JCUKEN (ЙЦУКЕН, also known as YCUKEN, YTsUKEN and JTSUKEN) is the main Cyrillic keyboard layout[1] for the Russian language in computers and typewriters.
This article needs additional citations for verification. (March 2016) |
Earlier in Russia, the JIUKEN (ЙІУКЕН) layout was the main layout, but it was replaced by JCUKEN in 1953.[2]
Alternative layouts include the Russian phonetic keyboard layouts, in which Cyrillic letters correspond to similar-sounding Latin letters in QWERTY and other layouts.
JCUKEN for Russian
Summarize
Perspective
MICROSOFT layout
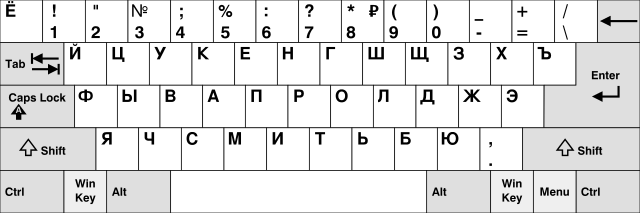
APPLE layout

Typewriters and UNIX layout
Used on typewriters before personal computers. In Unix-like operating systems this layout is standard (Keyboard GOST 6431-90). It is available in Microsoft Windows as a legacy layout.

JIUKEN, the predecessor
The JIUKEN layout was used before the Russian spelling reform of 1917. It includes the Cyrillic dotted or "decimal" I as well as Ѣ, which were eliminated after the reform, but it does not include the letters Ѳ and Ѵ, which were rare even before the reform. The numbers 1, 3 and 0 do not appear on the layout, and this forced the typist to replace them with the letters decimal I, Ze, and O respectively. The letters Ц and Э are located side-by-side; the Ѣ was between the letters Ч (Che) and С (Es). The letter Ё (yo) was not included in this layout.
After the reform, the JIUKEN layout sees the following modifications:[2]
- the Cyrillic dotted or "decimal" I is replaced by the number 1;
- the letter Ѣ (yat) is replaced by the letter Ё (yo).
JCUKEN, from typewriter to computer
It is only on July 1, 1953, that the norm GOST 6431-52 on the arrangement of letters, numbers and symbols on the keyboard began to operate.[2] Within a few years, Soviet typewriters switched to the new JCUKEN layout with the following modifications:
- all numbers 1, 3, 0 are present in the first line;
- the letter Ц is moved to the previous emplacement of number 1;
- letters Ъ, Э, Ё are moved to the end of the three lines of letters.
This version is also known today in modern computer as Russian (typewriter). In OpenSolaris and other Unix-like operating systems this layout is standard (Keyboard GOST 6431-90).
At the end of the 80s, when the Soviet Union began issuing analogues of IBM PC/XT personal computers, the Committee on Computer Science and Engineering proposed its own norm (GOST 14289-88).[3] But this version did not follow the same locations of punctuations (and various signs), neither those of the American QWERTY version, nor those of the 6431-90 version. Instead, Microsoft and the keyboard manufacturers delivered a Russian JCUKEN-QWERTY version for MS-DOS, almost analogous to the future version delivered in 1994 with Windows.
Other languages
Summarize
Perspective
JCUKEN is the basis for many other Cyrillic layouts. For the current moment Microsoft Windows supports the following layouts: Azerbaijani (Cyrillic), Bashkir, Belarusian, Kazakh, Kyrgyz, Mongolian, Tajik, Ukrainian, Uzbek (Cyrillic), Yakut (Sakha).[4] The Belarusian, Ukrainian and Mongolian layouts have been available since Windows 95; Azeri, Kazakh, Kyrgyz, Tatar, Uzbek since Windows XP; Bashkir and Tajik since Windows Vista; Yakut since Windows 7.
Other operating systems such as Linux may have their own additional custom layouts for the same or other languages.
Belarusian
The short U (Ў ў) is located in place of the shcha (Щ щ). It is the only JCUKEN keyboard that lacks a key for И, as it is the only language in the Cyrillic script that does not contain the letter И itself; the decimal I (І і) replaces it. It also lacks a hard sign (Ъ ъ), usually seen just to the right of letter ha (Х х) as that position is taken by the Apostrophe.

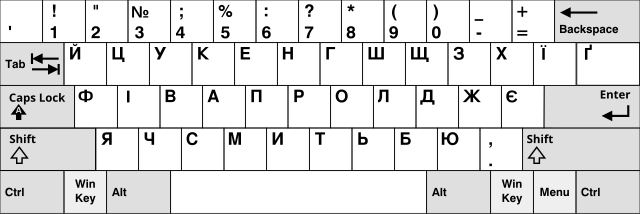
Ukrainian
The decimal I replaces the yeru (Ы ы) and the yest (Є є) replaces the E (Э э). The letter Yi (Ї ї) substitutes for the hard sign (Ъ ъ), and Ghe with upturn (Ґ ґ) is also used.
Tatar
The Russian letters which are rarely used in Tatar are typed with AltGr (right Alt). This layout is also suitable for Kalmyk and Turkmen (Cyrillic) as their alphabets are practically identical to Tatar. It is called as YÖUKEN.

