Loading AI tools
Numbering system for roads in Europe From Wikipedia, the free encyclopedia
The international E-road network is a numbering system for roads in Europe developed by the United Nations Economic Commission for Europe (UNECE). The network is numbered from E1 up and its roads cross national borders. It also reaches Central Asian countries like Kyrgyzstan, since they are members of the UNECE.
This article has multiple issues. Please help improve it or discuss these issues on the talk page. (Learn how and when to remove these messages)
|

Main international traffic arteries in Europe are defined by ECE/TRANS/SC.1/2016/3/Rev.1 which consider three types of roads: motorways, limited access roads, and ordinary roads.
In most countries, the roads carry the European route designation alongside national designations. Belgium, Norway and Sweden have roads which only have the European route designations (examples: E18 and E6). The United Kingdom, Albania and the Asian part of Russia only use national road designations and do not show the European designations at all. All route numbers in Andorra are unsigned. Denmark only uses the European designations on signage, but also has formal names for every motorway (or part of such), by which the motorways are referred to, for instance in news and weather forecasts. In Asia, Turkey and Russia show the European designations on signage; this is not the case in many other Asian countries.
Other continents have similar international road networks, e.g., the Pan-American Highway in the Americas, the Trans-African Highway network, and the Asian Highway Network.

UNECE was formed in 1947, and their first major act to improve transport was a joint UN declaration no. 1264, the Declaration on the Construction of Main International Traffic Arteries,[1][2] signed in Geneva on 16 September 1950, which defined the first E-road network. Originally it was envisaged that the E-road network would be a motorway system comparable to the US Interstate Highway System.[citation needed] The declaration was amended several times until 15 November 1975, when it was replaced by the European Agreement on Main International Traffic Arteries or "AGR",[3] which set up a route numbering system and improved standards for roads in the list. The AGR last went through a major change in 1992 and in 2001 was extended into Central Asia to include the Caucasus nations.[citation needed] There were several minor revisions since, last in 2008 (as of 2009[update]).

The route numbering system is as follows:[3]

In the first established and approved version, the road numbers were well ordered. Since then a number of exceptions to this principle have been allowed.
Two Class-A roads, E6 and E4 were originally scheduled to be renamed into E47 and E55, respectively. However, since Sweden and Norway have integrated the E-roads into their national networks, signposted as E6 and E4 throughout, a decision was made to keep the pre-1992 numbers for the roads in those two countries. These exceptions were granted because of the excessive expense connected with re-signing not only the long routes themselves, but also the associated road network in the area. The new numbers are, however, used from Denmark and southward, though, as do other European routes within Scandinavia. These two roads are the most conspicuous exceptions to the rule that even numbers signify west–east E-roads.
Further exceptions are:
These irregularities exist just because it is hard to maintain good order when extending the network, and the UNECE want to avoid changing road numbers.
Because the Socialist People's Republic of Albania refused to participate in international treaties such as the AGR, it was conspicuously excluded from the route scheme, with E65 and E90 making noticeable detours to go around it. In the 1990s, Albania opened up to the rest of Europe, but only ratified the AGR in August 2006, so its integration into the E-road network remains weak.
Where the European routes are signed, green signs with white numbers are used.

There are different strategies for determining how frequently to signpost the roads.
The following design standards should be applied to Euroroutes unless there are exceptional circumstances (such as mountain passes etc.):[3]
These requirements are meant to be followed for road construction. When new E-roads have been added these requirements have not been followed stringently. For example, the E45 in Sweden, added in 2006, has long parts with 6 m (20 ft) width or the E22 in eastern Europe forcing drivers to slow down to 30 km/h (20 mph) by taking the route through villages. In Norway, parts of the E10 are 5 m (16 ft) wide and in Central Asia even some gravel roads have been included.
In Belgium, for example, motorway E-numbers have taken on the same kind of persistent cultural integration and significance as M-numbers in the UK, or Interstate numbers in the United States. Local businesses will refer to, or even incorporate the road designator in their business name. The annual road cycling race "E3 Harelbeke" takes part of its name from the former E3 (the part between Antwerp and Lille was renamed E17 in 1992). The same applies to the retail chain "E5-mode" (E5-fashion) that started with shops easily accessible from the former E5 (renamed E40 in 1992).
In Sweden, the ice hockey games between HV71 from Jönköping and Linköping HC from Linköping have come to be called "the E4-derby".[6] It's about 130 km between the cities, and they are situated in different provinces and counties, so the "derby" denomination is really far fetched, and it's often joked about that HV71's meetings with the teams from Stockholm or even as far north as Luleå would be an "E4 derby" just as much.
In Norway, the band D.D.E. released a song named after E6.
In the road listings below,[3] a dash ('–') indicates a land road connection between two towns/cities—the normal case—while an ellipsis ('...') denotes a stretch across water. Not all such places are connected by ferry, and operating ferry connections are usually run by private companies without support from the respective governments, i.e. they may cease operating at any time.



