| General characteristics | |
| Type | Nuclear attack submarine |
| Displacement |
|
| Length |
|
| Beam | 13.6 m (45 ft) |
| Draught | 9.7 m (32 ft) |
| Propulsion |
|
| Speed |
|
| Endurance | 100 days[3] |
| Test depth |
|
| Complement | 73 for Akula I & Improved,[5] 62 (31 officers) for Akula II & III.[6] |
| Sensors and processing systems |
|
| Electronic warfare & decoys | |
| Armament | |
| Notes | |
Some confusion may exist as the name Akula (Russian: Акула, meaning 'shark' in Russian) was used by the Soviets for a different class of submarines, the Project 941, which is known in the West as the Typhoon class. The Project 971 was named Shchuka-B by the Soviets but given the designation Akula by the West after the name of the lead ship, K-284.
According to defense analyst Norman Polmar, the launch of the first submarine in 1985, "shook everyone [in the West] up", as Western intelligence agencies had not expected the Soviet Union to produce such a boat for another ten years.[8]
Design
Summarize
Perspective
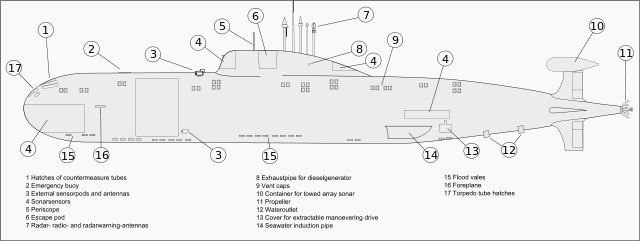
The Akula incorporates a double hull system composed of an inner pressure hull and an outer "light" hull. This allows more freedom in the design of the exterior hull shape, resulting in a submarine with more reserve buoyancy than its western analogs.
The distinctive "bulb" or "can" located on top of the Akula's rudder houses its towed sonar array when retracted. Most Akulas have the wake detection system (Russian: Система обнаружения кильватерного следа) (SOKS) hydrodynamic sensors, which detect changes in temperature and salinity. They are located on the leading edge of the sail, on the outer hull casing in front of the sail and on the bottom of the hull forward of the sail.[9][10]
Akulas (excluding Nerpa) are armed with four 533 mm torpedo tubes which can use Type 53 torpedoes or the RPK-2, RPK-6 missile, and four 650 mm torpedo tubes which can use Type 65 torpedoes or the RPK-7 missile. These torpedo tubes are arranged in two rows of four tubes each. The external tubes are mounted outside the pressure hull in one row, above the torpedo tubes, and can only be reloaded in port or with the assistance of a submarine tender. The 650 mm tubes can be fitted with liners to use the 533 mm weaponry. The submarine is also able to use its torpedo tubes to deploy naval mines.
Versions
Summarize
Perspective
As with many Soviet/Russian craft, information on the status of the Akula-class submarines is sparse, at best. Information provided by sources varies widely.
Project 971 (Akula I)

Of the seven original Akulas, only three are known to still be in service. These boats are equipped with MGK-540 Skat-3 sonar system (NATO reporting name Shark Gill).[11][12] The lead boat of the class, K-284 Akula, was decommissioned in 2001, apparently to help save money in the cash-strapped Russian Navy. K-322 Kashalot and K-480 Bars [currently Ak Bars] are in reserve. K-480 Bars was put into reserve in 1998,[3] and was being dismantled in February 2010. Pantera returned to service in January 2008 after a comprehensive overhaul.[13] All were retrofitted with the SOKS hydrodynamic sensors. All submarines before K-391 Bratsk have reactor coolant scoops that are similar to the ones of the Typhoon class SSBNs, long and tubular. Bratsk and subsequent submarines have reactor coolant scoops similar to the short ones on the Oscar IIs (the Typhoon, Akula and Oscar classes use the similar OK-650 reactor).
Project 971 and 971I (Improved Akula I)
The six Akulas of this class are all thought to be in service. They are quieter than the original Akulas. Sources also disagree as to whether construction of this class has been suspended, or if there are a further two units planned.
Improved Akula I Hulls: K-328 Leopard, K-461 Volk, K-154 Tigr, K-419 Kuzbass, K-295 Samara and K-152 Nerpa. These submarines are much quieter than early Akula-class submarines and all have the SOKS hydrodynamic sensors except Leopard.[14][failed verification]
Project 971U (Akula II)
K-157 Vepr is the only completed Akula II (see the table below).[15] The Akula II is 3 metres (9.8 ft) longer and displaces about 700 tons (submerged displacement) more than the Akula I. The added space was used for additional quieting measures. K-157 Vepr became the first Russian submarine that was quieter than the latest U.S. attack submarines of that time, which was the improved Los Angeles class (SSN 751 and later).[16] Two of these submarines were used to build the Borei-class SSBNs.
