一氧化二氯是氯的氧化物之一,也是次氯酸的酸酐,化學式為Cl2O。它在1834年由安托萬·巴拉爾首次合成,[4]之後蓋-呂薩克確定了其化學組成。在室溫下,一氧化二氯是可溶於水和有機溶劑的棕黃色氣體,在液態下呈紅棕色,在固態下則變成櫻桃紅色[1]。它是強氧化劑和氯化劑。
Quick Facts 一氧化二氯, 識別 ...
| 一氧化二氯
|
|
|
| 識別
|
| CAS號
|
7791-21-1  Y Y
|
| PubChem
|
24646
|
| ChemSpider
|
23048
|
| SMILES
|
|
| InChI
|
|
| InChIKey
|
RCJVRSBWZCNNQT-UHFFFAOYAA
|
| ChEBI
|
30198
|
| 性質
|
| 化學式
|
Cl2O
|
| 摩爾質量
|
86.91 g·mol−1
|
| 外觀
|
棕黃色氣體[1]
|
| 密度
|
2.089 g/cm3(90 K,-183 °C)[1]
|
| 熔點
|
−120.6 °C[1]
|
| 沸點
|
2.0 °C[1]
|
| 溶解性(水)
|
143.6 g/100 ml[1],緩慢水解
|
| 溶解性
|
可溶於四氯化碳[2]
|
| 結構
|
| 偶極矩
|
0.78 ± 0.08 D
|
| 熱力學
|
| ΔfHm⦵298K
|
+80.3 kJ mol−1
|
| S⦵298K
|
265.9 J K−1 mol−1
|
| 危險性
|
| MSDS
|
[3]
|
GHS危險性符號
 
|
| GHS提示詞
|
DANGER
|
| H-術語
|
H290, H314, H400, H411
|
| P-術語
|
P234, P260, P264, P273, P280, P301+330+331, P303+361+353, P304+340, P305+351+338, P310, P311, P321, P363, P390
|
| NFPA 704
|
|
| 相關物質
|
| 其他陽離子
|
水
二氟化氧
一氧化二溴
一氧化二碘
|
| 相關氯的氧化物
|
七氧化二氯
二氧化氯
|
| 若非註明,所有數據均出自標準狀態(25 ℃,100 kPa)下。
|
Close
一氧化二氯最早的製備方法是使氯氣和氧化汞反應而成,[5]但此法成本昂貴,且因有汞中毒的風險而非常危險。
- 2 Cl2 + HgO → HgCl2 + Cl2O
一個較為安全方便的製備方法是使氯氣和濕潤的碳酸鈉在20–30 °C下反應:[5]
- 2 Cl2 + 2 Na2CO3 + H2O → Cl2O + 2 NaHCO3 + 2 NaCl
- 2 Cl2 + 2 NaHCO3 → Cl2O + 2 CO2 + 2 NaCl + H2O
氯氣和無水碳酸鈉也能反應,但需將反應溫度提高到150–250 °C。由於一氧化二氯在高溫下不穩定,[6]因此需要不斷從反應體系中移去產物一氧化二氯來避免分解。
- 2 Cl2 + Na2CO3 → Cl2O + CO2 + 2 NaCl
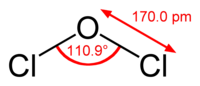
一氧化二氯的結構與水和次氯酸相似,都是角形分子。它的Cl-O鍵長為170.0 pm,Cl-O-Cl鍵角為110.9°。[7]這個比水和次氯酸大的鍵角是兩個氯原子的位阻效應導致的。
固態的一氧化二氯呈四方晶系,空間群 I41/amd,與冰VIII同構。[8]
一氧化二氯易溶於水,[9]並與HOCl達成平衡。
- 2 HOCl ⇌ Cl2O + H2O K (0 °C) = 3.55x10−3 dm3/mol
雖然一氧化二氯在平衡中處於劣勢,但它才是飲水氯化中的活性物質。[10]
一氧化二氯可和金屬鹵化物反應,產生氯氧化物並放出Cl2。[11][12][5]
- VOCl3 + Cl2O → VO2Cl + 2 Cl2
- TiCl4 + Cl2O → TiOCl2 + 2 Cl2
- SbCl5 + 2 Cl2O → SbO2Cl + 4 Cl2
某些非金屬鹵化物也可以參與類似的反應。[13][14]
- AsCl3 + 2 Cl2O → AsO2Cl + 3 Cl2
- NOCl + Cl2O → NO2Cl + Cl2
它和五氧化二氮反應,得到硝酸氯(ClNO3),[15]和三氟氧化氯反應則可以得到一氟化氯和氯酰氟。[16]一氧化二氯和氨的反應會爆炸,生成氮氣、氯氣和水。[1]
一氧化二氯與鹼金屬和鹼土金屬的氫氧化物溶液反應生成相應的次氯酸鹽[1],而乾燥的次氯酸鹽可被一氧化二氯進一步氧化成氯酸鹽。[1]
一氧化二氯是有效的氯化劑,可以把芳香化合物的側鏈氯化[17],而和酚或芳香醚的反應則主要氯化芳香環。[18]它和醇反應會生成次氯酸酯,如和叔丁醇反應生成次氯酸叔丁酯。[19]一氧化二氯也是次氯酸和烯烴或芳香化合物的反應中的活性物質。[20][21]
一氧化二氯見光分解,產生O2和Cl2。這個反應是自由基反應,閃光光解表明一氧化氯(ClO·)是反應的主要中間體。[22]
- 2 Cl2O → 2 Cl2 + O2
一氧化二氯會爆炸,但對它的研究不充分。一氧化二氯的爆炸下限很高,達到23.5%,即它和氧氣在室溫下的混合物需要含有至少23.5% Cl2O才能被電火花引爆。[23]有研究稱一氧化二氯在強光下會爆炸,但此研究有爭議。[24][25]將一氧化二氯迅速加熱或緩慢加熱到120 °C都會使它爆炸。[5]液態一氧化二氯對衝擊敏感。[26]
