Top Qs
Timeline
Chat
Perspective
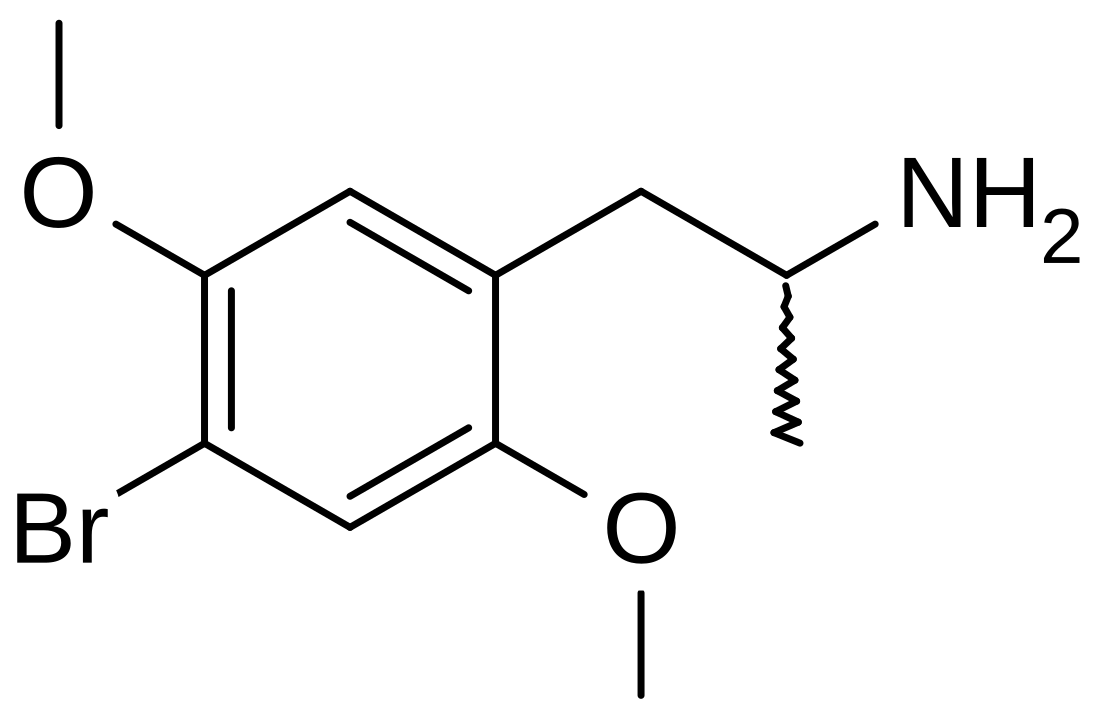
2,5-Dimethoxy-4-bromoamphetamine
Chemical compound From Wikipedia, the free encyclopedia
Remove ads
2,5-Dimethoxy-4-bromoamphetamine (DOB), also known as brolamfetamine (INN),[4] is a psychedelic drug of the phenethylamine, amphetamine, and DOx families.[1][2] For many years, prior to the discovery of newer compounds, DOB was the most potent known phenethylamine psychedelic.[1][2] It is taken orally.[1][2]
The drug acts as an agonist of the serotonin 5-HT2 receptors, including of the serotonin 5-HT2A receptor.[5][6] Analogues of DOB include 2C-B, DOM, DOI, and Bromo-DragonFLY (DOB-DFLY), among others.[1][7]
DOB was first synthesized by Alexander Shulgin in 1967 and was described by him and his colleagues in the scientific literature in 1971.[1][8] Shulgin subsequently further described the effects of DOB in his 1991 book PiHKAL (Phenethylamines I Have Known and Loved).[1]
Remove ads
Use and effects
Summarize
Perspective
In his book PiHKAL (Phenethylamines I Have Known and Loved), Alexander Shulgin lists DOB's dose as 1 to 3 mg orally and its duration as 18 to 30 hours.[1] In an earlier publication, he listed its dose as 2 to 3 mg for racemic DOB and 1 to 2 mg for the preferentially active (R)-DOB enantiomer.[1] In addition, he described the duration as being extremely long, with a gradual descent and baseline being achieved after 24 to 36 hours.[2][1] The onset has been described as 1 to 2 hours, the time to peak as 3 or 4 hours, and a plateau occurring from 4 to 10 hours.[1][2] Its onset is said to be relatively slow.[1]
The effects of DOB and (R)-DOB have been reported to include visual changes such as prismatic-colored rings around the moon and long-lasting "after-images" following seeing points of light, little visual distortion, an "incredible Moebius strip representation of reality at the intellectual level", rich fantasy, flashes of depersonalization, cosmic thinking, introspection, insights, intoxication, impairment, stimulation, brief lapses in attention or "little fugue states", body load, cramps, muscle tremors, and sleep disruption.[1][2] At a low dose of 0.4 mg DOB, there was only enhanced visual perception, strengthening of colors, enriched emotional affect, a comfortable good feeling, and colorful and important dreams.[1]
(R)-DOB produced moderate effects at a dose of 0.5 mg and pronounced effects at 1.0 to 1.5 mg, whereas there were no effects with 0.5 mg (S)-DOB and only threshold and very slight effects with 1.0 mg (S)-DOB.[1] In relation to this, (R)-DOB is described as the more active enantiomer and (S)-DOB as much less active.[1] In one report, 1 mg (R)-DOB was described as not as strong as 2 mg DOB, suggesting that it is more potent than the racemate but is not double its potency and hence that (S)-DOB also contributes to the effects of the racemate.[1] (S)-DOB has never been tested up to fully active doses.[1] In another source however, by Richard Glennon and colleagues, the approximate hallucinogenic dose was listed as 0.8 to 2.0 mg for racemic DOB, 0.5 mg for (R)-DOB, and 5.0 mg for (S)-DOB.[9]
Remove ads
Side effects
Side effects of DOB include body load, muscle tremors, muscle cramps, attention lapses described as "little fugue states", sleeping difficulties, and bizarre dreams.[1][2]
Overdose
Overdose of DOB has been reported to produce cardiovascular symptoms and convulsions.[2] Excessively high doses of DOB may cause diffuse arterial spasm.[10] The vasospasm responded readily to intra-arterial and intravenous vasodilators, such as tolazoline.[10] A 35 mg overdose resulted in death, while a 75 mg overdose in a person with tolerance resulted in ergotism-like complications that required amputation.[2]