Project 971M (Akula III)
The K-335 Gepard is the 14th submarine of the class and the only completed Akula III (see the table below) built for the Russian Navy.[17] It was the first submarine commissioned in the Russian Navy since the Kursk disaster, as a result, its commissioning ceremony was an important morale boost for the Russian Navy with President Vladimir Putin in attendance.[18][19] There is no NATO classification for the Akula III. It is longer and has a larger displacement compared to the Akula II, also it has an enlarged sail and a different towed-array dispenser on the vertical fin. Again, more noise reduction methods were employed. The Gepard was the most advanced Russian submarine before the submarines of the Severodvinsk and Borei class were commissioned.
The Soviet advances in sound quieting were of considerable concern to the West, for acoustics was long considered the most significant advantage in U.S. submarine technology compared to the Soviets.
In 1983–1984 the Japanese firm Toshiba sold sophisticated, nine axis milling equipment to the Soviets along with the computer control systems, which were developed by Norwegian firm Kongsberg Vaapenfabrik. U.S Navy officials and Congressmen announced that this technology enabled the Soviet submarine builders to produce more accurate and quieter propellers.[20] This is known as the Toshiba–Kongsberg scandal.
Due to the breakup of the Soviet Union in 1991, production of all Akulas slowed.
The 1999–2000 edition of Jane's Fighting Ships incorrectly listed the first Akula III as Viper (the actual name is "Vepr", "wild boar" in Russian), commissioned on 25 November 1995. Gepard (Cheetah), was launched in 1999 and was commissioned 5 December 2001.
Operational history
Summarize
Perspective
Between December 1995 and February 1996, submarine Volk was deployed to the Mediterranean along the Russian aircraft carrier Admiral Kuznetsov, where she monitored activities of several NATO submarines under Captain 1st rank S. V. Spravtsev.
Between April and June 1996, Tigr was deployed in the Atlantic, where she detected a U.S. Ohio class SSBN and tracked it on its combat patrol.[21] On 23 July 1996, its commander, Captain 1st rank Alexey Burilichev, received a Hero of the Russian Federation award.[22]
In August 2009, the news media reported that two Akula-class submarines operated off the East Coast of the United States, with one of the submarines being identified as a Project 971 Shchuka-B type. U.S. military sources noted that this was the first known Russian submarine deployment to the western Atlantic since the end of the Cold War, raising concerns within U.S. military and intelligence communities.[23][24] U.S. Northern Command confirmed that this 2009 Akula-class submarine deployment did occur.[25] One of the boats was likely Gepard that finished a relatively lengthy combat patrol between June and September that year[26] under the command of the Captain 1st rank Alexey Vyacheslavovich Dmitrov, who on 15 February 2012 was awarded a title Hero of the Russian Federation for courage shown at work.[27] The other submarine could have been Tigr under the command of Captain E. A. Petrov, given that she performed a combat patrol sometime between March and November 2009.[28] It is unlikely that other submarines of the project 971 could have been present in the Atlantic that year. Pantera was in Severemorsk during summer,[29] while Vepr, Leopard and Volk did not report any kind of activity in that year (1-3 submarines of the project are usually active with the Northern Fleet at any given moment).
