Venus
planet second-closest to the Sun in the Solar System From Wikipedia, the free encyclopedia
Remove ads
Venus is the second planet from the Sun.[3] Venus is the only planet in the Solar System that has a day longer than a year. The year length of Venus is 225 Earth days. The day length of Venus is 243 Earth days.[3]
This page or section needs to be cleaned up. (December 2024) |
Remove ads
Overview
Venus is a terrestrial planet because it has a solid, rocky surface like other planets in the inner Solar System. Astronomers have known Venus for thousands of years. The ancient Romans named it after their goddess Venus, goddess of love and beauty.[3]
Venus is the brightest thing in the night sky except for the Moon. It is sometimes called the morning star or the evening star as at some elongations it is easily seen just before the Sun comes up in the morning. At other times, it can be seen just after the sun goes down in the evening. Venus comes closer to the Earth than any other planet does.
Composition
Venus is sometimes called the sister planet of Earth as they are quite similar in size and gravity. In other ways the planets are very different. Venus' atmosphere is mostly carbon dioxide (CO2) with clouds of sulphuric acid (H2SO4).[4] H2SO4 is a chemical that is poisonous to life. For this it is sometimes known as the Earth's "evil twin".[5][6]
The thick atmosphere makes it hard to see the surface. Until the late twentieth century many thought there might be life there. The pressure on Venus' surface is 92 times that of Earth. Venus is one of only two planets in the Solar System (the other being Mercury) that has no moons. Venus spins very slowly on its axis and it spins in the opposite direction to the other planets.
Remove ads
Physical properties
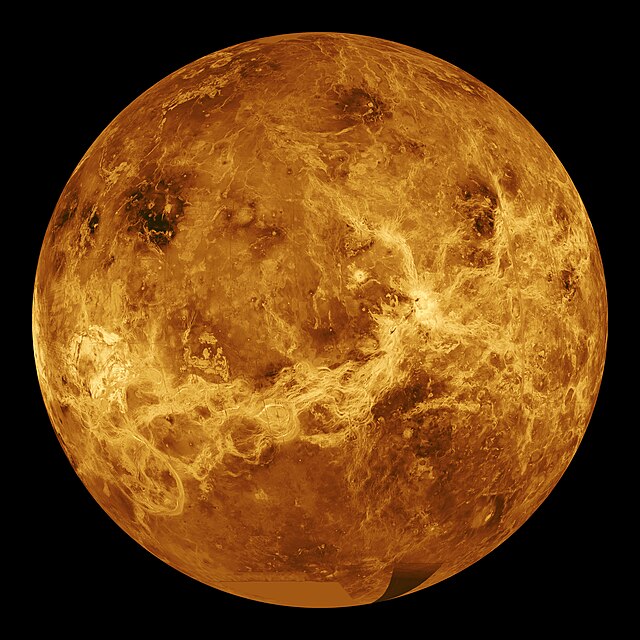

Venus is a terrestrial planet so, like the Earth, its surface is made of rock. Venus is much hotter than Earth. All the carbon dioxide in the atmosphere acts like a blanket, trapping heat from the Sun. This effect is called the greenhouse effect and it is very strong on Venus. This makes the surface of Venus the hottest of any planet's surface in the Solar System with an estimated average temperature of 480 °C (896.0 °F).[7][8] This is hot enough to melt lead or zinc.
Geography
Venus has no oceans because it is much too hot for water. Venus' surface is a dry desert. Because of the clouds, only radar can map the surface. It is about 80% smooth, rocky plains, made mostly of basalt. Two higher areas called continents make up the north and south of the planet. The north is called Ishtar Terra and the south is called Aphrodite Terra. They are named after the Babylonian and Greek goddesses of love.[9]
The surface of Venus looks like it has been shaped by volcanic activity. Venus has a lot of volcanoes.[10] The surface of Venus is estimated to be 300–600 million years old.[10][11]
Unlike Earth or Mars, Venus does not have defined highlands or lowlands, and it does not have tectonic plates.
Atmosphere
Venus' atmosphere is mostly carbon dioxide and nitrogen gas with clouds of sulphuric acid. Because the atmosphere is so thick or dense the pressure is very high. The pressure is 92 times the pressure on Earth, enough to crush many things.
It is impossible to see the planet's surface from space as the thick cloud layer reflects 60% of the light that hits it. The only way scientists are able to see it is by using infrared and ultraviolet cameras and radar.
Scientists believe that billions of years ago, the atmosphere of Venus could have been like Earth's atmosphere. There may have been lots of water on the surface of Venus. But after 600 million to several billion years, the evaporation of the water put greenhouse gases into its atmosphere.[12]
Magnetic field
In 1967, Venera 4 found that the magnetic field of Venus was much weaker than that of Earth. This magnetic field is induced by an interaction between the ionosphere and the solar wind. Venus' magnetosphere is not strong enough to protect the atmosphere from cosmic rays.[13]
Transit of Venus
Venus can sometimes be seen passing between the Sun and Earth. Venus looks like a black dot when seen through a special telescope. These passages are called "transits". These "transits" happen in pairs eight years apart. Then it is more than a hundred years to the next pair.
Remove ads
Orbit and rotation
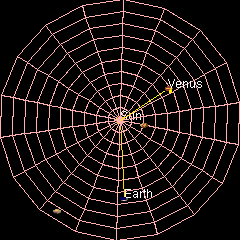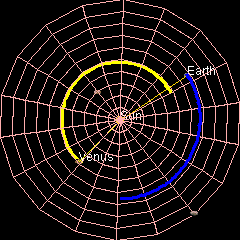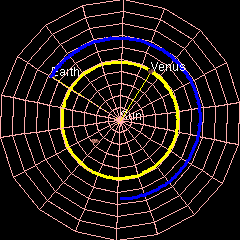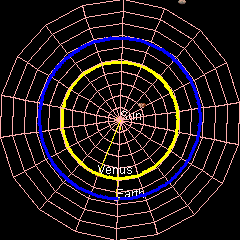
Venus orbits the Sun at an average distance of about 108 million km (68~ million mi). It completes an orbit every 224.7 days.[14] The rotation of Venus is slow. A Venusian sidereal day is longer than a Venusian year.
List of satellites sent to Venus
Many man-made satellites have been sent to Venus to study it. They are:
Mariner
Venera
Remove ads
Related pages
Notes
- Venera was a name only given to Venus missions that left Low Earth orbit. Missions that failed to do so where given either Sputnik or Kosmos names instead. They are still included in the Venera list, as that was their intended name.
- No lander means that no lander or impactor ever went into the Venusian atmosphere with the goal of landing or impacting. Launch failures, or satellites that failed to reach Venus, do not count.
Remove ads
References
Other websites
Wikiwand - on
Seamless Wikipedia browsing. On steroids.
Remove ads