一氧化二氯是生產次氯酸鈣、氯代溶劑和氯代異氰尿酸鹽的中間體。[1]它還用於漂白木漿和布[27],也是半導體工業的刻蝕劑。[28]
Wojtowicz, John A., Dichlorine Monoxide, Hypochlorous Acid, and Hypochlorites, Hoboken, NJ, USA: John Wiley & Sons, Inc., 2004-04-16, doi:10.1002/0471238961.0409030823151020.a01.pub2 CHLORINE MONOXIDE. CAMEO Chemicals. National Oceanic and Atmospheric Administration. [12 May 2015]. (原始內容存檔於2015-11-17). Renard, J. J.; Bolker, H. I. The chemistry of chlorine monoxide (dichlorine monoxide). Chemical Reviews. 1 August 1976, 76 (4): 487–508. doi:10.1021/cr60302a004. Hinshelwood, Cyril Norman; Prichard, Charles Ross. CCCXIII.—A homogeneous gas reaction. The thermal decomposition of chlorine monoxide. Part I. Journal of the Chemical Society, Transactions. 1923, 123: 2730–2738. doi:10.1039/CT9232302730. Herberich, G. E.; Jackson, R. H.; Millen, D. J. The microwave spectrum of dichlorine oxide. Molecular structure, centrifugal distortion coefficients, and force field. Journal of the Chemical Society A: Inorganic, Physical, Theoretical (Royal Society of Chemistry (RSC)). 1966: 336. ISSN 0022-4944. doi:10.1039/j19660000336. Davis, D. S. Nomograph for the Solubility of Chlorine Monoxide in Water. Industrial & Engineering Chemistry. 1942, 34 (5): 624. doi:10.1021/ie50389a021. Oppermann, H. Untersuchungen an Vanadinoxidchloriden und Vanadinchloriden. I. Gleichgewichte mit VOCl3, VO2Cl und VOCl2. Zeitschrift für anorganische und allgemeine Chemie. 1967, 351 (3–4): 113–126. doi:10.1002/zaac.19673510302. Dehnicke, Kurt. Titan(IV)-Oxidchlorid TiOCl2. Zeitschrift für anorganische und allgemeine Chemie. 1961, 309 (5–6): 266–275. doi:10.1002/zaac.19613090505. Dehnicke, Kurt. Über die Oxidchloride PO2Cl, AsO2Cl und SbO2Cl. Chemische Berichte. 1 December 1964, 97 (12): 3358–3362. doi:10.1002/cber.19640971215. Martin, H. Kinetic Relationships between Reactions in the Gas Phase and in Solution. Angewandte Chemie International Edition in English. 1 January 1966, 5 (1): 78–84. doi:10.1002/anie.196600781. Schack, Carl J.; Lindahl, C. B.; Pilipovich, Donald; Christe, Karl O. Chlorine trifluoride oxide. IV. Reaction chemistry. Inorganic Chemistry (American Chemical Society (ACS)). 