Aardwolf
species of mammal From Wikipedia, the free encyclopedia
The aardwolf (Proteles cristata) is a small, insectivorous mammal, native to East Africa and Southern Africa. Its name means "earth wolf" in the Afrikaans / Dutch language. It is also called "maanhaar jackal" in Afrikaans,[2] or civet hyena, based on the secretions (civet) from their anal glands.[3]
| Aardwolf Temporal range: Pleistocene – Recent | |
|---|---|
 | |
| An aardwolf in Namib-Nord, Namibia | |
| Scientific classification | |
| Domain: | Eukaryota |
| Kingdom: | Animalia |
| Phylum: | Chordata |
| Class: | Mammalia |
| Order: | Carnivora |
| Suborder: | Feliformia |
| Family: | Hyaenidae |
| Subfamily: | Protelinae |
| Genus: | Proteles |
| Species: | P. cristata |
| Binomial name | |
| Proteles cristata Sparrman, 1783 | |
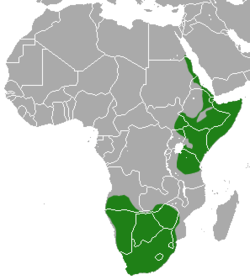 | |
| Aardwolf range | |
The aardwolf is in the same family as the hyenas. Unlike many of its relatives in the order Carnivora, the aardwolf does not hunt large animals, or even eat meat on a regular basis; instead it eats insects, mainly termites – one aardwolf can eat about 250,000 termites during a single night by using its long, sticky tongue to capture them.[4][5]
The aardwolf lives in the scrublands of eastern and southern Africa – these are open lands covered with stunted trees and shrubs. The aardwolf is nocturnal, resting in burrows during the day and coming out at night to eat.
Anal gland scent-marking plays an important role in mating-season in both sexes as it is the primary communication method.[6]
References
Wikiwand - on
Seamless Wikipedia browsing. On steroids.