In August 2012, the news media reported that another Akula-class submarine operated in the Gulf of Mexico purportedly undetected for over a month, sparking controversy within U.S. military and political circles, with U.S. Senator John Cornyn of the Senate Armed Services Committee demanding details of this deployment from Admiral Jonathan W. Greenert, the Chief of Naval Operations.[30] Most likely, this was Tigr, as its commander Captain 1st rank Pavel Bulgakov received the Order of Courage on the Defender of the Fatherland Day on 22 February 2013.[31]
Units
| # | Name | Project | Builders | Laid down | Launched | Commissioned | Fleet | Status |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| K-284 | Akula | 971 | Amur Shipyard | 11 November 1983 | 27 June 1984 | 30 December 1984 | Pacific Fleet | Decommissioned in 2001. |
| K-480 | Ak Bars | 971 | Sevmash | 22 February 1985 | 16 April 1988 | 29 December 1988 | Northern Fleet | Decommissioned in 2002, scrapping began in 2010 but the hull section was used in the construction of ballistic missile submarine Vladimir Monomakh.[32] |
| K-263 | Barnaul | 971 | Amur Shipyard | 9 May 1985 | 28 May 1986 | 30 December 1987 | Pacific Fleet | Decommissioned in 2011 |
| K-322 | Kashalot | 971 | Amur Shipyard | 5 September 1986 | 18 July 1987 | 30 December 1988 | Pacific Fleet | Decommissioned on 9 October 2019.[33] |
| K-317 | Pantera | 971 | Sevmash | 6 November 1986 | 21 May 1990 | 27 December 1990 | Northern Fleet | Active, overhaul and modernization completed in 2007.[34] |
| K-461 | Volk | 971 | Sevmash | 14 November 1987 | 11 June 1991 | 29 December 1991 | Northern Fleet | Overhaul and modernization to finish in 2028.[35][36][37][38] |
| K-391 | Bratsk | 971 | Amur Shipyard | 23 February 1988 | 14 April 1989 | 29 December 1989 | Pacific Fleet | Decommissioned 2022, awaiting scrapping.[39] |
| K-328 | Leopard | 971 | Sevmash | 26 October 1988 | 28 June 1992 | 30 December 1992 | Northern Fleet | Overhaul and modernization to finish in second half of 2021;[37][40][41][42] projected as likely to begin post-refit sea trials in 2022[43] |
| K-154 | Tigr | 971 | Sevmash | 10 September 1989 | 26 June 1993 | 29 December 1993 | Northern Fleet | Overhaul to finish in 2022.[44][45] |
| K-331 | Magadan | 971 | Amur Shipyard | 28 December 1989 | 23 June 1990 | 23 December 1990 | Pacific Fleet | In overhaul from July 2019 to 2022.[46][47][48] |
| K-157 | Vepr | 971U | Sevmash | 13 July 1990 | 10 December 1994 | 25 November 1995 | Northern Fleet | Active, overhaul and modernization completed in 2020.[49][50] |
| K-xxx | 971M | Amur Shipyard | 1990 | Not completed. | ||||
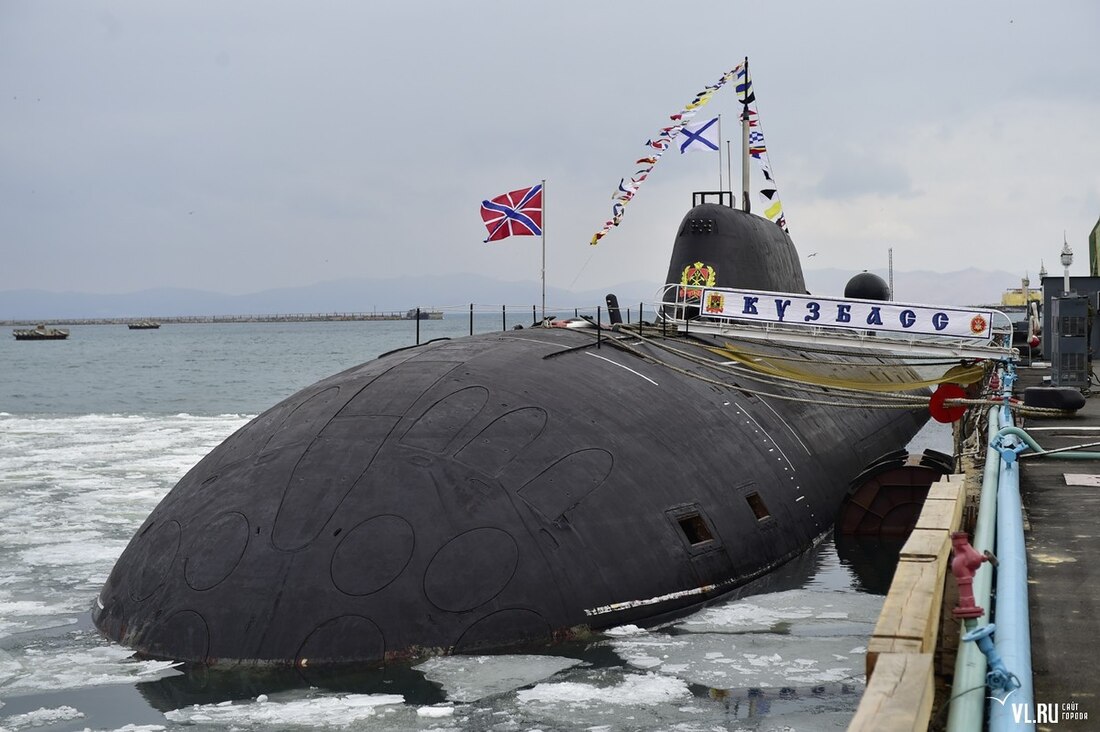
| K-419 | Kuzbass | 971 | Amur Shipyard | 28 July 1991 | 18 May 1992 | 31 December 1992 | Pacific Fleet | Active, overhaul and modernization completed in 2015.[51][52] |
| K-335 | Gepard | 971M | Sevmash | 23 September 1991 | 17 September 1999 | 5 December 2001 | Northern Fleet | Active, overhaul and modernization completed in 2015.[53] |
| K-xxx | 971M | Amur Shipyard | 1991 | Not completed. | ||||
| K-337 | Kuguar | 971U | Sevmash | 18 August 1992 | Not completed, the hull section was used in the construction of the Yury Dolgorukiy SSBN.[54] | |||
| K-333 | Rys | 971U | Sevmash | 31 August 1993 | Not completed, the hull section was used in the construction of the Alexander Nevsky SSBN.[55] | |||