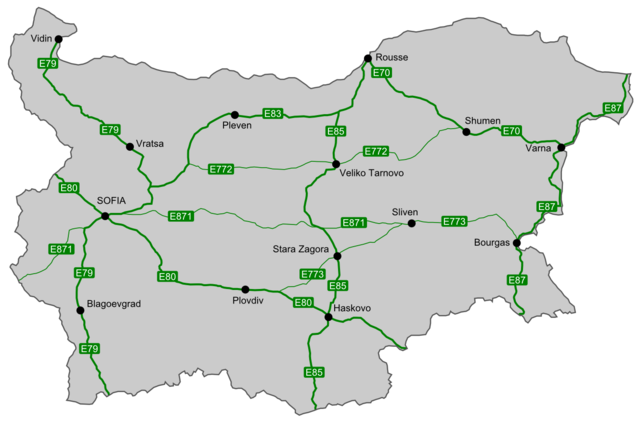









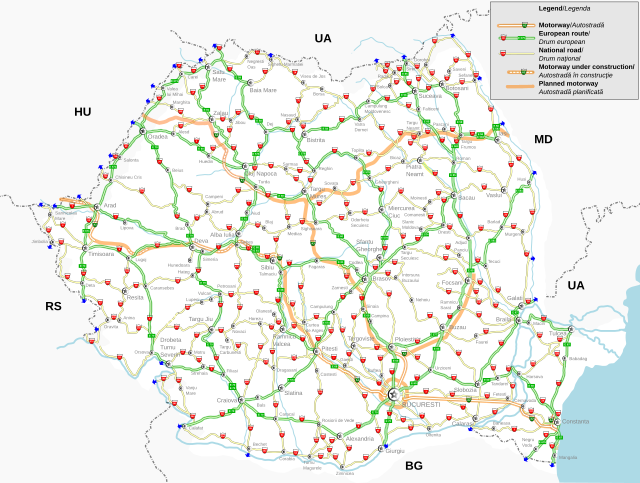
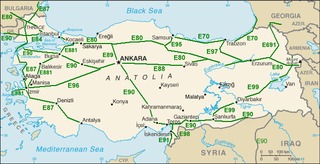