1972, 11 (9): 2201–2205. ISSN 0020-1669. doi:10.1021/ic50115a043. Marsh, F. D.; Farnham, W. B.; Sam, D. J.; Smart, B. E. Dichlorine monoxide: a powerful and selective chlorinating reagent. Journal of the American Chemical Society. 1 August 1982, 104 (17): 4680–4682. doi:10.1021/ja00381a032. Mintz, M. J.; C. Walling. t-Butyl hypochlorite. Organic Syntheses. 1969, 49: 9 [2023-02-19]. (原始內容存檔於2023-02-13). Swain, C. Gardner; Crist, DeLanson R. Mechanisms of chlorination by hypochlorous acid. The last of chlorinium ion, Cl+. Journal of the American Chemical Society. 1 May 1972, 94 (9): 3195–3200. doi:10.1021/ja00764a050. Sivey, John D.; McCullough, Corey E.; Roberts, A. Lynn. Chlorine Monoxide (Cl2O) and Molecular Chlorine (Cl2) as Active Chlorinating Agents in Reaction of Dimethenamid with Aqueous Free Chlorine. Environmental Science & Technology. 1 May 2010, 44 (9): 3357–3362. Bibcode:2010EnST...44.3357S. PMID 20302364. doi:10.1021/es9038903. Basco, N.; Dogra, S. K. Reactions of Halogen Oxides Studied by Flash Photolysis. II. The Flash Photolysis of Chlorine Monoxide and of the ClO Free Radical. Proceedings of the Royal Society A: Mathematical, Physical and Engineering Sciences. 22 June 1971, 323 (1554): 401–415. Bibcode:1971RSPSA.323..401B. S2CID 98084403. doi:10.1098/rspa.1971.0112. Cady, George H.; Brown, Robert E. Minimum Explosive Concentration of Chlorine Monoxide Diluted with Oxygen. Journal of the American Chemical Society. September 1945, 67 (9): 1614–1615. doi:10.1021/ja01225a501. Iredale, T.; Edwards, T. G. Photoreaction of Chlorine Monoxide and Hydrogen. Journal of the American Chemical Society. April 1937, 59 (4): 761. doi:10.1021/ja01283a504. Wallace, Janet I.; Goodeve, C. F. The heats of dissociation of chlorine monoxide and chlorine dioxide. Transactions of the Faraday Society. 1 January 1931, 27: 648. doi:10.1039/TF9312700648. Pilipovich, Donald; Lindahl, C. B.; Schack, Carl J.; Wilson, R. D.; Christe, Karl O. Chlorine trifluoride oxide. I. Preparation and properties. Inorganic Chemistry. 1972, 11 (9): 2189–2192. ISSN 0020-1669. doi:10.1021/ic50115a040. US 3619349A,Norman Liebergott, Henry Irving Bolker,「Bleaching of shredded or fluffed cellulosic pulp with gaseous chlorine monoxide」,發表於1971-11-09 US 5200032A,Keiji Shinohara,「Dry etching method」,發表於1993-04-06
- 鍾興厚,蕭文錦,袁啟華,婁潤和。《無機化學叢書》第六卷,鹵素、銅分族、鋅分族。北京:科學出版社,1984年。



