Pyrimidine
chemical compound From Wikipedia, the free encyclopedia
Pyrimidines include three of the bases in DNA and RNA.
| |||
| |||
| Names | |||
|---|---|---|---|
| IUPAC name
Pyrimidine | |||
| Other names
1,3-Diazine, m-Diazine | |||
Except where otherwise noted, data are given for materials in their standard state (at 25 °C [77 °F], 100 kPa). | |||
| verify (what is ?) | |||
| Infobox references | |||
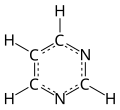
A pyrimidine is an aromatic heterocyclic organic compound, similar to purine.[1] It has nitrogens at positions 1 and 3 in the ring.[2][3]
Pyrimidines
The pyrimidine ring system occurs widely in nature.[4]
- Cytosine (C),
- Thymine (T),
- Uracil (U).
- Thiamine (vitamin B1)
It is also found in many synthetic compounds such as barbiturates and the HIV drug, zidovudine. Uric acid is a pyrimidine derivative.
References
Wikiwand - on
Seamless Wikipedia browsing. On steroids.