These were the historical roads before 1975:
| Number | Start | via | End |
|---|---|---|---|
| E1 | London | – Southampton – Le Havre – Paris – Lyon – Nice – Ventimiglia – Genoa – La Spezia – Pisa – Livorno – Rome – Naples – Salerno – Reggio di Calabria – Messina – | Palermo |
| E2 | London | – Dover – Calais – Reims – Dijon – Dole – Lausanne – Simplon – Milan – Parma – Modena – Bologna – Ancona – Foggia – Bari – | Brindisi |
| E3 | Lisbon | – Salamanca – San Sebastián – Bordeaux – Paris – Lille – Gent – Antwerp – Eindhoven – Venlo – Oberhausen – Bielefeld – Hannover – Hamburg – Flensburg – Kolding – Frederikshavn – Gothenburg – Arboga – | Stockholm |
| E4 | Lisbon | – Elvas – Mérida – Madrid – Zaragoza – Barcelona – Nîmes – Chambéry – Genf – Lausanne – Bern – Basel – Karlsruhe – Frankfurt (Main) – Kassel – Göttingen – Hannover – Hamburg – Lübeck – Fehmarn – Vordingborg – Copenhagen – Helsingør – Helsingborg – Jönköping – Stockholm – Uppsala – Sundsvall – Umeå – Tornio – Lahti – | Helsinki |
| E5 | London | – Dover – Calais – Gent – Brussels – Liège – Cologne – Frankfurt (Main) – Würzburg – Nuremberg – Passau – Linz – Melk – Vienna – Nickelsdorf – Győr – Budapest – Szeged – Belgrade – Gevgelija – Thessaloniki – Alexandroupolis – Peplos – Ipsala – Silivri – Istanbul – İzmit – Bolu – Ankara – Aksaray – Adana – İskenderun – | Turkey/Syria border |
| E6 | Rome | – Florence – Bologna – Modena – Verona – Trento – Brenner – Innsbruck – Griesen – Munich – Nuremberg – Hof – Leipzig – Berlin – Stralsund – Sassnitz – Trelleborg – Malmö – Helsingborg – Gothenburg – Svinesund – Oslo – Hamar – Otta – Trondheim – Mo i Rana – Alta | Kirkenes |
| E7 | Rome | – Perugia – Forlì – Bologna – Ferrara – Padua – Mestre – Cervignano – Udine – Villach – Bruck an der Mur – Vienna – Brno – Český Těšín – Krakow – | Warsaw |
| E8 | London | – Harwich – Hook of Holland – The Hague – Utrecht – Osnabrück – Hannover – Magdeburg – Berlin – Poznan – Krośniewice – Warsaw – | Poland/USSR border |
| E9 | Amsterdam | – Maastricht – Liège – Arlon – Luxembourg – Metz – Strasbourg – Mulhouse – Basel – Olten – Luzern – Andermatt – (Gotthard) – Lugano – Chiasso – Como – Milan – Tortona – | Genoa |
| E10 | Paris | – Cambrai – Brussels – Antwerp – Rotterdam – The Hague – | Amsterdam |
| E11 | Paris | – Saint-Dizier – Nancy – Strasbourg – Karlsruhe – Stuttgart – Munich – | Salzburg |
| E12 | Paris | – Metz – Saarbrücken – Mannheim – Nuremberg – Pilsen – Prague – Náchod – Kłodzko – Łódź – Warsaw – Białystok – | Moscow |
| E13 | Lyon | – Modena – Turin – Milan – Brescia – Verona – Padua – | Venice |
| E14 | Trieste | – Ronchi – Udine – Villach – Salzburg – Linz – Tábor – Prague – Jablonec – | Szczecin |
| E15 | Hamburg | – Berlin – Dresden – Zinnwald – Prague – Brno – Břeclav – Bratislava – | Budapest |
| E16 | Bratislava | – Český Těšín – Katowice – Łódź – Gdańsk – | Gdynia |
| E17 | Chagny | – Dijon – Basel – Zürich – Winterthur – St. Gallen – St. Margarethen – Innsbruck – Wörgl – | Salzburg |
| E18 | Stavanger | – Kristiansand – Larvik – Oslo – Karlstad – Arboga – Köping – | Stockholm |
| E19 | Albania/Greece border | – Ioannina – Arta – Agrinio – Antirion – Rion – | Corinth |
| E20 | Koritza | – Vari – Edessa – Thessaloniki – | Sofia |
| E21 | Aosta | – Turin – | Savona |
| E21a | Martigny | – Grosser St. Bernhard – | Aosta |
| E21b | Geneva | – Bonneville – Mont-Blanc – | Aosta |
| E22 | Berlin | – Wroclaw – Opole – Bytom – Krakow – Rzeszów – Przemyśl – | Poland/USSR border |
| E23 | Ankara | – Kirsehir – Kayseri – Sivas – Erzincan – Erzurum – Agri – | Turkey/Iran border |
| E24 | Kömürler | – Gaziantep – Urfa – Mardin – Cizre – Hakkari – Bajerge – | Turkey/Iran border |
| E25 | Burgos | – Madrid – Bailén – Sevilla – Cádiz – | Algeciras |
| E26 | Barcelona | – Tarragona – Castellón de la Plana – Valencia – Granada – Málaga – | Algeciras |
| E31 | London | – St. Albans – Northampton – Doncaster – Scotch Corner – Carlisle – Abington – | Glasgow |
| E32 | Abington | Edinburgh | |
| E33 | Northampton | – Coventry – Cannock – Warrington – | Liverpool |
| E34 | Amsterdam | – Cannock – Shrewsbury – Corwen – | Holyhead |