Interactions
Pharmacology
Summarize
Perspective
Pharmacodynamics
DOB is a serotonin 5-HT2A, 5-HT2B, and 5-HT2C receptor agonist.[5][6] Its psychedelic effects are mediated by its agonistic properties at the 5-HT2A receptor. Due to its selectivity, DOB is often used in scientific research when studying the 5-HT2 receptor subfamily.
It is a very weak agonist of the human trace amine-associated receptor 1 (TAAR1) and a weak agonist of the rhesus monkey TAAR1.[19][6] In contrast to the serotonin releasing agent MDMA, DOB does not produce protein kinase C (PKC) activation in the brains of rodents in vivo.[20][21] The PKC activation by MDMA appears to be dependent on uptake by the serotonin transporter (SERT).[20][21]
DOB has been found to reduce aggression in rats.[22][23]
DOB is one of the most potent compounds in PiHKAL; while the active dose is similar to that of DOI, another psychedelic amphetamine, DOB has been shown to have a higher efficacy in triggering downstream effects mediated by serotonin 5-HT2 receptors.[24]
Remove ads
Chemistry

The full name of the chemical is 2,5-dimethoxy-4-bromoamphetamine.[1] DOB has a stereocenter and R-(−)-DOB is the eutomer. This is an important finding as it is suggestive that it is targeting different receptors relative to most other phenethylamines (e.g. MDMA) where the R-isomer serves as the distomer.
Synthesis
The chemical synthesis of DOB has been described.[1]
Analogues
Omission of the amphetamine related α-methyl leads to 2C-B, a compound that possesses a lower affinity for the 5-HT2A receptor and is a weaker receptor agonist.[citation needed] Other analogues of DOB include 4C-B, Bromo-DragonFLY, DOB-FLY, DOB-5-hemiFLY, and 25B-NBOMe, among others.
Remove ads
History
DOB was first synthesized by Alexander Shulgin in 1967.[1] It was first described in the scientific literature in a paper by Shulgin, Claudio Naranjo, and another colleague in 1971.[8] The INN of DOB, brolamfetamine, was proposed and recommended by the World Health Organization (WHO) in 1986.[25][26] This was the same year that the Multidisciplinary Association for Psychedelic Studies (MAPS) was founded.[27] DOB was registered with the WHO as a supposed "anorexic" (appetite suppressant).[28]
Remove ads
Society and culture
Legal status
Internationally, DOB is a Schedule I substance under the Convention on Psychotropic Substances and the drug is legal only for medical, industrial or scientific purposes.[29]
Canada
Listed as a Schedule 1 as it is an analogue of amphetamine.[30]
Australia
DOB is considered a Schedule 9 prohibited substance in Australia under the Poisons Standard (February 2017).[31] A Schedule 9 substance is a substance which may be abused or misused, the manufacture, possession, sale or use of which should be prohibited by law except when required for medical or scientific research, or for analytical, teaching or training purposes with approval of Commonwealth and/or State or Territory Health Authorities.[31]
Russia
Schedule I, possession of at least 10 mg is a criminal offence.[32]
United Kingdom
DOB is a Class A drug in the United Kingdom under the Misuse of Drugs Act 1971.
United States
DOB is a Schedule I controlled substance under federal law in the United States.[7] It was scheduled in 1973.[33]
Remove ads
See also
References
External links
Wikiwand - on
Seamless Wikipedia browsing. On steroids.
Remove ads