Lorenz cipher
Cipher machines used by the German Army during World War II From Wikipedia, the free encyclopedia
The Lorenz cipher was a class of German rotor stream cipher machines used by the German Army during World War II. It was mostly used for messages among headquarters. This machine and its messages were eventually worked out by the team at Bletchley Park during World War II.
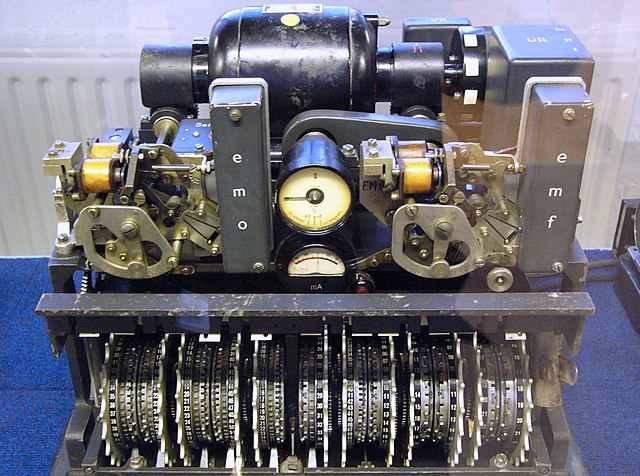
British cryptanalysts (codebreakers) worked out its logical structure three years before they saw the machine.[1][2]
References
Wikiwand - on
Seamless Wikipedia browsing. On steroids.
