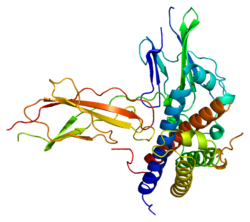
生长激素受体(英语:Growth hormone receptor)是一种由人类基因GHR 编码的蛋白质[1],GHR的直系同源物[2]广泛存在于各种哺乳动物中。
Quick Facts Growth hormone receptor 生长激素受体, 有效结构 ...
Close
此基因编码的蛋白是结合生长激素的跨膜受体。
生长激素受体能与SGTA[3]、PTPN11[4][5]、JAK激酶2[6][7][8]、SOCS1[9]和CISH[9]发生交互作用。
GHR 基因曾作为动物核DNA系统发育标记[2],对其10号外显子基因多态性的探究第一次阐释了啮齿目主要类群间的亲缘关系[10][11][12]。GHR也用于较低阶元的分类,在鼠总科[13][14]、八齿鼠科[15]、田鼠亚科[16]、鼠亚科[17]、白足鼠属[18]等啮齿动物,及熊型总科[19]、猫科[20]等肉食动物以及皮翼目[21]的分类上有重要作用。GHR的9号内含子也用于阐释鼬科[22]、鬣狗科[23]的系统发生。
Stofega, M R; Herrington J, Billestrup N, Carter-Su C. Mutation of the SHP-2 binding site in growth hormone (GH) receptor prolongs GH-promoted tyrosyl phosphorylation of GH receptor, JAK2, and STAT5B. Mol. Endocrinol. (UNITED STATES). September 2000, 14 (9): 1338–50. ISSN 0888-8809. PMID 10976913. doi:10.1210/me.14.9.1338. Moutoussamy, S; Renaudie F, Lago F, Kelly P A, Finidori J. Grb10 identified as a potential regulator of growth hormone (GH) signaling by cloning of GH receptor target proteins. J. Biol. Chem. (UNITED STATES). June 1998, 273 (26): 15906–12. ISSN 0021-9258. PMID 9632636. doi:10.1074/jbc.273.26.15906. Frank, S J; Yi W, Zhao Y, Goldsmith J F, Gilliland G, Jiang J, Sakai I, Kraft A S. Regions of the JAK2 tyrosine kinase required for coupling to the growth hormone receptor. J. Biol. Chem. (UNITED STATES). June 1995, 270 (24): 14776–85. ISSN 0021-9258. PMID 7540178. doi:10.1074/jbc.270.24.14776. VanderKuur, J A; Wang X, Zhang L, Campbell G S, Allevato G, Billestrup N, Norstedt G, Carter-Su C. Domains of the growth hormone receptor required for association and activation of JAK2 tyrosine kinase. J. Biol. Chem. (UNITED STATES). August 1994, 269 (34): 21709–17. ISSN 0021-9258. PMID 8063815. Adkins R. M., Walton A. H. & Honeycutt R. L. Higher-level systematics of rodents and divergence time estimates based on two congruent nuclear genes. Mol. Phylogenet. Evol. 2003, 26 (3): 409–420. PMID 12644400. doi:10.1016/S1055-7903(02)00304-4. Steppan S. J., Adkins R. M. & Anderson J. Phylogeny and divergence-date estimates of rapid radiations in muroid rodents based on multiple nuclear genes. Syst. Biol. 2004, 53 (4): 533–553. PMID 15371245. doi:10.1080/10635150490468701. Rowe K. C., Reno M. L., Richmond D. M., Adkins R. M. & Steppan S. J. Pliocene colonization and adaptive radiations in Australia and New Guinea (Sahul): multilocus systematics of the old endemic rodents (Muroidea: Murinae). Mol. Phylogenet. Evol. 2008, 47 (1): 84–101. PMID 18313945. doi:10.1016/j.ympev.2008.01.001. Honeycutt R. L., Rowe D. L. & Gallardo M. H. Molecular systematics of the South American caviomorph rodents: relationships among species and genera in the family Octodontidae. Mol. Phylogenet. Evol. 2003, 26 (3): 476–489. PMID 12644405. doi:10.1016/S1055-7903(02)00368-8. Miller J. R. & Engstrom M. D. The relationships of major lineages within peromyscine rodents: a molecular phylogenetic hypothesis and systematic reappraisal. J. Mammal. 2008, 89 (5): 1279–1295. doi:10.1644/07-MAMM-A-195.1. Fulton T. L. & Strobeck C. Molecular phylogeny of the Arctoidea (Carnivora): effect of missing data on supertree and supermatrix analyses of multiple gene data sets. Mol. Phylogenet. Evol. 2006, 41 (1): 165–181. PMID 16814570. doi:10.1016/j.ympev.2006.05.025. Johnson W. E., Eizirik E., Pecon-Slattery J., Murphy W. J., Antunes A., Teeling E. & O'Brien S. J. The late Miocene radiation of modern Felidae: a genetic assessment. Science. 2006, 311 (5757): 73–77. PMID 16400146. doi:10.1126/science.1122277. Janecka J. E., Helgen K. M., Lim N. T., Baba M., Izawa M., Boeadi & Murphy W. J. Evidence for multiple species of Sunda colugo. Curr. Biol. 2008, 18 (21): R1001–R1002. PMID 19000793. doi:10.1016/j.cub.2008.09.005. Koepfli K. P. & Wayne R. K. Type I STS markers are more informative than cytochrome B in phylogenetic reconstruction of the Mustelidae (Mammalia: Carnivora). Syst. Biol. 2003, 52 (5): 571–593. PMID 14530127. doi:10.1080/10635150390235368. Koepfli K. P., Jenks S. M., Eizirik E., Zahirpour T., Van Valkenburgh B. & Wayne R. K. Molecular systematics of the Hyaenidae: relationships of a relictual lineage resolved by a molecular supermatrix. Mol. Phylogenet. Evol. 2006, 38 (3): 603–620. PMID 16503281. doi:10.1016/j.ympev.2005.10.017.