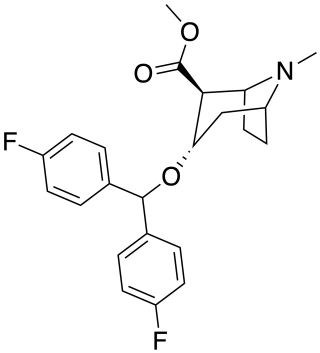
Difluoropine
Chemical compound From Wikipedia, the free encyclopedia
Difluoropine (O-620) is a stimulant drug synthesised from tropinone, which acts as a potent and selective dopamine reuptake inhibitor. Difluoropine is unique among the tropane-derived dopamine reuptake inhibitors in that the active stereoisomer is the (S) enantiomer rather than the (R) enantiomer, the opposite way round compared to natural cocaine.[1] It is structurally related to benztropine and has similar anticholinergic and antihistamine effects in addition to its dopamine reuptake inhibitory action.[2]
 | |
| Clinical data | |
|---|---|
| Other names | (S)-(+)-2β-Carbomethoxy-3α-(bis(4-fluorophenyl)methoxy)tropane |
| ATC code |
|
| Identifiers | |
| |
| CAS Number | |
| PubChem CID | |
| ChemSpider | |
| UNII | |
| ChEMBL | |
| CompTox Dashboard (EPA) | |
| Chemical and physical data | |
| Formula | C23H25F2NO3 |
| Molar mass | 401.454 g·mol−1 |
| 3D model (JSmol) | |
| |
| |
| (verify) | |
Difluoropine has some stimulant effects in animals, although it is significantly less powerful than many of the potent phenyltropane derived stimulant drugs such as WIN 35,428 and RTI-55.[3] It showed promising effects in alleviating the symptoms of Parkinson's disease in an animal model of the disorder.[4]
It is not explicitly illegal anywhere in the world as of 2008[update], but might be considered to be a controlled substance analogue of cocaine on the grounds of its related chemical structure, in some jurisdictions such as the United States, Canada, Australia and New Zealand.
See also
References
Wikiwand - on
Seamless Wikipedia browsing. On steroids.