| E35 | Amsterdam | – Amersfoort – Zwolle – Groningen – Winschoten – Oldenburg – | Hamburg |
| E36 | Hook of Holland | – Rotterdam – Gouda – Utrecht – Arnhem – Oberhausen – | Cologne |
| E37 | Breda | – Gorinchem – | Utrecht |
| E38 | Breda | Eindhoven | |
| E39 | Antwerp | – Heerlen – | Aachen |
| E40 | Brussels | – Namur – | Bastogne |
| E41 | Calais | – Valenciennes – Mons – Charleroi – Namur – | Liège |
| E42 | Phalsbourg | – Sarreguemines – Saarbrücken – Luxembourg – Echternach – Bitburg – Prüm – Euskirchen – | Cologne |
| E43 | Avallon | Dijon | |
| E44 | Belfort | Mulhouse | |
| E45 | Dole | – La Curs – La Faucille – Gex – | Geneva |
| E46 | Lyon | – Amberieu – | Geneva |
| E47 | Aix-en-Provence | Marseille | |
| E48 | Nîmes | Marseille | |
| E49 | Bordeaux | – Toulouse – | Narbonne |
| E50 | Coimbra | – Porto – Vigo – A Coruña – Oviedo – Santander – Bilbao – | San Sebastián |
| E51 | Albergaria a Velha | – Viseu – | Celorico da Beira |
| E52 | Vila Franca de Xira | – Pegões – Beja – Vila Verde de Ficalho – Rosal de la Frontera – | Sevilla |
| E53 | Turin | – Asti – Alessandria – | Tortona |
| E54 | Canteggio | Piacenza | |
| E55 | Pisa | – Migliarino – | Pistoia |
| E56 | Ponte-Garigliano | – Caserta – | Foggia |
| E57 | Naples | Arienzo | |
| E58 | Bari | Tarent | |
| E59 | Messina | Syracuse | |
| E60 | Arth | Zürich | |
| E61 | Bellinzona | – San Bernardino – Chur – St. Margrethen – Bregenz – Lindau – | Munich |
| E62 | Hof | – Karl-Marx-Stadt – Leipzig – Halle – | Magdeburg |
| E63 | Hamm | – Kassel – Herleshausen – Erfurt – Karl-Marx-Stadt – | Dresden |
| E64 | Berlin | – Neubrandenburg – Rostock – Warnemünde – Gedser – Nykøbing – Vordingborg – | Copenhagen |
| E65 | Lübeck | – Rostock – | Stralsund |
| E66 | Esbjerg | – Kolding – Middelfart – Nyborg – Korsør – Copenhagen – | Malmö |
| E67 | Vejle | Middelfart | |
| E68 | Bergen | – Gudvangen – Laerdalsöyra – Nystua – Fagernes – | Oslo |
| E69 | Ålesund | – Åndalsnes – | Dombås |
| E70 | Winterthur | – Schaffhausen – Donaueschingen – Tübingen – Stuttgart – Heilbronn – Schwäbisch Hall – Würzburg – Fulda – Hersfeld – | Herleshausen |
| E71 | Hannover | – Bremen – | Bremerhaven |
| E72 | Oldenzaal | – Lingen – | Bremen |
| E73 | Cologne | Hamm | |
| E74 | Berlin | Szczecin | |
| E75 | Stjördal | – Storlien – Östersund – | Sundsvall |
| E77 | Feldkirch | Buchs | |
| E78 | Tornio | Kilpisjärvi | |
| E79 | Vaasa | – Tampere – | Helsinki |
| E80 | Turku | – Helsinki – Lappeenranta – | Imatra |
| E81 | Gdańsk | – Elbląg – Ostróda – Mława – Warsaw – Lublin – | Poland/USSR border |
| E82 | Piotrkow | Warsaw | |
| E83 | Jelenia Gora | – Wrocław – Poznań – Świecie – | Grudziądz |
| E84 | Prague | – Jihlava – Znojmo – | Vienna |
| E85 | Olomouc | – Žilina – Prešov – Košice – | Romania/Bulgaria border |
| E86 | Wörgl | Rosenheim | |
| E87 | Ioannina | – Trikkala – Larissa – | Volos |
| E88 | Ioannina | Preveza | |
| E89 | Rion | Patras | |
| E90 | Vevi | Kozani | |
| E91 | Cervignano | Ronchi | |
| E92 | Thessaloniki | – Aghios Athanasios – Verria – Kozani – Larissa – Lamia – Athens – Corinth – Argos – | Kalamai |
| E93 | Bruck an der Mur | – Graz – Spielfeld – Sentilj – Maribor – | Ljubljana |
| E94 | Klagenfurt | – Loibltunnel – Ljubljana – Zagreb – Belgrad – Bela Crkva – | Yugoslavia/Romania border |
| E95 | Nis | – Dimitrovgrad – | Yugoslavia/Bulgaria border |
| E96 | Rijeka | – Zagreb – Čakovec – Donja Lendava – | Yugoslavia/Hungary border |
| E97 | Bulgaria/Turkey border | – Edirne – Büyükkarıştıran – | Silivri |
| E98 | Kemerhisar | – Niğde – | Kayseri |
| E99 | Toprakkale | – Kahramanmaraş – Malatya – Elazığ – Tunceli – | Selepür |
| E101 | Madrid | Valencia | |
| E102 | Mérida | Link with E52 | |
| E103 | Bailén | – Granada – Motril – | Málaga |
Seamless Wikipedia browsing. On steroids.
Every time you click a link to Wikipedia, Wiktionary or Wikiquote in your browser's search results, it will show the modern Wikiwand interface.
Wikiwand extension is a five stars, simple, with minimum permission required to keep your browsing private, safe and transparent.