Bashkir

Kazakh

Kyrgyz
An "upgraded" version based on the basic Russian one, the additional Kyrgyz letters are typed with AltGr (right Alt). Thus, AltGr + У is Ү, AltGr + О is Ө, and AltGr + Н is Ң.

Yakut (Sakha)

Tajik
This is a modified version of JCUKEN called YQUKEN, in which the Ka with descender (Қ қ) substitutes the C (Ц ц). The yeru (Ы ы) is replaced by the letter Che with descender (Ҷ ҷ). Also, the soft sign (Ь ь) is replaced by the I with macron (Ӣ ӣ). Further, the Kha with descender (Ҳ ҳ) substitutes for Shcha (Щ щ), and the U with macron (Ӯ ӯ), and the ghayn (Ғ ғ) are used. (In Unicode, Kha with descender is known as "Ha with descender".)

Uzbek
The short U substitutes the shcha, like the Belarusian keyboard (see above), and the ka with descender substitutes the yery. Moreover, the letter ghayn substitutes the minus sign and the underscore, while the kha with descender substitutes the plus sign and equal sign.

Azerbaijani
This layout is a modified version called the JÜUKEN, and includes the Che with vertical stroke, shha, Ka with vertical stroke, and the Je. It is the only JCUKEN without the usual Й, as the language lacks the glyph, which was replaced by Je in 1958.
Substitutions to this keyboard are: having the schwa replacing the ya, the oe replacing the yu, the ghayn replacing the soft sign, the Che with vertical stroke replacing the hard sign, the ue replacing the tsa and the shha replacing the shcha.

Mongolian
The Mongolian keyboard uses a modified version of JCUKEN, called FCUZHEN (ФЦУЖЭН), where letters specific to Russian are replaced by letters that see more use in Mongolian.

Other Cyrillic layouts
Summarize
Perspective
Serbian
Because Serbian and Russian alphabet are different, the Serbian keyboard LjNjERTZ (ЉЊЕРТЗ) lacks the yers and yeru (Ъ ъ, Ь ь and Ы ы), Э, and Ё, as they are not used in the Serbian language, but has a key for dze (Ѕ ѕ) in spite of that. It is based on the QWERTZ keyboard layout.

Macedonian
The Macedonian layout is a modification of the Serb-style keyboard layout. On the Macedonian keyboard layouts under Microsoft Windows, AltGr can be used to access additional letters and punctuation. Notably, it resembles QWERTY to a larger extent and has the placement of Ѕ and З switched.

Bulgarian Keyboards
Phonetic, Traditional

Phonetic, BDS 5237:2006
In 2006, Dimiter Skordev, from the Faculty of Mathematics and Informatics at Sofia University, co-authored a proposal for a new phonetic keyboard layout.[5] This proposal was included in the draft of the national standard BDS 5237:2006, titled "Keyboard Layouts for Devices Typing in Bulgarian".[5][6]
The introduction of the new phonetic keyboard layout as part of the BDS 5237:2006 standard sparked considerable controversy. It was not announced to the public until its implementation. There were no extensive public consultations, nor was the opinion of the Bulgarian Association of Information Technologies taken into account. According to the creators of the standard, tests were conducted in elite schools in Sofia during the project's development. However, the methodology and results of these tests were not disclosed.[7]
The creators argued that new generations would adapt to the layout and type faster. However, it was unclear why a more efficient layout from 1978, which is still in use, was not promoted, especially since the new phonetic layout differs from the widely used traditional one.[7]

Typewriter layout
In October 1907, Teodor Galabov, then head of the Stenographic Bureau of the National Assembly of Bulgaria, conducted, along with a team of stenographers, the first corpus study of the Bulgarian language. The study analyzed "10,000 words from various fields of human life" to create a unified Bulgarian keyboard layout. Although typewriters had been available in Bulgaria since 1902, no standard letter arrangement existed. The study resulted in a booklet, the first documented source regulating Bulgarian typewriting and introducing professional ten-finger typing. It was published in early 1908.[8][9]
The layout is highly ergonomic, and its efficiency has been demonstrated in competitions among keyboard operators. No significant changes have been made to the layout ever since, and in 1978, it was officially recognized as the Bulgarian National Standard (BDS 5237:1978).[8][9]

See also
References
Wikiwand - on
Seamless Wikipedia browsing. On steroids.