disorder resulting in recurrent moderate-severe headaches From Wikipedia, the free encyclopedia
A migraine is a medical condition which usually causes a pounding, throbbing headache on one side of the head. The pain may be very bad and hurt so much that a person may have a hard time doing anything. While most people who have migraines get a headache, not everyone does. There are different kinds of migraines, and some do not cause a headache but do have other symptoms.
Most migraines cause a headache and nausea and might make the person dizzy or very sensitive to bright lights or loud noises. Some people have "auras" before a migraine starts, which means their ability to see becomes different. They may see funny patterns, have blurry vision, or may not be able to see at all. Other senses can change before or during a migraine, and the person may sense funny smells or tastes. Migraines can last a long time. Migraines usually last between four and 72 hours.
Migraines have been classified, based on how often they happen in a month: If a person has a headache for less than fifteen days, the migraine is called episodic migraine (EM). If it happens more than fifteen days, it is called chronic migraine (CM). Chronic means it happens over a long amount of time. Some people who start off getting episodic migraines may start to get chronic migraines later. Chronic migraine then may revert or go back to episodic migraine.
Scientists have discovered that something called CGRP is the cause of migraines. CGRP stands for "calcitonin gene-related peptide". CGRP is a protein that causes migraines when it is released around the brain. What CGRP does, is that it causes a lot of inflammation in the meninges, a covering above the brain.
There are different risk factors which make a person more likely to have migraines. Being a female is a risk factor, and so is having family members who had migraines. For a person who has migraines, there are different trigger factors which may set off a migraine attack. In a large group of females who have migraines, one of the main trigger factors is when the amount of the hormone estrogen in their body either drops too low or fluctuates (goes up and down).
The World Health Organization says that migraine headache is the most costly brain problem for treatment and disability in the European Union and the United States.[1]

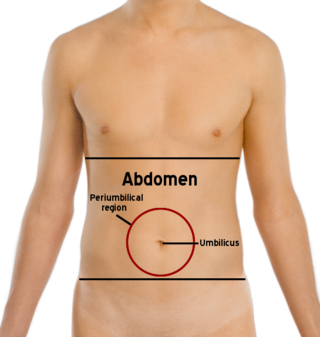
Childhood periodic syndromes are a group of migraine syndromes that children may have. When a child has one of these child periodic syndromes there is a greater chance that they will get one of the other, more common types of migraines when they become adults.
Abdominal migraine is a kind of migraine which causes a very bad pain in the area of the abdomen, usually around the 'belly-button' which is called the periumbilical area. Abdominal migraine usually affects children starting at about age 7, but it may affect younger children and older children,[7] and it may also sometimes affect adults.[8]
Benign paroxysmal vertigo of childhood (BPVC for short): (this means harmless dizziness, that happens again and again and happens suddenly) is a medical condition which occurs in children usually starting between two and five years of age; it often disappears by the age of eight. BPVC causes vertigo.
Cyclic vomiting syndrome or cyclical vomiting syndrome (CVS), is a medical condition whose main symptoms are nausea and repeated vomiting. CVS happens more often in children, but it can occur at any age.

Episodic migraine (EM) is when a person has migraine symptoms for 14 days or less in one month, while chronic migraine (CM) is when a person has migraine symptoms for 15 or more days in one month. When compared to persons with episodic migraine, those with CM where less likely to have full-time jobs and had a larger risk of headache-related disability.[9] Persons with CM are almost twice as likely to have anxiety, chronic pain, and/or depression; they also have a 40% greater chance of having heart disease and angina and are 70% more likely to have a history of stroke.
About 7.68% of total migraine cases are chronic migraines and about 1% of people in the United States have CM, with a higher rate among females, middle-aged people, and in those households that had the lowest annual income. (The American Migraine Prevalence and Prevention Study)
Aura (from the Greek word for breeze) is the word used to describe a series of neurological symptoms that may begin before an epileptic seizure or a migraine headache. About 15% of people who have a migraine will have the kind with an aura. The symptoms may include visual problems such as scotomas (losing vision for a short time, seeing zig-zag lines or floating spots etc.), vertigo, a ringing noise in the ears (tinnitus) and problems speaking.[10]
Scotoma (came from the Greek word for darkness: skotos): a blind spot or area of reduced vision surrounded by a normal visual field. i.e.: A person can see normally except where the scotoma is.[11] Scotomas may affect one or both eyes and be either and be either absolute where nothing can be seen within the scotoma or, relative with some ability to see within the area of the scotoma.
Scotomas may also have different patterns and shapes like the fortification scotoma; it is called fortification because it looks like the outline of an old fort. Scotomas can start of small and then get bigger, move around to different parts of a person's visual field, and they can also look like flickering lights.[12]
In medicine a factor is a substance, a condition or an activity, or a lack thereof that increases the chance of a certain outcome or condition happening. If it increases the chance of something unhealthy it is a risk factor. A trigger factor or 'trigger' for short is a factor that may cause an activity or the signs and/or symptoms of a medical condition to begin.[17]

There are no specific tests to diagnose migraine but a doctor may use different tests to rule out other causes for a person's symptoms. The diagnosis of migraine is a clinical diagnosis which means it is based upon a person's medical history that a person reports to the doctor.[21] The medical history for a possible migraine diagnosis which can be called the headache history includes information such as:
Differential diagnoses are different medical disorders which may cause the same symptoms. Before a doctor makes a final diagnosis, which means they are sure of what medical disorder is causing the problem, they think of what other medical conditions have the same or almost the same symptoms, and make sure it's not one of them.[22]

Often, having one medical condition makes it more likely a person will also have one or more other medical or psychiatric disorders. These other disorders are the "comorbid disorders" or "comorbidities".[23] There are various comorbid medical and psychiatric conditions associated with migraines. The treatment and prognosis (if a disease gets better, worse or stays the same over time)[24] of migraine is affected by the comorbid disorders which may be present and/or the chance of getting comorbid disorders.[25]

Comorbid psychiatric conditions
In medicine, a complication is a problem that happens because of, a procedure (like surgery), treatment (like medication), or illness (like migraines).[28]

In medicine epidemiology is the study of what causes diseases and medical conditions, how often they happen, where they happen and who they happen to.[29]
Migraine is more common among boys than girls until the beginning of puberty when girls start getting migraines more often than boys. By the later part of the teenage years girls get migraines almost twice as much as boys do. The number of people who get migraines is highest between the ages of 25 to 55 years in both men and women, after which, the risk of getting migraines get lower as a person gets older.
Between 65-75% of adult migraine sufferers are women and of these women, about two-thirds have menstrual migraines. Migraines are more common in people who make less money, there may be different reasons why such as stress.
About two-thirds of migraines are migraines without aura and the remaining one-third of cases are migraine with aura.
Symptoms that mimic those of migraines have been recorded in various cultures throughout written history. The first known mention was found on cuneiform tablets from Babylonia dating to 2000-1880 B.C.E.[30] A treatment for migraine can be found in the Ebers Papyrus, an Ancient Egyptian medical text named after George Ebers, the German Eygptologist who discovered them. In the ancient text dated to 1552 B.C.E. migraine is refereed to as "suffering in half the head".[31]
The Ancient Greek physician Aretaeus of Cappadocia's description of a type of headache he dubbed heterocrania is considered a description of migraine.[32]
Seamless Wikipedia browsing. On steroids.
Every time you click a link to Wikipedia, Wiktionary or Wikiquote in your browser's search results, it will show the modern Wikiwand interface.
Wikiwand extension is a five stars, simple, with minimum permission required to keep your browsing private, safe and transparent.