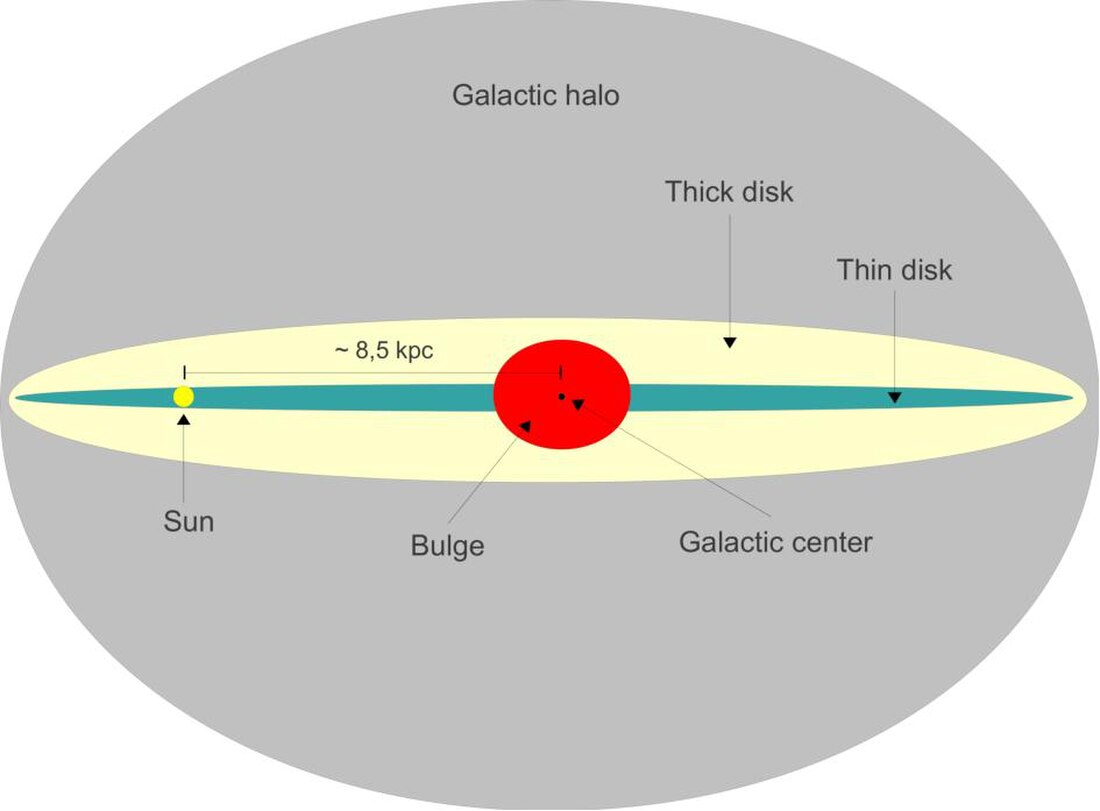
厚盘 是某些星系 的构成元件之一,包括我们的银河系 。吉尔摩(Gilmore)和李德(Reid)在1983年首次提出星系结构 有薄盘 、厚盘 和星系晕 等独特的结构[ 1] 1至5千秒差距 (3.3至16.3千光年 ) 主导恒星数量和密度[ 1] 薄盘 中的恒星不同[ 2] [ 3]
从侧面观看银河系与呈现的一些结构(未依照比例),厚盘以黄色呈现。 厚盘被认为是星系早期运动和化学组成的证据来源,因而被认为是了解星系形成 的一个非常巨大的元件。
对这种结构的形成已经提出了各种的方案,包括:
厚盘来自薄盘 的加热[ 4]
在较大的半径上,较有活力的恒星从星系的内部向外迁徙,形成厚盘[ 5]
它是银河系和其它的矮星系 之间,合并造成的结果[ 6]
在薄盘形成后不久,因高红移而形成厚盘[ 7]
虽然在许多的科学研究中确实提到星系的厚盘结构,而且它甚至被认为是在一潘情形下供通的星系结构[ 8]
最近的一项研究声称有证据显示银河系 盘面的厚度有着连续和单调的分布,意味着没有厚厚的盘面[ 9]
Gilmore & Reid, 1983, "New light on faint stars. III - Galactic structure towards the South Pole and the Galactic thick disc", [1] (页面存档备份 ,存于互联网档案馆 ) Bensby & Feltzing, "The Galactic thin and thick discs in the context of galaxy formation", [2] (页面存档备份 ,存于互联网档案馆 ) Kordopatis et al., "A spectroscopic survey of thick disc stars outside the solar neighbourhood", [3] (页面存档备份 ,存于互联网档案馆 ) Matthias Steinmetz, The Galactic thin and thick disk (2012), p. 4 (页面存档备份 ,存于互联网档案馆 )" Ken Freeman, Structure and Evolution of the Milky Way (2012), p. 4 (页面存档备份 ,存于互联网档案馆 )" Bensby et. al. The Galactic thin and thick discs in the context of galaxy formation. Proceedings of the International Astronomical Union. August 2009, 5 (Symposium S265): 300–303. arXiv:0908.3807v1 doi:10.1017/S1743921310000773 Ken Freeman, Structure and Evolution of the Milky Way (2012), p. 4 (页面存档备份 ,存于互联网档案馆 ): "Thick disks are very common in disk galaxies."