9
Integer number 9 From Wikipedia, the free encyclopedia
9 (nine) is the natural number following 8 and preceding 10.
Evolution of the Hindu–Arabic digit
Summarize
Perspective
This section needs additional citations for verification. (September 2024) |

Circa 300 BC, as part of the Brahmi numerals, various Indians wrote a digit 9 similar in shape to the modern closing question mark without the bottom dot. The Kshatrapa, Andhra and Gupta started curving the bottom vertical line coming up with a 3-look-alike.[1] How the numbers got to their Gupta form is open to considerable debate. The Nagari continued the bottom stroke to make a circle and enclose the 3-look-alike, in much the same way that the sign @ encircles a lowercase a. As time went on, the enclosing circle became bigger and its line continued beyond the circle downwards, as the 3-look-alike became smaller. Soon, all that was left of the 3-look-alike was a squiggle. The Arabs simply connected that squiggle to the downward stroke at the middle and subsequent European change was purely cosmetic.
While the shape of the glyph for the digit 9 has an ascender in most modern typefaces, in typefaces with text figures the character usually has a descender, as, for example, in ![]() .
.
The form of the number nine (9) could possibly derived from the Arabic letter waw, in which its isolated form (و) resembles the number 9.

The modern digit resembles an inverted 6. To disambiguate the two on objects and labels that can be inverted, they are often underlined. It is sometimes handwritten with two strokes and a straight stem, resembling a raised lower-case letter q, which distinguishes it from the 6. Similarly, in seven-segment display, the number 9 can be constructed either with a hook at the end of its stem or without one. Most LCD calculators use the former, but some VFD models use the latter.
Mathematics
Summarize
Perspective
9 is the fourth composite number, and the first odd composite number. 9 is also a refactorable number.[2]
Casting out nines is a quick way of testing the calculations of sums, differences, products, and quotients of integers in decimal, a method known as long ago as the 12th century.[3]
9 is the only square number that is the sum of two consecutive, positive cubes: [4]
If an odd perfect number exists, it will have at least nine distinct prime factors.[5]

9 is the sum of the cubes of the first two non-zero positive integers which makes it the first cube-sum number greater than one.[6] A number that is 4 or 5 modulo 9 cannot be represented as the sum of three cubes.[7]
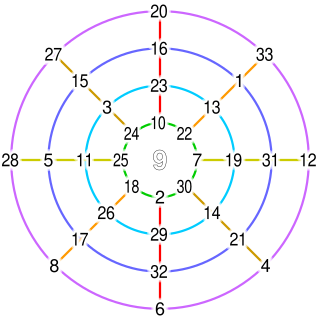
There are nine Heegner numbers, or square-free positive integers that yield an imaginary quadratic field whose ring of integers has a unique factorization, or class number of 1.[8]
Geometry
A polygon with nine sides is called a nonagon.[9] A regular nonagon can be constructed with a regular compass, straightedge, and angle trisector.[10]
The lowest number of squares needed for a perfect tiling of a rectangle is 9.[11]
9 is the largest single-digit number in the decimal system.
List of basic calculations
| Division | 1 | 2 | 3 | 4 | 5 | 6 | 7 | 8 | 9 | 10 | 11 | 12 | 13 | 14 | 15 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 9 ÷ x | 9 | 4.5 | 3 | 2.25 | 1.8 | 1.5 | 1.285714 | 1.125 | 1 | 0.9 | 0.81 | 0.75 | 0.692307 | 0.6428571 | 0.6 |
| x ÷ 9 | 0.1 | 0.2 | 0.3 | 0.4 | 0.5 | 0.6 | 0.7 | 0.8 | 1 | 1.1 | 1.2 | 1.3 | 1.4 | 1.5 | 1.6 |
| Exponentiation | 1 | 2 | 3 | 4 | 5 | 6 | 7 | 8 | 9 | 10 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 9x | 9 | 81 | 729 | 6561 | 59049 | 531441 | 4782969 | 43046721 | 387420489 | 3486784401 |
| x9 | 1 | 512 | 19683 | 262144 | 1953125 | 10077696 | 40353607 | 134217728 | 387420489 | 1000000000 |
Culture and mythology
This article needs additional citations for verification. (November 2023) |
Indian culture
Nine is a number that appears often in Indian culture and mythology.[12] For example, there are nine influencers attested to in Indian astrology. In the Vaisheshika branch of Hindu philosophy, there are nine universal substances or elements: Earth, Water, Air, Fire, Ether, Time, Space, Soul, and Mind.[13] And Navaratri is a nine-day festival dedicated to the nine forms of Durga.[14][15]
Chinese culture
- Nine (九; pinyin: jiǔ) is considered a good number in Chinese culture because it sounds the same as the word "long-lasting" (久; pinyin: jiǔ).[16]
- Nine is strongly associated with the Chinese dragon, a symbol of magic and power. There are nine forms of the dragon, it is described in terms of nine attributes, and it has nine children. It has 117 scales – 81 yang (masculine, heavenly) and 36 yin (feminine, earthly). All three numbers are multiples of 9 (9 × 13 = 117, 9 × 9 = 81, 9 × 4 = 36).[17]
Anthropology
Idioms
- "To go the whole nine yards"
- "A cat has nine lives"
- "To be on cloud nine"
- The word "K-9" pronounces the same as canine and is used in many US police departments to denote the police dog unit. Despite not sounding like the translation of the word canine in other languages, many police and military units around the world use the same designation.
- Someone dressed "to the nines" is dressed up as much as they can be.
- In North American urban culture, "nine" is a slang word for a 9mm pistol or homicide, the latter from the Illinois Criminal Code for homicide.

Religion and philosophy
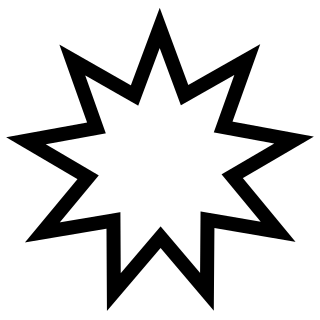
- Nine, as the largest single-digit number (in base ten), symbolizes completeness in the Baháʼí Faith. In addition, the word Baháʼ in the Abjad notation has a value of 9, and a 9-pointed star is used to symbolize the religion.
- The number 9 is revered in Hinduism and considered a complete, perfected and divine number because it represents the end of a cycle in the decimal system, which originated from the Indian subcontinent as early as 3000 BC.
- In Norse mythology, the number nine is associated with Odin, as that is how many days he hung from the world tree Yggdrasil before attaining knowledge of the runes.
- Nine is the number associated with Satan in LaVeyan Satanism. Anton LaVey wrote in The Satanic Rituals that this is because nine is the number of the ego since it "always returns to itself" even after being multiplied by any number.
Science
Chemistry
The purity of chemicals (see Nine (purity)).
Physiology
The centrioles of many living organisms, including humans, contain a 9-fold symmetry.
A human pregnancy normally lasts nine months, the basis of Naegele's rule.
Psychology
Common terminal digit in psychological pricing.
See also
Look up nine in Wiktionary, the free dictionary.
References
Further reading
Wikiwand - on
Seamless Wikipedia browsing. On steroids.



![{\displaystyle \mathbb {Q} \left[{\sqrt {-n}}\right]}](http://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/media/math/render/svg/a37339cc5863cd1cc13ad03632ca125674625fc3)