Homo naledi
Ape-like Hominid species. From Wikipedia, the free encyclopedia
Homo naledi is a species of archaic human found in the Rising Star Cave, Cradle of Humankind, South Africa. The species possibly lived in the Middle Pleistocene 335,000–236,000 years ago.[1] The initial discovery comprises 1,569 specimens, representing 737 different elements, and at least 69 different people.[2] Despite this exceptionally high number of specimens, their ranking with the Homo genus remains unclear.
| Homo naledi Temporal range: Middle Pleistocene | |
|---|---|
 | |
| The 737 known elements of H. naledi | |
| Scientific classification | |
| Domain: | Eukaryota |
| Kingdom: | Animalia |
| Phylum: | Chordata |
| Class: | Mammalia |
| Order: | Primates |
| Suborder: | Haplorhini |
| Infraorder: | Simiiformes |
| Family: | Hominidae |
| Subfamily: | Homininae |
| Tribe: | Hominini |
| Genus: | Homo |
| Species: | †H. naledi |
| Binomial name | |
| Homo naledi Berger et al., 2015 | |
 | |
| Location of Rising Star Cave in the Cradle of Humankind, South Africa | |
Even though it is in the Homo genus, they have some similarities with the Australopithecus genus and the first human species. For example, they have a small brain compared to modern humans.[3] They were more adapted to climbing and tree-dwelling (aboreal) than running through long distances.[4]

Gallery
- Skeletal elements
- Top skull digital reconstruction
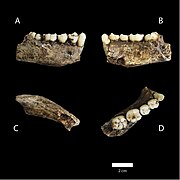
- Jaws of LES1 (left) and DH1 (right)
- Upper jawbone of LES1 (left) and DH1 (right)
- A lower jawbone
- A clavicle
- A humerus
- An ulna
- Metacarpals from different specimens
- 10th thoracic vertebra
- 11th thoracic vertebra
- A femur
- A tibia
- Ankle bones from different specimens
- 1) adult right foot, 2) juvenile left, 3 and 4) adult left, 5) juvenile right
References
Wikiwand - on
Seamless Wikipedia browsing. On steroids.