| K-295 | Samara | 971 | Amur Shipyard | 7 November 1993 | 5 August 1994 | 17 July 1995 | Pacific Fleet | Modernization to finish in 2023.[56] |
| K-152 | Nerpa (ex-Chakra) |
971I | Amur Shipyard | 1993 | 26 July 2006 | 28 December 2009 | Active, has been leased to India from 2012 until 2022,[57] returned already in 2021.[58] Proposed to decommission in 2023.[59] | |
| K-519 | Iribis | 971I | Amur Shipyard | 1994 | Construction halted at 42% in 1996,[60] may be completed and leased to India.[61][62] |
Nerpa 2008 accident
On 27 October 2008, it was reported that K-152 Nerpa of the Russian Pacific Fleet had begun her sea trials in the Sea of Japan before handover under a lease agreement to the Indian Navy.[citation needed] On 8 November 2008, while conducting one of these trials, an accidental activation of the halon-based fire-extinguishing system took place in the fore section of the vessel. Within seconds the halon gas had displaced all breathable air from the compartment. As a result, 20 people (17 civilians and 3 seamen)[63] were killed by asphyxiation. Dozens of others suffered freon-related injuries and were evacuated to an unknown port in Primorsky Krai.[citation needed] This was the worst accident in the Russian navy since the loss of the submarine K-141 Kursk in 2000. The submarine itself did not sustain any serious damage and there was no release of radiation.[64]
Lease to India
Summarize
Perspective
Chakra II

Three hundred Indian Navy personnel were trained in Russia for the operation of the Akula II submarine Nerpa. India has finalised a deal with Russia, in which at the end of the lease of these submarines, it has an option to buy them. The submarine is named INS Chakra as was the previous India-leased Soviet Charlie-I SSGN.[65] Chakra was officially commissioned into the Indian Navy on 4 April 2012.[66][67]
Whereas the Russian Navy's Akula-II could be equipped with 28 nuclear-capable cruise missiles with a striking range of 3,000 km (1,620 nmi; 1,864 mi), the Indian version is reportedly armed with the 300 km (162 nmi; 186 mi)-range Club-S nuclear-capable missiles.[68] Missiles with ranges greater than 300 km (162 nmi; 186 mi) cannot be exported due to arms control restrictions, since Russia is a signatory to the MTCR treaty.
In June 2021, Nerpa was reported in Singapore with Indian crew aboard and on its way back to Russia, despite one year remaining of the 10-year lease, commenced in April 2012. The stated reason was problems with maintenance of the nuclear reactors. Accordingly, the lease will not be prolonged after 2022, as was initially expected.[58]
Chakra III
Russia said in December 2014 that it is ready to lease India more nuclear-powered submarines a day after President Vladimir Putin and Prime Minister Narendra Modi pledged to deepen defence ties.[69]
In January 2015, it was reported that India was involved in negotiations involving the leasing of the Kashalot and the Iribis.[70]
On 7 March 2019, India and Russia signed a $3 billion deal for lease of another Akula-class nuclear-powered attack submarine. The submarine, dubbed as Chakra III, should be delivered to the Indian Navy by 2025.[71][72]
As of November 2024, the deal was delayed until at least 2028 according to multiple sources.[73][74]
Gallery
- Submarine K-322 Kashalot
- An Akula-class submarine during the Russian Navy Day in 2009
- Submarine K-419 Kuzbass
- Submarine K-317 Pantera

See also
References
External links
Wikiwand - on
Seamless Wikipedia browsing. On steroids.



